概要
本文主要分析动态代理的方法执行链,以及被代理的private方法中的service为何是null
下面将以controller的private方法为例
spring代理流程
本案例默认controller被动态代理,请求方法如下
@GetMapping("/requireUser")
@ValidAuth(hasRole = 1)
private UserEntity requireUser(String id) {
return userService.requireUser(id);
}
启动时创建代理的具体代码在
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization中,其中有个wrapIfNecessary,
由于springboot2.x默认使用cglib代理,所以到CglibAopProxy.getProxy()
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
这里就是正常的生成enhance,注意其中的callbacks数组,这些相当于是拦截器,而里面的第一个callback则是CglibAopProxy的内部类DynamicAdvisedInterceptor的实例,这个是重中之重,后面方法的invoke以及使用targetSource都是依赖该类
在了解完代理类的class文件后得知
final UserEntity CGLIB$requireUser$5(String var1) {
return super.requireUser(var1);
}
public final UserEntity requireUser(String var1) {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
return var10000 != null ? (UserEntity)var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$requireUser$5$Method, new Object[]{var1}, CGLIB$requireUser$5$Proxy) : super.requireUser(var1);
}
这里的var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;就是上面的dynamicAdvisedInterceptor
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor 详见下图
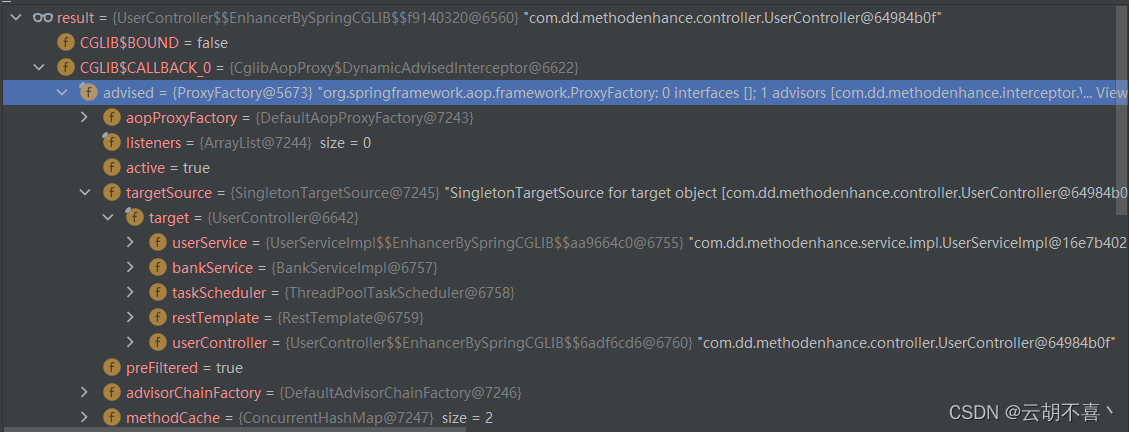
CGLIB$CALLBACK_0为DynamicAdvisedInterceptor
而CGLIB$CALLBACK_0的作用就是开启执行代理方法的入口,后续的interceptor的执行都依赖这个
下图为DynamicAdvisedInterceptor.intercep方法源码
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
if (chain.isEmpty() && CglibMethodInvocation.isMethodProxyCompatible(method)) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
try {
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException ex) {
CglibMethodInvocation.logFastClassGenerationFailure(method);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
我们重点看下new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();这块代码,
第一个是proxy对象,很好理解
第二个是原对象,也就是被代理的对象
第三个是调用的method对象
第四个是方法入参
第五个是被代理类的class类
第六个是拦截器链
第七个是methodProxy对象
有了这些参数之后进入proceed方法,调用的是super ReflectiveMethodInvocation的proceed
如下
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
这个方法大致就是循环调用拦截器方法,结束之后调用invokeJoinpoint,实际调用的是子类CglibMethodInvocation的invokeJoinpoint,如下
@Override
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
if (this.methodProxy != null) {
try {
return this.methodProxy.invoke(this.target, this.arguments);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException ex) {
logFastClassGenerationFailure(this.method);
}
}
return super.invokeJoinpoint();
}
methodProxy.invoke(this.target, this.arguments)这里看过fastClass的都知道调用的是f1的invoke,把target强转为原对象,调用对应的方法,然后会进入到controller的requireUser方法,此时这里的this必是spring托管的类,不是代理类,如果是代理类就有问题了
private、方法的执行区别
在熟悉上面的代码之后,我们再来看看一个请求过来之后,private和public处理方式的区别
private
在invocableHandlerMethod的doInvoke
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
Method method = getBridgedMethod();
try {
if (KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method)) {
return CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, getBean(), args);
}
return method.invoke(getBean(), args);
}
.............
这里的getBean本文中得到的是代理类
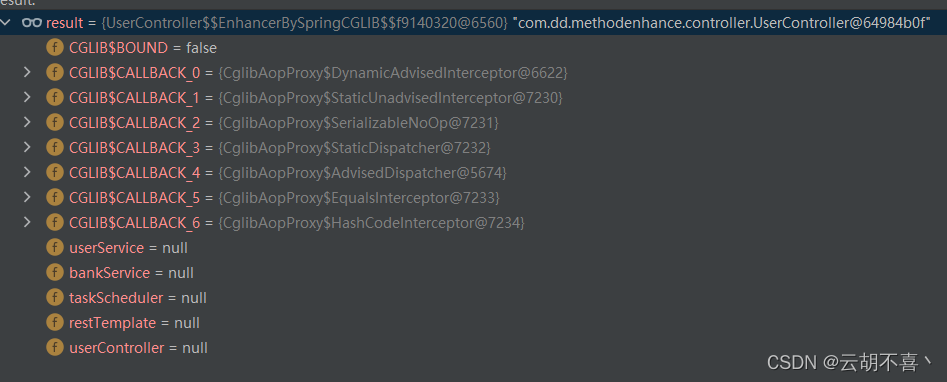
然后到Method的invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
{
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null) {
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
在第一次调用的时候会获得方法的访问权限,得到MethodAccessor对象,调用其invoke,obj为代理类,一路跟到NativeMethodAccessorImpl的invoke
public Object invoke(Object var1, Object[] var2) throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
if (++this.numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold() && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(this.method.getDeclaringClass())) {
MethodAccessorImpl var3 = (MethodAccessorImpl)(new MethodAccessorGenerator()).generateMethod(this.method.getDeclaringClass(), this.method.getName(), this.method.getParameterTypes(), this.method.getReturnType(), this.method.getExceptionTypes(), this.method.getModifiers());
this.parent.setDelegate(var3);
}
//此方法是分水岭
return invoke0(this.method, var1, var2);
}
method为private方法对象,var1为代理类,var2为方法入参
注意invoke0方法的后续调用,此时private的方法后续会直接进入controller中,如下图
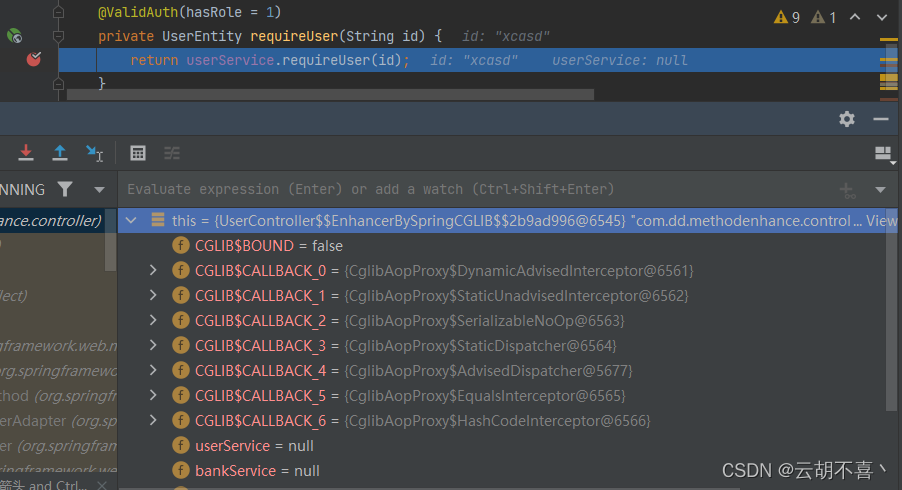
然后不出意外的空指针了,后面看完public的执行流程后会有总结
public
public的方法执行流程前半部分和private一致,一直到invoke0
此时出现分水岭,public的后续会进入CglibAopProxy的内部类DynamicAdvisedInterceptor的interceptor方法中
然后会执行new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
在执行完所有自定义拦截器之后到ReflectiveMethodInvocation的proceed方法,执行invokeJoinpoint
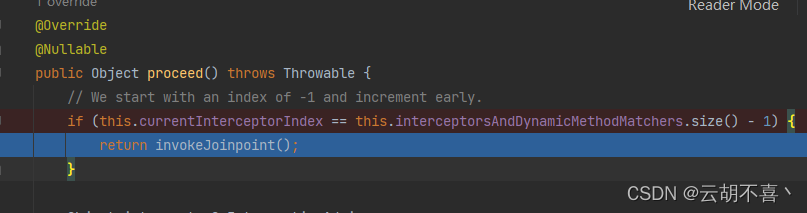
后续代码就和上面介绍的一模一样了

此时利用fastClass,实现快速调用userController的requireUser方法,此时的this就是spring托管的对象,非代理类

至此,方法正常结束
答疑
1.为何private方法最后到controller中,方法注入都为null
因为invoke0(this.method, var1, var2)方法
这一步是利用反射调用var1的method,上面的例子中可知,var1为代理对象,
从其class文件以及cglib动态代理的实现方式可以,该class中并无private方法的重写,因为spring不会代理私有方法
但是,通过给method设置setAccessible为true的话,则可以实现调用父类的private方法
因此使用反射调用了父类UserController的private方法,但是this确实代理类自身,代理类只是继承UserController,自身并没有被spring管理,且本身并未持有其他service对象,都是其父类的属性,因此反射时方法内的各种service均是使用的this里的,也就是代理类的,那必然是null
2.为什么public方法的后续代码会多执行很多且内部service不为null?
再看invoke0(this.method, var1, var2)
此时的var1同为代理对象,但是代理类的class文件中已经有了
final UserEntity CGLIB$requireUser$5(String var1) {
return super.requireUser(var1);
}
public final UserEntity requireUser(String var1) {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
return var10000 != null ? (UserEntity)var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$requireUser$5$Method, new Object[]{var1}, CGLIB$requireUser$5$Proxy) : super.requireUser(var1);
}
实际invoke的是代理类的requireUser方法,而var10000 就是DynamicAdvisedInterceptor,自然而然的进入到其intercep方法内,后续使用methodProxy.invoke(target,args),这里才是关键之处,DynamicAdvisedIntercetor持有的advised对象可以拿到target,也就是spring管理的userController的实例对象,通过fastClass快速调用实例对象的对应方法,内部依赖自然不为null
注意,此处只讨论controller被动态代理的情况,未被代理时,private和public均能实现正常调用
总结
之前学习动态代理的时候遇到的这个问题,兜兜转转一大圈,见到最多的说法就是spring无法代理private方法,但究竟为何,仍然没有一个让我通透的答案
只有当你亲自去拨开迷雾时,一切才会变得明朗起来,理解也会愈发深刻






















 2173
2173











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








