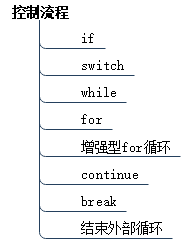
java控制流程
先看个思维导图呗
- if
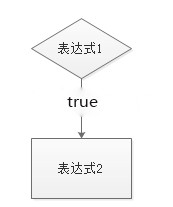
1.语法
if(表达式1){
表达式2;
}
如果表达式1的值是true,就执行表达式2。
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean bb = true;
//如果成立就打印yes
if(bb){
System.out.println("yes");
}
}
}
2.多表达式(用大括弧包括起来)与一个表达式(可以不用写括弧)
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean bb = false;
//如果有多个表达式,必须用大括弧包括起来
if(bb){
System.out.println("yes1");
System.out.println("yes2");
}
//不用括号,表达式yes2,无论bb是否为true都会执行
if(bb)
System.out.println("yes1");
System.out.println("yes2");
//如果只有一个表达式可以不用写括弧,看上去会简约一些
if(bb){
System.out.println("yes1");
}
if(bb)
System.out.println("yes1");
}
}

3.if 使用过程中可能遇到的坑
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean bb = false;
//分号也是一个完整的表达式
//bb为false,不会执行这个分号表达式,然后打印yes
if(bb);
System.out.println("yes");
//bb为true,会执行这个分号表达式,然后打印yes
if(!bb);
System.out.println("yes");
}
}

4.if else

public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean bb = false;
if (bb)
System.out.println("yes");
else
System.out.println("no");
}
}
5.else if
else if 是多条件判断
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//如果只使用 if,会执行4次判断
int i = 2;
if (i==1)
System.out.println(1);
if (i==2)
System.out.println(2);
if (i==3)
System.out.println(3);
if (i==4)
System.out.println(4);
//如果使用else if, 一旦判断成立,其他判断就不会执行了,节约了运算资源
if (i==1)
System.out.println(1);
else if (i==2)
System.out.println(2);
else if (i==3)
System.out.println(3);
else if (i==4)
System.out.println(4);
}
}
6练习
判断某一年是否为闰年
通过Scanner 输入一个年份,然后判断该年是否是闰年
闰年判断标准(满足任何一个)
- 如果能够被4整除,但是不能被100整除
- 能够被400整除
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Year {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入年份:");
int year =scanner.nextInt();
if(year%400 == 0||(year%4==0&&year%100!=0)) {
System.out.println("您输入的年份是闰年!");
}else {
System.out.println("您输入的年份不是闰年!!");
}
}
}
- switch
1.switch (语句相当于 if else的另一种表达方式)
switch可以使用byte,short,int,char,String,enum
注: 每个表达式结束,都应该有一个break;
注: String在Java1.7之前是不支持的, Java从1.7开始支持switch用String的,编译后是把String转化为hash值,其实还是整数。
注: enum是枚举类型。
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//如果使用if else
int day = 5;
if (day==1)
System.out.println("星期一");
else if (day==2)
System.out.println("星期二");
else if (day==3)
System.out.println("星期三");
else if (day==4)
System.out.println("星期四");
else if (day==5)
System.out.println("星期五");
else if (day==6)
System.out.println("星期六");
else if (day==7)
System.out.println("星期天");
else
System.out.println("这个是什么鬼?");
//如果使用switch
switch(day){
case 1:
System.out.println("星期一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("星期二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("星期三");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("星期四");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("星期五");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("星期六");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("星期天");
break;
default:
System.out.println("这个是什么鬼?");
}
}
}
2.枚举类型(enum)
枚举enum是一种特殊的类(还是类),使用枚举可以很方便的定义常量
比如设计一个枚举类型 季节,里面有4种常量(一般都是全大写)
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Season season = Season.SPRING;
switch (season) {
case SPRING:
System.out.println("春天");
break;
case SUMMER:
System.out.println("夏天");
break;
case AUTUMN:
System.out.println("秋天");
break;
case WINTER:
System.out.println("冬天");
break;
}
}
}
enum Season {
SPRING,SUMMER,AUTUMN,WINTER
}
借助增强型for循环,可以很方便的遍历一个枚举都有哪些常量
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Season s : Season.values()) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
enum Season {
SPRING,SUMMER,AUTUMN,WINTER
}
- while和do-while循环语句
1.while 条件为true时,重复执行。
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while(i<5){
System.out.println(i);//打印0到4
i++;
}
}
}
2.do while 条件为true时,重复执行,至少会执行一次。
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
//与while的区别是,无论是否成立,先执行一次,再进行判断
do{
System.out.println(i); //打印0到4
i++;
} while(i<5);
}
}
3.练习
通Scanner 获取一个整数,然后使用while计算这个整数的阶乘
N的阶乘等于 N* (N-1) * (N-2) * … * 1
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int i = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("阶乘是:"+method(i));
}
public static int method(int i){
if (i == 1){
return 1;
}
return i*method(i-1);//等于i*(i-1)*method(i-2)等于i*(i-1)*(i-2)*...*1
}
}

- for
1.for(for循环,和while一样,只是表达方式不一样)
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
//使用while打印0到4
while(i<5){
System.out.println("while循环输出的"+i);
i++;
}
//使用for打印0到4
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
System.out.println("for 循环输出的"+j);
}
}
}
2.增强型for循环
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int values [] = new int[]{18,62,68,82,65,9};
//常规遍历
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
int each = values[i];
System.out.println(each);
}
//增强型for循环遍历
for (int each : values) {
System.out.println(each);
}
}
}
3.练习
天朝有一个乞丐姓洪,去天桥要钱
第一天要了1块钱
第二天要了2块钱
第三天要了4块钱
第四天要了8块钱
以此类推
问题: 洪乞丐干10天,收入是多少?
public class Count {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
sum+=Math.pow(2,i);
System.out.println("洪乞丐干"+(i+1)+"天,收入是"+sum+"元");
}
}
}
用增强型for循环求最大值
public class foreach {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[10];
System.out.println("数组中的各个随机数是:");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
a[i]=(int) (Math.random() * 100);
System.out.print(a[i]+"\t");
}
int max=a[0];
for(int A:a){
if(max<A){
max=A;
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("增强型for循环中最大值是:"+max);
}
}
- continue
1.continue(继续下一次循环)
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印单数
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
if(0==j%2)
continue; //如果是双数,后面的代码不执行,直接进行下一次循环
System.out.println(j);
}
}
}
- break
1.break(结束循环)
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印单数
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
if(0==j%2)
break; //如果是双数,直接结束循环,无任何输出
System.out.println(j);
}
}
}
2.练习
假设你月收入是3000,除开平时花销,每个月留下1000块钱进行投资。
然后你认真的钻研了 《股票和基金 21天从入门到精通》,达到了每年20%的投资回报率。
那么问题来了,以每个月投资1000块钱的节奏,持续投资多少年,总收入达到100万
(复利计算按照每年12000投入计算,不按照每月计息(本息按年))
复利公式:
F = p* ( (1+r)^n );
F 最终收入
p 本金
r 年利率
n 存了多少年
假设情景一:
p = 10000
r = 0.05
n = 1
解读:
本金是10000
年利率是5%
存了一年 1次
复利收入 10000*( (1+0.05)^1 ) = 10500
假设情景二:
p = 10000
r = 0.05
n = 2
解读:
本金是10000
年利率是5%
存了两年
复利收入 10000*( (1+0.05)^2 ) = 11025
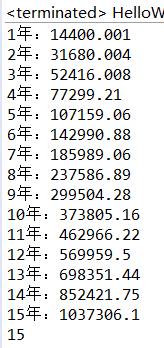
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Runnian{
public static void main(String[] args) {
float F=0;
float p=12000;
float r=0.2f;
int n;
for(n=1;n>=1;n++){
p=p*(1+r);
F+=p;
System.out.println(n+"年:"+F);
if(F>=1000000){
break;
}
}
System.out.println(n);
}
}
- 结束外部循环(break是结束当前循环)
1.结束当前循环(break; 只能结束当前循环)
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印单数
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println(i+":"+j);
if(0==j%2)
break; //如果是双数,结束当前循环
}
}
}
}
2.使用boolean变量结束外部循环
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean breakout = false; //是否终止外部循环的标记
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println(i + ":" + j);
if (0 == j % 2) {
breakout = true; //终止外部循环的标记设置为true
break;
}
}
if (breakout) //判断是否终止外部循环
break;
}
}
}
3.使用标签结束外部循环
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印单数
outloop: //outloop这个标示是可以自定义的比如outloop1,ol2,out5
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println(i+":"+j);
if(0==j%2)
break outloop; //如果是双数,结束外部循环
}
}
}
}
- 综合练习
1.黄金分割点
寻找某两个数相除,其结果 离黄金分割点 0.618最近
分母和分子不能同时为偶数
分母和分子 取值范围在[1-20]
public class GoldenMean {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double firstNumber = 0;// 为了接收最后的结果
double secondNumber = 0;// 为了接收最后的结果
double a = 0.618;// 定义一个比较的初始基准
// 两个循环相除
for (double i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
for (double j = 1; j <= 20; j++) {
//不可同为偶数
if (0 == i % 2 && 0 == j % 2)
continue;
else {
double b = i / j; // 两数相除
double c = Math.abs(0.618 - b);// 结果离0.618的距离
if (c < a) {
a = c;// 基准减小为上一次距离的最小值,如0.1<0.618,那下次0.05<0.1,依次找出最小的,此时i,j都知道
firstNumber = i;
secondNumber = j;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(
"在1-20中,离黄金分割点(0.618)最近的两个数相除是:" + firstNumber + "/" + secondNumber + "=" + firstNumber / secondNumber);
}
}
离黄金分割点(0.618)最近的两个数相除是:8/13
注:
Math.abs(x) ; //该方法返回x的绝对值,x的取值可以是各种类型参数。
Math.abs(’-1’); // 1
Math.abs(-2); // 2
Math.abs(null); // 0
Math.abs(’’); // 0
Math.abs([]); // 0
Math.abs([2]); // 2
Math.abs([1,2]); // NaN
Math.abs({}); // NaN
Math.abs(‘string’); // NaN
Math.abs(); // NaN
2.水仙花数
水仙花数定义:
- 一定是3位数
- 每一位的立方,加起来恰好是这个数本身,比如153=111+555+333
寻找所有的水仙花数(153,370,371,407)
方法1:
public class sxhs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=9;j++){
for(int k=0;k<=9;k++){
if((i*100+j*10+k)==(i*i*i+j*j*j+k*k*k)){
System.out.println(""+i+j+k);
}
}
}
}
}
}
方法2:
public class sxhs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i,k,j;
for(int num=100;num<1000;num++) {
i = num/100;
j = num/10%10;
k = num%100%10;
if(num == i*i*i + j*j*j + k*k*k) {
System.out.println(num);
}
}
}
}
3.小学算术题
使用多层循环嵌套解决
3 5
11 5

public class LittleSchoolCount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<=14;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=14;j++){
for(int k=0;k<=14;k++){
for(int l=0;l<=14;l++){
if((i+j==8)&&(i+k==14)&&(j+l==10)&&(k-l==6)){
System.out.println("i,j,k,l: "+i+" "+j+" "+k+" "+l);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}






















 409
409











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








