1.什么是线程池
线程池其实就是一个容纳多个线程的容器 ,其中的线程可以反复使用,省去了频繁创建线程对象的操作 ,无需反复创建线程而消耗过多资源。
2.使用线程池有什么好处
a.降低资源消耗,通过重复利用已创建的线程,降低线程创建和销毁造成的资源消耗。
b.提交响应速度,当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等待线程创建就能执行。
c.提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限的创建,不仅会消耗系统的资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以统一的分配,调优和监控。
3.JDK默认的Excutors提供的四种线程池
A.newCachedThreadPool创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则创建线程
源码图:

源码:
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
代码实现:
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();// 缓存线程池,无上限
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
cachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
cachedThreadPool.shutdown();// 将线程池关闭 在做项目的时候一般是不会将线程池关闭的
B.newFixedThreadPool创建一个定长的线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待
源码图:
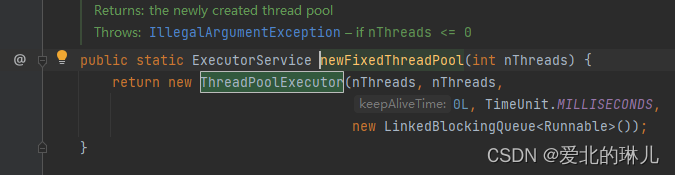
源码:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
代码实现:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int processors = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();// 获得计算机有几个内核
// System.out.println("pro : " + processors);
//第一种线程池:固定个数的线程池
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(processors * 100);// 固定线程个数的线程池 让一个CPU核绑定100个线程,这种方式经常使用.
// System.out.println(fixedThreadPool);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
fixedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());// pool-1-thread-1
}
});
}
fixedThreadPool.shutdown();// 将线程池关闭 在做项目的时候一般是不会将线程池关闭的.
实际业务体现
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPoolExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建固定大小的线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
// 提交多个任务给线程池
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Runnable worker = new WorkerThread(String.valueOf(i));
executor.execute(worker);
}
// 关闭线程池
executor.shutdown();
// 检查任务是否全部执行完成
while (!executor.isTerminated()) {
// 等待所有任务完成
}
System.out.println("所有任务执行完毕");
}
}
class WorkerThread implements Runnable {
private String taskName;
public WorkerThread(String taskName) {
this.taskName = taskName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("任务 " + taskName + " 正在执行");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务 " + taskName + " 执行完成");
}
}
C.newSingleThreadExecutor创建一个单线程化的线程池,只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序进行
源码图:
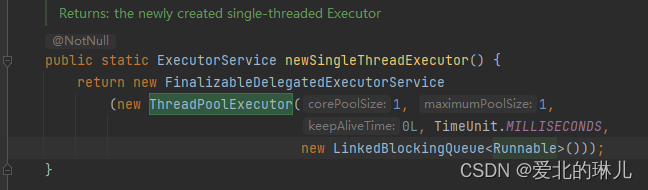
源码:
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
代码实现:
ExecutorService singleThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();// 单一线程池,永远会维护存在一条线程
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int j = i;
singleThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
/*
* if(j == 3) throw new RuntimeException("出异常了...");
*/
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":"
+ j);
}
});
}
singleThreadPool.shutdown();
D.newScheduledThreadPool创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行
源码图如下,这个比较特殊,但内部还是使用的ThreadPoolExecutor/第四种线程池:固定个数的线程池,相比于第二个固定个数的线程池 强大在 ①可以执行延时任务,②也可以执行带有返回值的任务。scheduledThreadPool.submit(); 执行带有返回值的任务scheduledThreadPool.schedule() 用来执行延时任务.
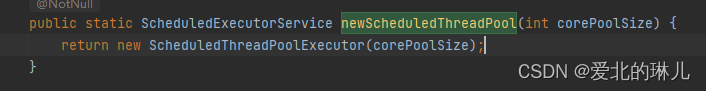
第一步:ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor点进去
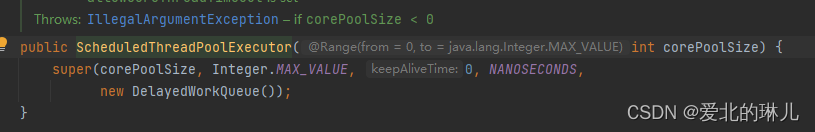
第二步:super点进去
第三步:可以发现还是使用的ThreadPoolExecutor
源码:
第一步源码:
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
第二步源码:
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
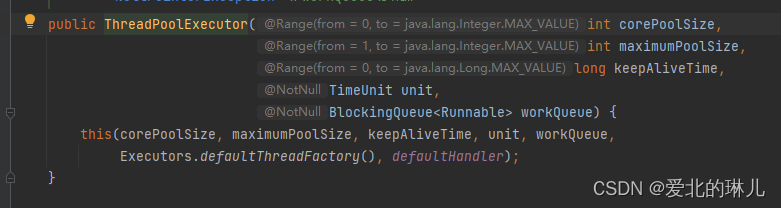
第三步源码:也就是ThreadPoolExecutor源码的一部分,下面会细说。
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
代码实现:
FutureTask<String> ft = new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("hello");
return Thread.currentThread().getName();
}
});
scheduledThreadPool.submit(ft);
String result = ft.get();//通过FutureTask对象获得返回值.
System.out.println("result : "+result);
scheduledThreadPool.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : bobm!");
}
}, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
注意:阿里巴巴java开发手册中提到,不使用默认线程池,并说明了原因。

ThreadPoolExecutor 源码:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
参数分析
A.corePoolSize:核心线程数,初始创建的线程都是核心线程数,线程池中正常情况下始终保留该大小的线程实例存活
B.maximumPoolSize:最大线程数,当核心线程都在执行任务,任务队列满的情况下会创建非核心线程来执行任务,当非核心线程处于空闲时间,且超过keepAliveTime时,会销毁非核心线程
C.keepAliveTime:存活时间,用于控制非核心线程的空闲时存活时间
D.unit:存活时间的单位。具体是TimeUnit枚举,有毫秒、秒、分钟、小时等等
E.workQueue:线程池的任务队列,当线程池的核心线程都处于繁忙状态,且有新任务到来,则会进入任务队列,当任务队列满了,则会创建非核心线程执行新任务 threadFactory:线程池创建线程实例的线程工厂,一般默认为Executors.defaultThreadFactory
F.handler:线程池拒绝策略,当核心线程全部繁忙,任务队列已满,非核心线程全部繁忙,会触发线程池拒绝策略。有四种策略:
AbortPolicy(默认),直接抛出异常并且拒绝。
源码图:
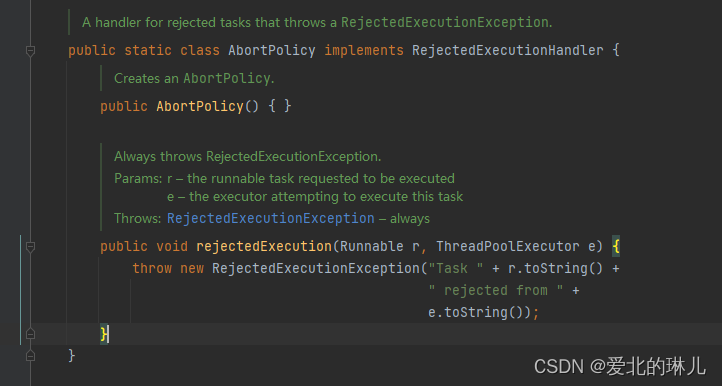
源码:
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates an {@code AbortPolicy}.
*/
public AbortPolicy() { }
/**
* Always throws RejectedExecutionException.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException always
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}
CallerRunsPolicy:该策略既不会抛弃任务,也不会抛出异常,而是将任务回推到调用者。"顾名思义,在饱和的情况下,调用者会执行该任务。
源码图:

源码:
public static class CallerRunsPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code CallerRunsPolicy}.
*/
public CallerRunsPolicy() { }
/**
* Executes task r in the caller's thread, unless the executor
* has been shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
}
DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃线程队列的旧的任务,将新的任务添加
源码图:
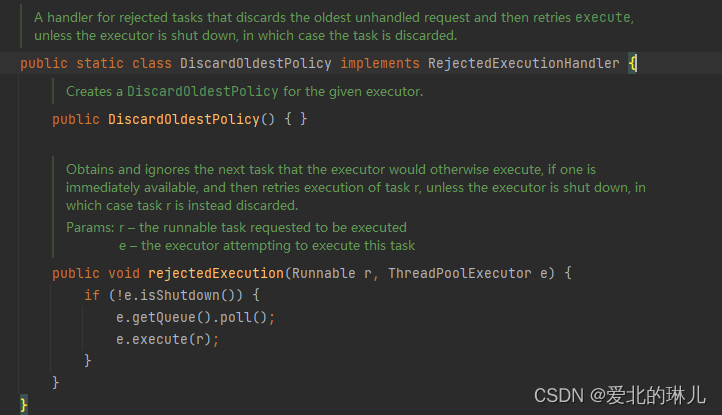
源码:
public static class DiscardOldestPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardOldestPolicy} for the given executor.
*/
public DiscardOldestPolicy() { }
/**
* Obtains and ignores the next task that the executor
* would otherwise execute, if one is immediately available,
* and then retries execution of task r, unless the executor
* is shut down, in which case task r is instead discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
}
}
}
DiscardPolicy:由调用线程处理该任务 【谁调用,谁处理】
源码图:
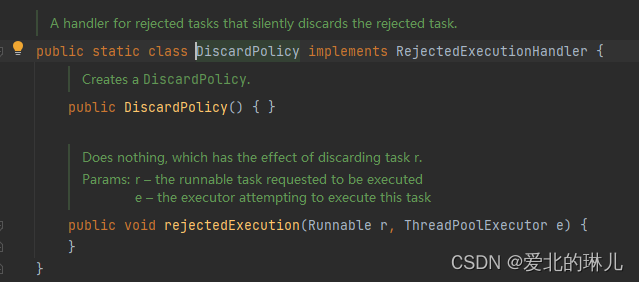
源码:
public static class DiscardPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardPolicy}.
*/
public DiscardPolicy() { }
/**
* Does nothing, which has the effect of discarding task r.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
// 发现这里面什么都没做
}
}
自定义线程池(多线程并发编程使用execute和submit执行)
代码示例:
public class TestThreadPoolExecutors {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 使用ThreadPoolExecutor创建线程池
ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 20, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
// 用execute执行,没有返回值结果
executor.execute(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
// 每次执行前睡眠1秒钟(方便我们区别)
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-" + "用execute执行的test线程池" + "-" + i);
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println("异常处理");
}
}
});
//用submit执行,有返回值结果
Future<?> result = executor.submit(() -> {
for (int i = 101; i < 106; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-" + "用submit执行的test线程池" + "-" + i);
}
});
// 打印返回值
System.out.println(result);
// 执行完成记得关闭,不然程序一直在进行
executor.shutdown();
}
}
运行结果:
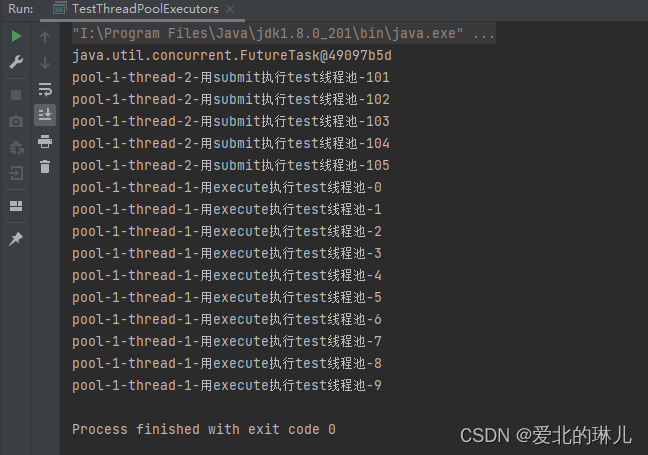
以上就是jdk自带线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的理解
























 1164
1164











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








