三大特殊类
- String类
- Object类
- 包装类
String类:
final class String
被final修饰的类不能被继承(为保证所有用户用到的String类都一样,只能使用,不能修改)
1.实例化方式
- 直接赋值
String str = "hello world";
- 通过构造方法赋值
String str = new String("hello world");
例子:
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//直接赋值
Test test = new Test();
String str = "hello world";
//通过构造方法赋值
String str1 = new String("hello world");
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
2.字符串的相等比较
“==”操作符用于比较两个变量的值是否相等,对于基本类型而言,比较的就是数值的大小;
对于引用类型而言,比较的实际上是保存的地址是否相等而不会比较内容。
所以在字符串内容比较时,需要使用String类提供的equals()方法。(equals对象,区分大小写)
str1.equals(str2);
equalsIngoreCase() //不区分大小写比较
举例:
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//直接赋值
Test test = new Test();
String str = "hello world";
//通过构造方法产生对象
String str1 = new String("hello world");
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str.equals(str1));//比较的是内容,不是地址
System.out.println(str.equalsIgnoreCase(str1));
}
}
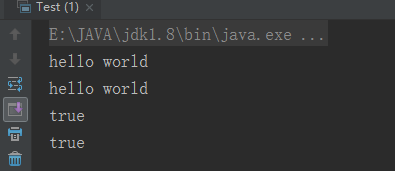
运行结果:
3.String类的匿名对象
——没有任何栈内存指向的对象(没有名字的对象),所有字符串常量(“ ”)都是String类的匿名对象。
在比较字符串是否等于特定字符串时,将字符串常量写在equals前,通过字符串常量来比较。
"hello world".equals(str);
举例:
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new St







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 229
229











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








