Spring Boot 快速入门
Spring Boot是一个便捷搭建 基于spring工程的脚手架;作用是帮助开发人员快速搭建大型的spring 项目。简化工程的配置,依赖管理;实现开发人员把时间都集中在业务开发上。
简单入门
实现步骤:
- 创建工程;
- 添加依赖(启动器依赖,spring-boot-starter-web);
- 创建启动类;
- 创建处理器Controller;
- 测试
添加依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<version>2.1.5.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
创建启动类
package junmu;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* Springboot 都有一个启动器
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
创建controller
package junmu.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String Hello(){
return "Hello SpringBoot";
}
}
- 这样,我们运行application主函数就可以直接进行项目的启动了。
- 超级方便
数据库的配置
- 对于我们数据库,我们先使用常规的代码方式配置。
- 我们先建立建立一个jdbc.properties配置文件
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_test?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
- 然后创建一个配置类
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
String driverClassName;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
}
- 通过 @PropertySource 注解直接读取,这样,就可以使用数据池了。
然后还有种就是 spring boot 属性注入的方式,这也是我们重点学的
- 先建立一个JdbcProperties 的数据类
package junmu.config;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/**
* ConfigurationProperties 从application 配置文件中读取配置
* prefix 表示前缀
* 可以进行松散绑定
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "jdbc")
public class JdbcProperties {
private String url;
private String driverClassName;
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getDriverClassName() {
return driverClassName;
}
public void setDriverClassName(String driverClassName) {
this.driverClassName = driverClassName;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
- 通过ConfigurationProperties 对jdbc.properties 进行绑定数据。
- 对了,jdbc.properties 必须改名为 application.properties这样才能使用那个注解哈
- 然后在配置文件里面就可以简写了
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(JdbcProperties.class)
public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(JdbcProperties jdbcProperties){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(jdbcProperties.getDriverClassName());
dataSource.setUrl(jdbcProperties.getUrl());
dataSource.setUsername(jdbcProperties.getUsername());
dataSource.setPassword(jdbcProperties.getPassword());
return dataSource;
}
}
- 这样我们通过属性注入的方式,也是可以直接访问到数据库的。
- 因为ConfigurationProperties 注解放在方法上面可以自动注入,所以我们可以直接简单。
@Configuration
public class JdbcConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "jdbc")
public DataSource dataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}
- 你没有看错,就是这样就可以了,他会自动的去application.properties中寻找然后相匹配
yml配置文件
- yml配置文件和properties都是被spring boot数据支持的。
- 他们只是语法不一样,并且定义的时候只能 application.yml
jdbc:
url: ****
username: ***
password: ***
// properties语法
jdbc.url = ***
jdbc.username = ***
- 如果定义了***.yml
- 那么需要在application.yml中去激活他,不然使用无效
- 当两种配置文件冲突的时候,我们以application.properties为准
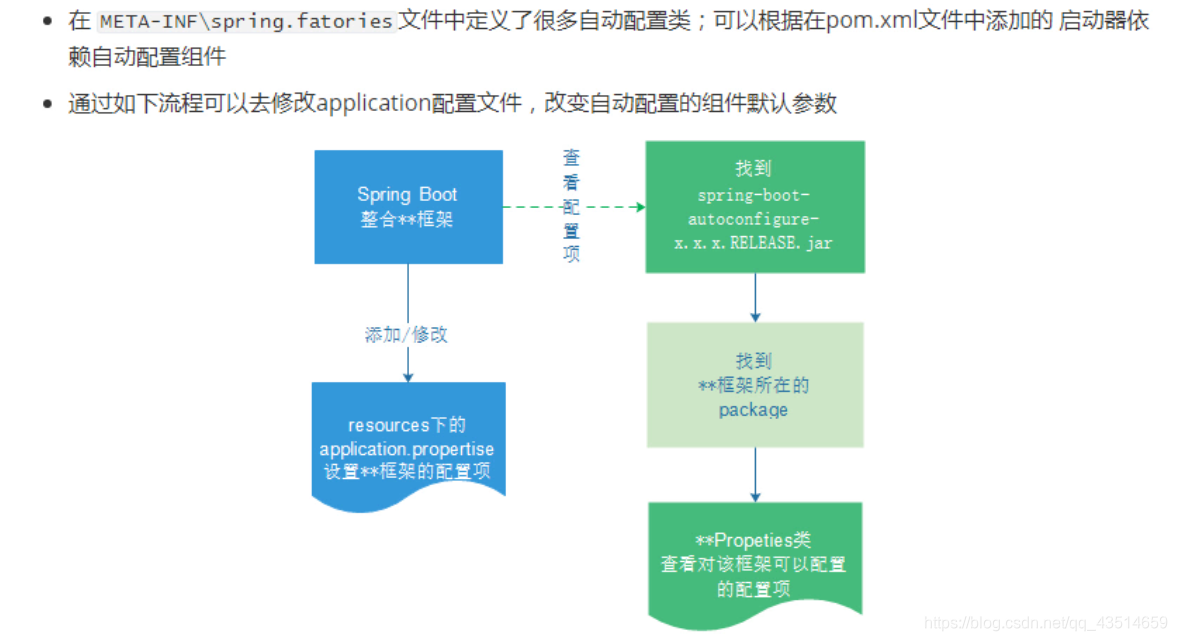
spring boot 自动配置原理
Lombok插件
- 这玩意就是个神器了哈,平时呢,我们写实体类,每次都需要写getter和setter方法。
- 现在有了Lombok就可以不用写了,
- 直接使用Data注解就可以完成大量方法的自动写入
package junmu.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
// 在编译阶段会根据注解自动的生成对应的方法,很全
@Data
public class User {
private Long id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer sex;
private Date birthday;
private Date created;
private Date updated;
}
spring boot 整合MVC拦截器
- 我们先写一个拦截器
package junmu.interceptor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Slf4j
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
log.debug("这是MyInterceptor的pre方法!!!");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
log.debug("这是MyInterceptor的post方法!!!");
HandlerInterceptor.super.postHandle(request, response, handler, modelAndView);
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
log.debug("这是MyInterceptor的after方法!!!");
HandlerInterceptor.super.afterCompletion(request, response, handler, ex);
}
}
- 然后建立一个拦截器的配置文件 MVCConfig
package junmu.config;
import junmu.interceptor.MyInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
// 注册拦截器
@Bean
public MyInterceptor myInterceptor(){
return new MyInterceptor();
}
// 添加拦截器到拦截器链
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/*");
}
}
- 这样就可以正常拦截了。
springboot 整合通用Mapper
- 平时呢,我们需要自己去写个mapper里面的语句,以及SQL语句,
- 但是我们使用通用mapper的话,就可以连sql语句都不写了
- 那么具体怎么实现呢
第一步: 先把依赖带进去
<!--通用mapper-->
<dependency>
<groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.5</version>
</dependency>
第二步:建立一个UserMapper继承 Mapper < User>
import junmu.pojo.User;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper;
public interface UserMapper extends Mapper<User> {
}
- 注意哈,如果使用了这个,那么在主启动函数里面就要换个MapperScan进行扫描了
package junmu;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import tk.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
/**
* Springboot 都有一个启动器
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("junmu.mapper")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
注意,我们的MapperScan使用的是import tk.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;包哦
- 然后就是给User实体类进行添加 jpa 注解了
package junmu.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.annotation.KeySql;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import java.util.Date;
// 在编译阶段会根据注解自动的生成对应的方法,很全
@Data
@Table(name = "tb_user")
public class User {
@Id
@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)
private Long id;
//@Column
private String userName;
private String password;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
- 使用 table注解,直接进行绑定数据库的其中的一张表,将其转移到实体类中。
然后改造UserService实现业务功能即可
package junmu.service;
import junmu.mapper.UserMapper;
import junmu.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
// 根据id查询
public User queryById(Long id){
return userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
// 保存新用户
public void saveUser(User user){
// 选择性新增,如果没有,就会是空属性:
System.out.println("新用户。。。。");
userMapper.insertSelective(user);
}
}
- 方法都是自带的哦,都不需要我们自己去写的,啊哈哈哈,是不是超级方便。
- 然后用Controller进行测试就可以啦。
SpringBoot 整合 Junit
- 添加启动依赖 Spring-boot-starter-test
- 然后找到要进行单元测试的类, 按 Ctrl + shift + t 就可进行自动的设置了





 本文介绍了如何使用SpringBoot快速创建项目,包括添加启动依赖、创建启动类、Controller和数据库配置。通过实例演示了如何配置数据库连接,以及利用Lombok简化实体类和Spring MVC拦截器的使用。
本文介绍了如何使用SpringBoot快速创建项目,包括添加启动依赖、创建启动类、Controller和数据库配置。通过实例演示了如何配置数据库连接,以及利用Lombok简化实体类和Spring MVC拦截器的使用。

















 7495
7495

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










