DOM
获取元素、节点
节点:节点包括元素、注释、文本等内容
元素:DOM元素,是节点的子类
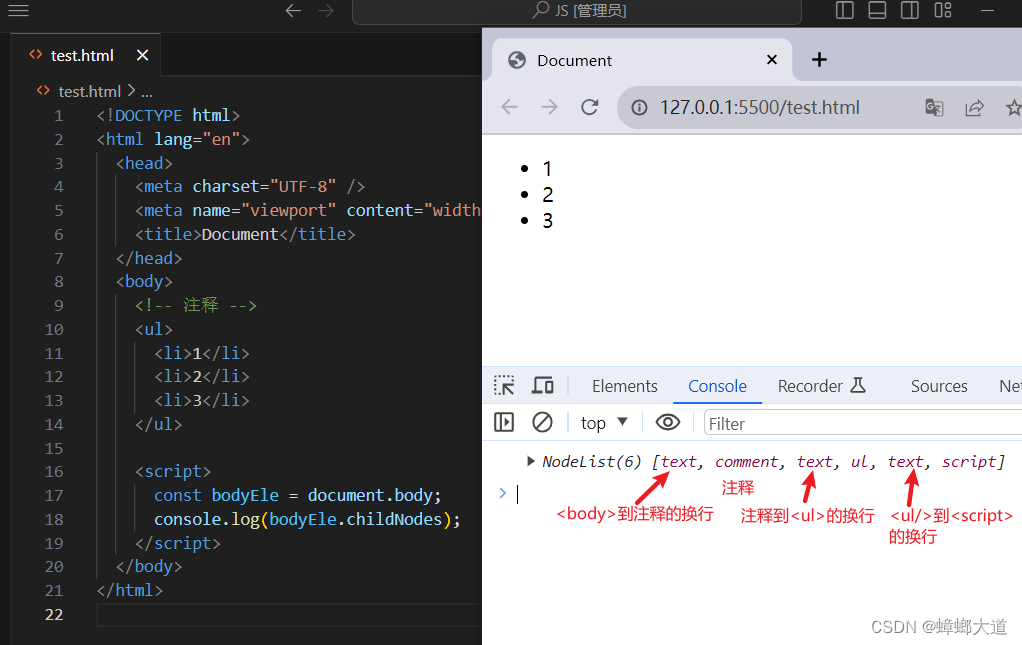
// 获取声明文档
document.doctype
// 获取<html>元素
document.documentElement
// 获取<head>元素
document.head
// 获取<body>元素
document.body
获取元素方法
- querySelector(‘css选择器’) 返回符合条件的第一个元素
- querySelectorAll(‘css选择器’) 返回类数组对象
节点之间的关系
获取一个节点后,根据该节点的关系获取其他节点
- parentNode 父节点
- previousSibling 前一个兄弟节点
- nextSibling 下一个兄弟节点
- childNodes 子节点
- firstChild 第一个子节点
- lastChild 最后一个子节点
元素之间关系
获取一个元素后,根据该元素的关系获取其他元素
- parentElement 父元素
- previousElementSibling 前一个兄弟元素
- nextElementSibling 下一个兄弟元素
- children 子元素
- firstElementChild 第一个子元素
- lastElementChild 最后一个子元素
DOM节点内容的获取与设置
const lis = document.querySelectorAll("ul>li");
// 获取
console.log(lis[0].innerHTML);
console.log(lis[1].textContent);
// 设置
lis[0].innerHTML = "<a href=''>1</a>";
lis[1].textContent = "<a href=''>2</a>";
DOM节点的attribute、property
Attributes
- 属性(Attributes)包含在HTML标签中,用于定义元素的初始属性。
- 在HTML文档中定义,并通常以字符串形式表示
- 通过JS的getAttribute方法获取元素的属性值,通过setAttribute方法设置元素的属性值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="radio" checked="checked" data-test1="test1" test2="test2" />
<script>
const radio = document.querySelector("input");
// 1.获取attribute
console.log(
radio.getAttribute("type"),
radio.getAttribute("checked"),
radio.getAttribute("data-test1"),
radio.getAttribute("test2")
);
// 2.获取所有attribute属性
for (let attr of radio.attributes) {
console.log(attr.name, attr.value);
}
// 3.设置attribute
radio.setAttribute("class", "className1 className2");
// 4.移除attribute
radio.removeAttribute("test2");
// 5.判定是否有attribute属性
console.log(radio.hasAttribute("data-test1")); //true
</script>
</body>
</html>
Properties
- 属性(Properties)是DOM元素对象的属性,用于表示元素在JavaScript中的当前属性
- 以JS对象的形式存在,它们提供了元素的当前状态,如文本内容、值、样式、事件处理程序等。
- 通过对象打点的方式获取/设置属性值
注:
- attribute与property是相互作用的
- 标准的attribute属性会在DOM对象上创建对应的property
- 自定义的attribute属性可以通过domEle.dataset.xxx获取
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="radio" checked="checked" data-test1="test1" test2="test2" />
<script>
const radio = document.querySelector("input");
// 1.获取property
console.log(
radio.type,
radio.checked,
radio.dataset.test1,
radio.dataset.test2
);
// 2.设置property
radio.checked = false;
</script>
</body>
</html>
DOM节点样式style、class
style样式
# 1.获取domEle的所有style样式
getComputedStyle(domEle).xxx
# 2.获取或设置行内样式
domEle.style.xxx
案例:每点击一次 .box,盒子的宽度+1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box" style="color: #fff">123</div>
<script>
const boxEle = document.querySelector(".box");
// 获取宽度
let width = Number(getComputedStyle(boxEle).width.replace("px", ""));
// 点击盒子 增加1px
boxEle.addEventListener("click", (target) => {
boxEle.style.width = width++ + "px";
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
class
# 0.覆盖类
elem.className = 'name1 name2'
# 1.追加类
elem.classList.add(className)
# 2.移除类
elem.classList.remove(className)
# 3.切换类
# 类存在则移除,类不存在则添加
elem.classList.toogle(className)
# 4.判断是否存在
elem.classList.contains(className)
DOM节点创建、移动、克隆、删除
# 1.创建元素节点
document.createElement("li");
# 2.移动
# 在ele的子元素的最后插入节点或字符串
ele.append(...nodes: (string | Node)[])
# 在ele的子元素的开头插入节点或字符串
ele.prepend(...nodes: (string | Node)[])
# 在ele之后插入(作为ele的兄弟节点)节点或字符串
ele.after(...nodes: (string | Node)[])
# 在node之前插入(作为ele的兄弟节点)节点或字符串
ele.before(...nodes: (string | Node)[])
# 将ele替换为给定节点或字符串
ele.replaceWith(...nodes: (string | Node)[])
# 3.克隆
ele.cloneNode(true)
# 4.删除
ele.remove()
DOM元素/window的大小、位置、滚动
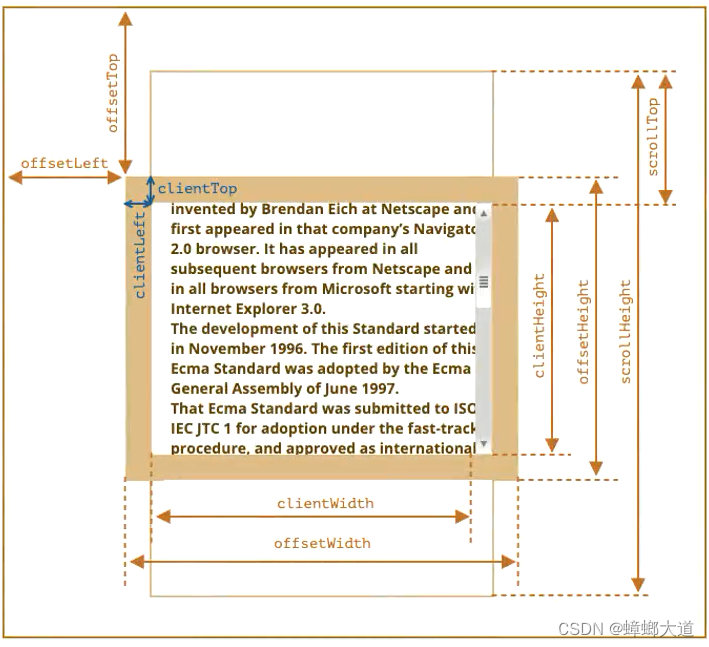
元素
clientWidth: contentWidth + padding (不包含滚动条)
clientHeight: contentHeight + padding
clientLeft: border-left
clientTop: border-top
offsetWidth: 元素完整宽度
offsetHeight: 元素完整高度
offsetLeft: 距离父元素的x
offsetTop: 距离父元素的y
scrollWidth: 整个可滚动区域宽度
scrollHeight: 整个可滚动区域高度
scrollLeft: 被滚动的宽度
scrollTop: 被滚动的高度
window
innerWidth、innerHeight: window窗口的宽高(包含滚动条)
outerWidth、outerHeight: window窗口的宽度(包含调试工具、工具栏)
documentElement.clientWidth、documentElement.clientHeight: html的宽度(不包含滚动条)
scrollX、scrollY: x轴y轴滚动的位置
scrollBy(x,y) 相对于当前坐标,再移动x,y
scrollTo(x,y) 移动到绝对坐标(x,y)
事件
事件处理三种方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 方式1 -->
<div class="box" onclick="console.log(1)">123</div>
<script>
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
// 方式2
// 给box元素添加onclick方法,故后面的同名方法会覆盖前面的
box.onclick = function () {
console.log(2);
};
box.onclick = function () {
console.log(3);
};
// 方式3
// 给box元素添加事件监听,可以添加多个同名事件
box.addEventListener("click", () => {
console.log(4);
});
box.addEventListener("click", () => {
console.log(5);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
每次点击box元素,打印结果
3
4
5
事件处理函数的this指向
this的指向在函数调用时确定。
当元素触发该事件时,事件处理函数如何被调用:
box.addEventListener("click", function (e) {
console.log(this); // this指向box
});
box.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
console.log(this); // this指向父级作用域window
});
box.onclick = function () {
console.log(this); // this指向box
};
事件流
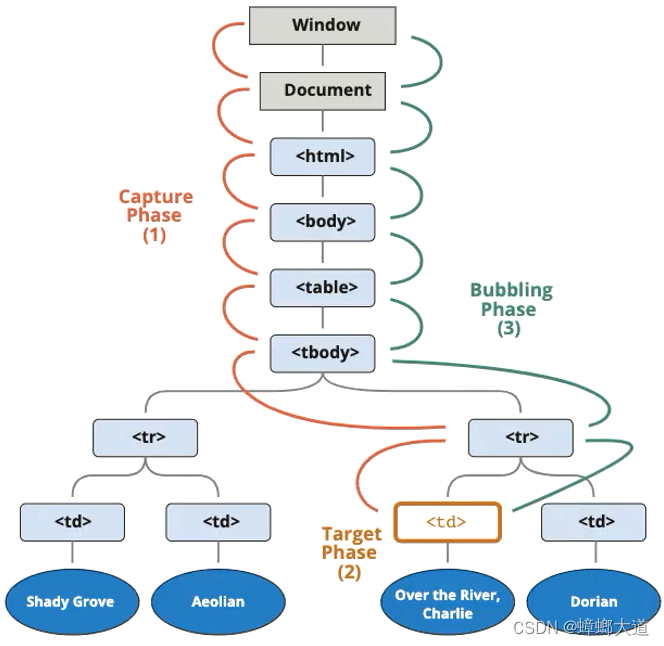
1.同时有捕获和冒泡阶段,则先执行捕获阶段,再执行冒泡阶段
2.addEventListener第三个参数默认值为false(表示冒泡阶段)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.box > span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<span></span>
</div>
<script>
const body = document.body;
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
const span = document.querySelector(".box>span");
body.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("body");
},
false
);
box.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("box");
},
false
);
span.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("span");
},
false
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
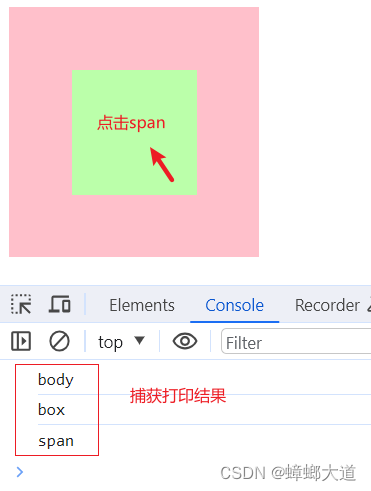
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.box > span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<span></span>
</div>
<script>
const body = document.body;
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
const span = document.querySelector(".box>span");
body.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("body");
},
true
);
box.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("box");
},
true
);
span.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("span");
},
true
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
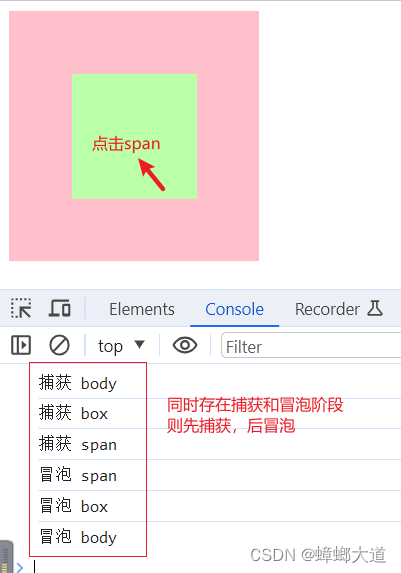
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.box > span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<span></span>
</div>
<script>
const body = document.body;
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
const span = document.querySelector(".box>span");
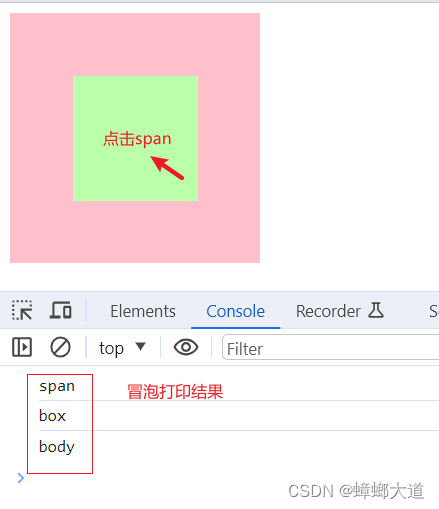
// 1.冒泡阶段
body.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("冒泡 body");
},
false
);
box.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("冒泡 box");
},
false
);
span.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("冒泡 span");
},
false
);
// 2.捕获阶段
body.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("捕获 body");
},
true
);
box.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("捕获 box");
},
true
);
span.addEventListener(
"click",
() => {
console.log("捕获 span");
},
true
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
事件对象
事件对象常用属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.box > span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<span></span>
</div>
<script>
const body = document.body;
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
const span = document.querySelector(".box>span");
box.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
// 事件对象常见属性
// 1.事件类型
console.log(e.type);
// 2.当前事件发生的元素
console.log(e.target);
// 3.当前事件处理的元素
console.log(e.currentTarget);
// 4.事件阶段 捕获1 当前元素2 冒泡3
console.log(e.eventPhase);
// 5.事件发生在元素内的位置
console.log(e.offsetX, e.offsetY);
// 6.事件发生在客户端内的位置
console.log(e.clientX, e.clientY);
// 7.事件发生在客户端相对于documnent的位置
console.log(e.pageX, e.pageY);
// 6.事件发生相对于屏幕的位置
console.log(e.screenX, e.screenY);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
e.target与e.currentTarget区别
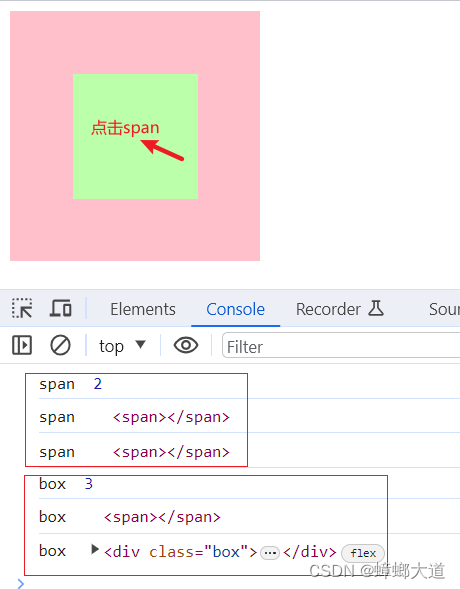
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.box > span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<span></span>
</div>
<script>
const body = document.body;
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
const span = document.querySelector(".box>span");
box.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
console.log("box ", e.eventPhase);
// 当前事件发生的元素
console.log("box ", e.target);
// 当前事件处理的元素
console.log("box ", e.currentTarget);
});
span.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
console.log("span ", e.eventPhase);
// 当前事件发生的元素
console.log("span ", e.target);
// 当前事件处理的元素
console.log("span ", e.currentTarget);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
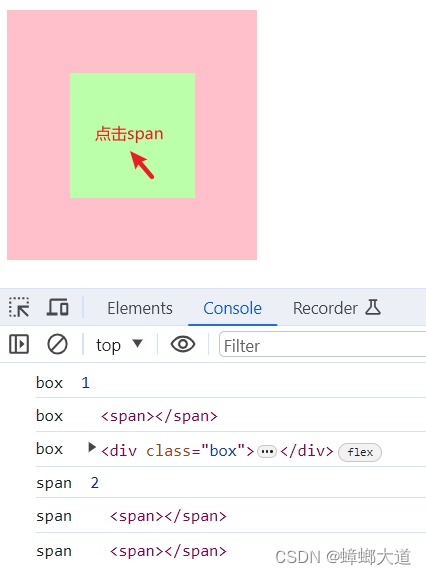
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.box > span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<span></span>
</div>
<script>
const body = document.body;
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
const span = document.querySelector(".box>span");
box.addEventListener(
"click",
(e) => {
console.log("box ", e.eventPhase);
// 当前事件发生的元素
console.log("box ", e.target);
// 当前事件处理的元素
console.log("box ", e.currentTarget);
},
true
);
span.addEventListener(
"click",
(e) => {
console.log("span ", e.eventPhase);
// 当前事件发生的元素
console.log("span ", e.target);
// 当前事件处理的元素
console.log("span ", e.currentTarget);
},
true
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
事件对象常用方法
// 阻止事件流(冒泡、捕获都能阻止)
e.stopPropagation();
// 阻止默认事件
e.preventDefault();
EventTarget类
window继承自EventTarget类
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button>移除click事件</button>
<script>
const button = document.querySelector("button");
// 1.监听事件
window.addEventListener("cjc", handleCjc, false);
window.addEventListener("click", handleClick, false);
function handleCjc(e) {
console.log("cjc事件处理函数", e);
}
function handleClick(e) {
console.log("click事件处理函数", e);
}
// 2.抛出自定义事件
// 注:抛出自定义事件应该在监听之后,否则可能监听不到
window.dispatchEvent(new Event("cjc"));
button.addEventListener("click", () => {
// 3.移除事件
window.removeEventListener("click", handleClick);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
事件委托(event delegation)
通过事件冒泡,将子元素的事件委托给父元素触发
e.target 事件触发的元素
e.currentTarget 事件处理的元素
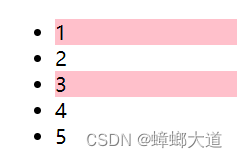
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.active {
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
</ul>
<script>
const ul = document.querySelector("ul");
const li = document.querySelector("li");
ul.addEventListener(
"click",
(e) => {
// e.target事件触发的元素
if (e.target !== ul) {
e.target.classList.add("active");
}
},
false
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
常见事件类型
鼠标事件
click
dblclick
contextmenu 右键打开菜单
mouseenter、mouseleave鼠标移入、移除
mouseover、mouseout鼠标移入、移除(支持冒泡,故能使用使用事件委托)
mousemove 鼠标移动
鼠标移入移出
1.当某个元素监听鼠标移入移出事件时,mouseenter与mouseover没有区别
2.嵌套元素时不一致
3.事件委托时,只能使用mouseover、mouseout,因为支持冒泡
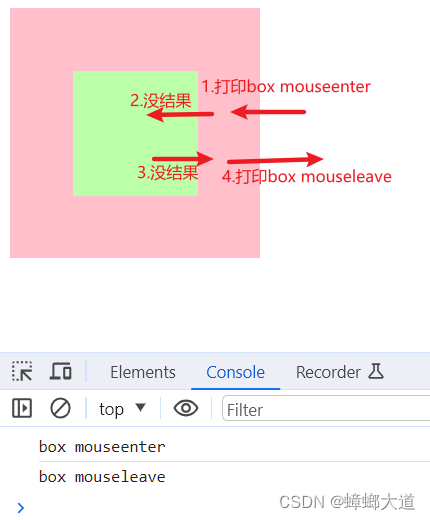
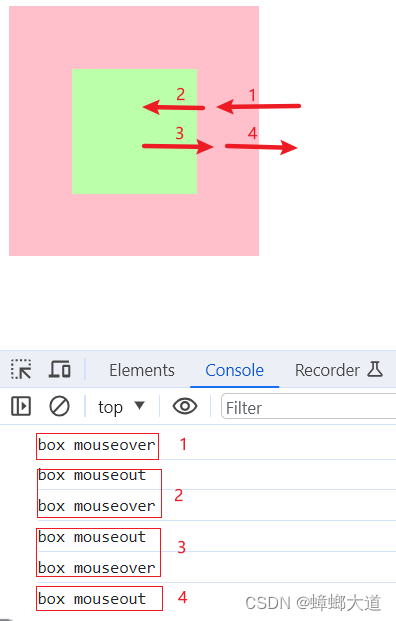
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.box > span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #bfa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<span></span>
</div>
<script>
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
// 1.mouseenter、mouseleave(不支持冒泡)
// 子元素作为父元素的一部分
// box.addEventListener("mouseenter", (e) => {
// console.log("box mouseenter");
// });
// box.addEventListener("mouseleave", (e) => {
// console.log("box mouseleave");
// });
// 2.mouseover、mouseout(支持冒泡)
// 子元素与父元素相互独立
box.addEventListener("mouseover", (e) => {
console.log("box mouseover");
});
box.addEventListener("mouseout", (e) => {
console.log("box mouseout");
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
鼠标移入小盒子时,变红:
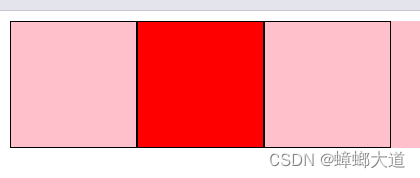
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
background-color: pink;
}
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="box box1"></div>
<div class="box box2"></div>
<div class="box box3"></div>
</div>
<script>
const container = document.querySelector(".container");
const boxs = document.querySelectorAll(".box");
// // 方式1:给每个盒子监听鼠标移入事件
// // 此时mouseover与mouseenter无区别
// for (let i = 0; i < boxs.length; i++) {
// boxs[i].addEventListener("mouseenter", (e) => {
// e.target.style.backgroundColor = "red";
// });
// boxs[i].addEventListener("mouseleave", (e) => {
// e.target.style.backgroundColor = "";
// });
// }
// 方式2:事件委托
// 只能使用mouseover、mouseout(因为支持冒泡)
container.addEventListener("mouseover", (e) => {
if (e.target !== container) {
e.target.style.backgroundColor = "red";
}
});
container.addEventListener("mouseout", (e) => {
if (e.target !== container) {
e.target.style.backgroundColor = "";
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
键盘事件
keydown 键盘按下
keypress 键盘按下(文本输入中)
keyup 键盘弹起(文本输入完成)
区分按键:e.code或e.key
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<script>
const input = document.querySelector("input");
// 按下s时,文本框聚焦
// 在整个文档document上监听键盘事件
document.addEventListener("keyup", (e) => {
console.log(e.key, e.code);
if (e.code === "KeyS") {
input.focus();
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
表单事件
input 用户输入时触发
focus 聚焦时触发
blur 失去焦点时触发
reset 表单重置时触发
submit 表单提交时触发
change 基于表单元素的类型和用户对元素的操作的不同,change 事件触发的时机也不同
- input元素的值被修改且失去焦点时触发change事件
- radio元素被选中时触发(而不是取消选中)
- checkbox元素被选中或取消选中时
- select点击某个下拉选项
- input:file 上传了文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
<input type="text" />
<label>
<span>男</span>
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="0" />
</label>
<label>
<span>女</span>
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="1" />
</label>
<button type="reset">重置</button>
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>
<script>
const form = document.querySelector("form");
const inputEle = document.querySelector("input");
const radioMale = document.querySelector('[type="radio"][value="0"]');
const radioFemale = document.querySelector('[type="radio"][value="1"]');
// input focus blur
inputEle.addEventListener("input", (e) => {
console.log("触发input事件", inputEle.value);
});
inputEle.addEventListener("focus", (e) => {
console.log("触发focus事件");
});
inputEle.addEventListener("blur", (e) => {
console.log("触发blur事件");
});
// reset submit
form.addEventListener("reset", (e) => {
console.log("触发reset事件");
});
form.addEventListener("submit", (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
console.log("触发submit事件");
});
// change
radioMale.addEventListener("change", (e) => {
console.log("触发change事件");
});
inputEle.addEventListener("change", (e) => {
console.log("触发change事件");
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
文档加载事件
DOMContentLoaded:浏览器全部加载完HTML,并构建了DOM树,但img和样式等外部资源可能未加载完成
load:浏览器全部加载完HTML,所有外部资源(图片、样式等)
自定义属性
某些情况下,需要使用自定义属性来区分不同的DOM元素

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<button data-action="1">按钮1</button>
<button data-action="2">按钮2</button>
<button data-action="3">按钮3</button>
</div>
<script>
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
// 使用自定义属性区分不同元素
box.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
const action = e.target.dataset.action;
switch (action) {
case "1":
e.target.style.color = "red";
break;
case "2":
e.target.style.color = "green";
break;
case "3":
e.target.style.color = "blue";
break;
default:
break;
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
排他思想
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.active {
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
</ul>
<script>
const ul = document.querySelector("ul");
const lis = document.querySelectorAll("li");
// 方式3 变量控制
let activeEle = null;
ul.addEventListener(
"click",
(e) => {
// 方式1 遍历
// 去除所有元素的active
// for (let i = 0; i < lis.length; i++) {
// lis[i].classList.remove("active");
// }
// if (e.target !== ul) {
// e.target.classList.add("active");
// }
// 方式2 直接获取到有active类的DOM元素
// const activeEle = document.querySelector(".active");
// activeEle && activeEle.classList.remove("active");
// if (e.target !== ul) {
// e.target.classList.add("active");
// }
// 方式3 变量控制
if (activeEle) {
activeEle.classList.remove("active");
}
if (e.target !== ul) {
e.target.classList.add("active");
}
activeEle = e.target;
},
false
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
BOM
window对象
window作为全局对象以及窗口相关
# 浏览器的全局对象:
window
# node中的全局对象:
global
# EMCMA规范了统一的全局对象:
globalThis
- window对象相关的属性方法查询MDN
location
location常见属性
 location常见方法
location常见方法

URLSearchParams
用来处理URL查询字符串
// 将查询字符串转化为URLSearchParams类型
let queryStr = new URLSearchParams("?name=ccc&age=999")

中文使用encodeURIComponent和decodeURIComponent进行编码和解码
history
history:浏览器历史

前端路由核心:修改了URL,但是页面不刷新
方式1:修改hash值
方式2:修改history
navigator
navigator:用户代理(浏览器)的状态和标识

screen
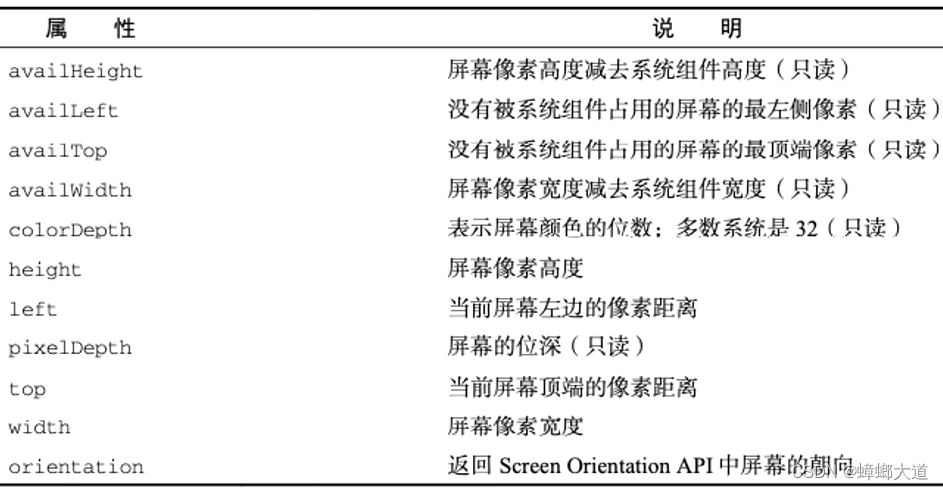
screen:屏幕信息
小案例
实时显示日期
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
<script>
// 日期格式化
function formateDate(timeStamp, formatStr) {
// 将时间戳转化为日期对象
const date = new Date(timeStamp);
if (/(y+)/.test(formatStr)) {
// 将正则匹配到的年份格式,替换为日期对象date解析出来的年份
formatStr = formatStr.replace(
RegExp.$1,
(date.getFullYear() + "").substr(4 - RegExp.$1.length)
);
}
let o = {
"M+": date.getMonth() + 1,
"d+": date.getDate(),
"h+": date.getHours(),
"m+": date.getMinutes(),
"s+": date.getSeconds(),
};
for (let k in o) {
if (new RegExp(`(${k})`).test(formatStr)) {
let str = o[k] + "";
// 将正则匹配到的格式,替换为日期对象date解析出来的
formatStr = formatStr.replace(
RegExp.$1,
RegExp.$1.length === 1 ? str : str.padStart(2, "0")
);
}
}
return formatStr;
}
const box = document.querySelector(".box");
setInterval(() => {
box.innerHTML = formateDate(+new Date(), "yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
}, 1000);
</script>
</body>
</html>
倒计时
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="countdown"></div>
<script>
// 设置目标日期和时间
const targetDate = new Date("2023-12-31 12:00:00").getTime();
// 更新倒计时的函数
function updateCountdown() {
const currentDate = new Date().getTime();
const timeLeft = targetDate - currentDate;
// 计算剩余的天、小时、分钟和秒
const days = Math.floor(timeLeft / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24));
const hours = Math.floor((timeLeft / (1000 * 60 * 60)) % 24);
const minutes = Math.floor((timeLeft / (1000 * 60)) % 60);
const seconds = Math.floor((timeLeft / 1000) % 60);
// 更新页面上的倒计时显示
const countdownElement = document.getElementById("countdown");
countdownElement.innerHTML =
days + "天 " + hours + "小时 " + minutes + "分钟 " + seconds + "秒";
}
// 初始调用一次,然后每秒更新一次
updateCountdown();
const countdownInterval = setInterval(updateCountdown, 1000);
</script>
</body>
</html>






















 140
140











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








