一
还是拿运算符重载中的模拟String类运算符重载来说事 参考
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
/
//length()
//operator[]
//operator+
//operator+=
//operator > < >= <= == !=
/
class String
{
public:
String(const char* str = "") //常类型到常类型
{
m_data = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, str);
}
String(const String& s)
{
m_data = new char[strlen(s.m_data) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, s.m_data);
}
~String()
{
delete[]m_data;
m_data = NULL;
}
public:
size_t length()const
{
return strlen(m_data);
}
char operator[](int i)
{
assert(i >= 0 && i < length());
return m_data[i];
}
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
delete[](this->m_data);
new char[s.length() + 1];
strcpy(this->m_data, s.m_data);
}
return *this;
}
String operator+(const String& s)
{
char* tmp = new char[length() + s.length() + 1]; //??????
strcpy(tmp, this->m_data);
strcat(tmp, s.m_data);
String temp(tmp);
delete []tmp;
return temp;
}
String& operator+=(const String& s)
{
size_t new_size = length() + s.length() + 1;
char* tmp = new char[new_size];
strcpy(tmp, m_data);
strcat(tmp, s.m_data);
delete[]m_data;
m_data = tmp;
return *this;
}
public:
bool operator==(const String& s)
{
if (strcmp(this->m_data, s.m_data) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator!=(const String& s)
{
if (strcmp(this->m_data, s.m_data) != 0)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator>(const String& s)
{
if (strcmp(this->m_data, s.m_data) > 0)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator<(const String& s)
{
if (strcmp(this->m_data, s.m_data) < 0)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator>=(const String& s)
{
if (strcmp(this->m_data, s.m_data) < 0)
return false;
return true;
}
bool operator<=(const String& s)
{
if (strcmp(this->m_data, s.m_data) > 0)
return false;
return true;
}
private:
char* m_data;
};
int main()
{
String s1("Hello"); //s1[0] ==> H
String s2("Bit.");
s1 = s2;
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); ++i)
cout << s1[i];
cout << endl;
String s = s1 + s2; //s = HelloBit
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i)
cout << s[i];
cout << endl;
s1 += s2; //
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); ++i)
cout << s1[i];
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
以上代码一运行就会发生悲剧:
如下图(找bug让楼主快发疯了,日夜煎熬,可都是徒劳)
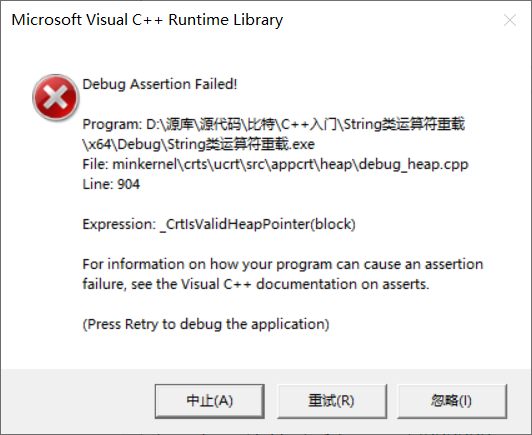
出现以上崩溃(就炸)仔细查看代码,并没有发现new和delete的部分有任何问题
调试起来看一下:
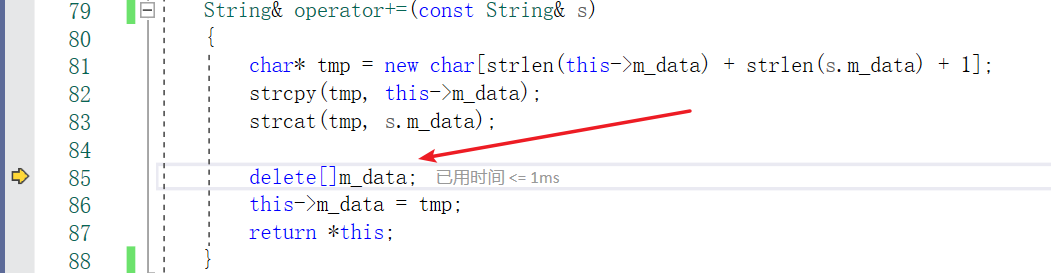
当运行到
s1 += s2;
F11进入函数会发现运行到
delete[]m_data;
程序就中断了
认真看+=运算符重载函数没任何问题可是;偏偏进入函数一delete就会有问题,说明两种情况:
一:delete的内存空间非法
二:要释放的内存在开辟时有问题
屏蔽s1 += s2; 前的代码发现没问题,那么就说明之前的代码中存在的问题导致的
依次释放
s1 += s2;
语句前注释的代码,发现当有
s1 = s2;
语句时,程序就会崩溃,说明问题出现在=运算符重载上
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
delete[](this->m_data);
new char[s.length() + 1];
strcpy(this->m_data, s.m_data);
}
return *this;
}
仔细查看发现new开辟的空间足够没任何问题,但是发现,只是开辟了空间,但没有任何指针指向这块空间,即m_data的空间被释放,然后m_data没拿到新开辟的空间又给m_data指向的释放前的空间写入数据

应该写成:

还有以下这句释放了对象m_data的空间
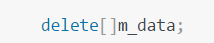
,然后+=运算符重载函数中又释放同一个对象s1的m_data空间,这就造成同一个内存空间释放两次,问题终于找到了,修改后:

实在是太不容易了,之前一直将问题集中在+=运算符重载函数中和编译器环境中,本身用的是VS2019就不信邪去VS2013也试了一下,发现可以通过,多次运行,发现有九成几率了能通过。VS2019是特别不给面子,一次都不过。看来VS2013能通过的是很多时候能通过的原因在编译器释放两次的空间可能不是重要的内存空间,或者VS2013编译器不是太严格
VS2013没有警告
关于编译器的严谨与否不再深究,但是一个人代码功底和调试bug的能力是很重要的
二
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
class String
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &out, const String &s);
public:
String(char *str = "")
{
m_data = new char[strlen(str)+1];
strcpy(m_data, str);
}
String(const String &s)
{
m_data = new char[strlen(s.m_data)+1];
strcpy(m_data, s.m_data);
}
String& operator=(const String &s)
{
if(this != &s)
{
free(m_data);
m_data = new char[strlen(s.m_data)+1];
strcpy(m_data, s.m_data);
}
return *this;
}
~String()
{
delete []m_data;
m_data = NULL;
}
public:
int length()const
{
return strlen(m_data);
}
public:
char operator[](int i)
{
assert(i>=0 && i<length());
return m_data[i];
}
String operator+(const String &s)
{
int total_size = length() + s.length() + 1;
char *tmp = new char[total_size];
strcpy(tmp, m_data);
strcat(tmp, s.m_data);
String tmps(tmp);
delete []tmp;
return tmps;
}
String& operator+=(const String &s)
{
int new_size = length() + s.length()+1;
char *tmp = new char[new_size];
strcpy(tmp, m_data);
strcat(tmp, s.m_data);
delete []m_data;
m_data = tmp;
return *this;
}
public:
bool operator==(const String &s)
{
if(strcmp(m_data, s.m_data) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator!=(const String &s)
{
return !(*this==s);
}
bool operator>(const String &s)
{
if(strcmp(m_data, s.m_data) == 1)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator<(const String &s)
{
if(strcmp(m_data, s.m_data) == -1)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator>=(const String &s)
{
return !(*this < s);
}
bool operator<=(const String &s)
{
return !(*this > s);
}
private:
char *m_data;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream &out, const String &s)
{
out<<s.m_data;
return out;
}
int main()
{
String s1("Hello"); //s1[0] ==> H
String s2("Bit.");
for(int i=0; i<s1.length(); ++i)
cout<<s1[i];
cout<<endl;
s1 = s2;
String s = s1 + s2; //s = HelloBit
cout<<s1<<endl;
s1 += s2;
cout<<s1<<endl;//
if(s1 == s2)
cout<<"s1 == s2"<<endl;
if(s1 != s2)
cout<<"s1 != s2"<<endl;
if(s1 > s2)
cout<<"s1 > s2"<<endl;
if(s1 < s2)
cout<<"s1 < s2"<<endl;
if(s1 >= s2)
cout<<"s1 >= s2"<<endl;
if(s1 <= s2)
cout<<"s1 <= s2"<<endl;
return 0;
}
以上代码编译运行都没有毛病
但是细心的朋友会发现一个巨大的问题
String& operator=(const String &s)
函数中有一个巨大的潜在问题,这个问题编译器没有识别出来
以上源代码全文的m_data数据成员都是用new开辟的,但是唯有这块是用free释放的。free是搭配malloc,realoc,calloc(C语言),而C++中是delete和new配对使用的不能混用,因为C和C++ 中的动态内存管理实现是不同的也就是实现是不同的(即使new和delete底层调用了malloc和free),所以就不能混用
如下:
new和delete内部原理模拟实现方式:
void* operator new(size_t sz) //1
{
void *ptr = malloc(sz);
return ptr;
}
void operator delete(void *ptr)
{
free(ptr);
}
void* operator new[](size_t sz) //1
{
void *ptr = malloc(sz);
return ptr;
}
void operator delete[](void *ptr)
{
free(ptr);
}
new和delete入门请看:
剖析构造函数和动态内存开辟函数new和delete
























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








