文章目录
1、Spring
1.1、Spring简介(了解)
- spring:春天 —> 给软件行业带来春天;
- spring雏形:2002年,首次退出了spring框架的雏形 --> interface 21;
- spring发布:2004年3月24号,以interface为基础,重新设计,正式发布了1.0版本;
- spring创始人:Rod Jognson,悉尼大学,音乐博士,非计算机专业;
- spring目的:使现有的技术更加容易,本身是一个大杂烩,整合了现有的技术;
官网:https://spring.io/projects/spring-framework#overview
官方下载地址:https://repo.spring.io/release/org/springframework/spring/
GitHub地址:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.13.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.13.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
1.2、spring优点
- Spring是一个开源的免费的框架(容器);
- Spring是一个轻量级的、非入侵式的框架;
- 控制反转(IOC)、面向切面编程(AOP);
- 支持事务处理,对框架整合的支持;
Spring就是一个轻量级的控制反转(IOC) 和 面向切面(AOE)的容器框架;
1.3、组成(七大模块)
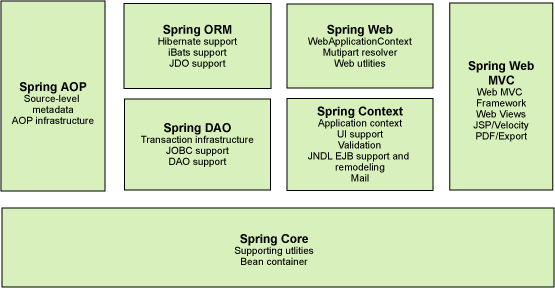
核心容器(Spring Core)
核心容器提供Spring框架的基本功能。Spring以bean的方式组织和管理Java应用中的各个组件及其关系。Spring使用BeanFactory来产生和管理Bean,它是工厂模式的实现。BeanFactory使用控制反转(IoC)模式将应用的配置和依赖性规范与实际的应用程序代码分开。
应用上下文(Spring Context)
Spring上下文是一个配置文件,向Spring框架提供上下文信息。Spring上下文包括企业服务,如JNDI、EJB、电子邮件、国际化、校验和调度功能。
Spring面向切面编程(Spring AOP)
通过配置管理特性,Spring AOP 模块直接将面向方面的编程功能集成到了 Spring框架中。所以,可以很容易地使 Spring框架管理的任何对象支持 AOP。Spring AOP 模块为基于 Spring 的应用程序中的对象提供了事务管理服务。通过使用 Spring AOP,不用依赖 EJB 组件,就可以将声明性事务管理集成到应用程序中。
JDBC和DAO模块(Spring DAO)
JDBC、DAO的抽象层提供了有意义的异常层次结构,可用该结构来管理异常处理,和不同数据库供应商所抛出的错误信息。异常层次结构简化了错误处理,并且极大的降低了需要编写的代码数量,比如打开和关闭链接。
对象实体映射(Spring ORM)
Spring框架插入了若干个ORM框架,从而提供了ORM对象的关系工具,其中包括了Hibernate、JDO和 IBatis SQL Map等,所有这些都遵从Spring的通用事物和DAO异常层次结构。
Web模块(Spring Web)
Web上下文模块建立在应用程序上下文模块之上,为基于web的应用程序提供了上下文。所以Spring框架支持与Struts集成,web模块还简化了处理多部分请求以及将请求参数绑定到域对象的工作。
MVC模块(Spring Web MVC)
MVC框架是一个全功能的构建Web应用程序的MVC实现。通过策略接口,MVC框架变成为高度可配置的。MVC容纳了大量视图技术,其中包括JSP、POI等,模型来有JavaBean来构成,存放于m当中,而视图是一个街口,负责实现模型,控制器表示逻辑代码,由c的事情。Spring框架的功能可以用在任何J2EE服务器当中,大多数功能也适用于不受管理的环境。Spring的核心要点就是支持不绑定到特定J2EE服务的可重用业务和数据的访问的对象,毫无疑问这样的对象可以在不同的J2EE环境,独立应用程序和测试环境之间重用。
1.4、拓展
- Spring Boot
- 一个快速开发的脚手架
- 基于SpringBoot可以快速的开发单个微服务
- Spring Cloud
- Spring Cloud是基于Spring Boot实现的
因为大多数公司都在使用Spring Boot进行快速开发,学习Spring Boot前提,需要完全掌握Spring和SpringMVC
弊端:发展太久之后违背了原来的理念,配置十分繁琐
2、IOC理论推导
-
UserDao接口
public interface UserDao { void getUser(); } -
UserDaoImpl实现类
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ public void getUser() { System.out.println("获取用户数据"); } } -
UserService业务接口
public interface UserService { void getUser(); } -
UserServiceImpl业务实现类
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ /* dao引入到service */ private UserDao userDao; private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl(); /* 利用set进行动态实现值的注入 */ public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } public void getUser() { userDao.getUser(); } } -
test测试类
public class UserTest { public static void main(String[] args) { /* 用户实际调用,用户不用接触dao */ /* 控制权在程序 */ UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl(); userService.getUser(); /* 控制权在用户, */ userService.setUserDao(new UserDaoImpl()); } }控制权在程序员
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-XplVJFbB-1615370612251)(C:\Users\y1361\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1615359645911.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20210310180842678.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3FxXzQ0MTI2MDI0,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
利用set注入, 控制权在用户,可以大大降低程序的耦合性
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-f2R4G2xI-1615370612254)(C:\Users\y1361\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1615359679518.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2021031018085634.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3FxXzQ0MTI2MDI0,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
2.1、IOC本质
控制反转IOC(Inversion of Control),是一种设计思想,DI(依赖注入)是实现IOC的一种方法,也有人认为DI只是IOC的另一种说法。没有IOC的程序中 , 我们使用面向对象编程 , 对象的创建与对象间的依赖关系完全硬编码在程序中,对象的创建由程序自己控制,控制反转后将对象的创建转移给第三方,个人认为所谓控制反转就是:获得依赖对象的方式反转了。
控制反转是一种通过描述(xml或注解)并通过第三方去生产或获取特定对象的方式,在spring中实现控制反转的是IOC容器,其实现方法是依赖注入
3、Hello Spring
先导入spring-context依赖
<dependency>
<!-- 单元测试 -->
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 无参有参构造注解 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-context依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
-
HelloSpring.java
public class HelloSpring { private String str; public String getStr() { return str; } public void setStr(String str) { this.str = str; } @Override public String toString() { return "HelloSpring{" + "str='" + str + '\'' + '}'; } } -
beans.xml
去官方文档 https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/ ,找到对应maven版本的spring版本,下一一步找 .RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/core.html#spring-core
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 使用spring来创建对象 类型 变量名 = new 类型(); bean = 对象 id -> 变量名 class -> new的对象 property -> 给对象中的属性设置值 --> <bean id="helloSpring" class="com.tian.pojo.HelloSpring"> <property name="str" value="Spring"/> </bean> </beans> -
HelloTest
public class HelloTest { public static void main(String[] args) { /* 获取spring的上下文对象 */ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); /* 我们的对象现在都在spring中管理,我们要使用直接去里面取出来就可以了 */ HelloSpring helloSpring = (HelloSpring) context.getBean("helloSpring"); System.out.println(helloSpring.toString()); } } -
打印结果
HelloSpring{str='Spring'}
当我们类左边有叶子标志的时候,说明我们的类已经被beans托管了,已经由Spring容器来给我们创建好了对象
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Fd0a4Ujw-1615370612261)(C:\Users\y1361\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1615362405585.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20210310180957950.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3FxXzQ0MTI2MDI0,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
所谓的IOC,对象由Spring来创建,管理,装备!
4、IOC创建对象方式
-
使用无参构造创建对象(默认)
-
有参构造
-
下标赋值
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="7500000"/> <constructor-arg index="1" value="42"/> </bean> -
类型赋值(不建议使用)
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean"> <constructor-arg type="int" value="7500000"/> <constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="42"/> </bean> -
直接通过参数名赋值
<beans> <bean id="beanOne" class="x.y.ThingOne"> <constructor-arg ref="beanTwo"/> <constructor-arg ref="beanThree"/> </bean> <bean id="beanTwo" class="x.y.ThingTwo"/> <bean id="beanThree" class="x.y.ThingThree"/> </beans>
-
Spring容器类似于婚介,当我们配置了beans之后,我们的对象就被创建! 内存中只有一份
5、Spring配置
5.1、别名
就是多了一个名字,和数据库一模一样
<!-- 如果添加了别名,也可以用别名获取其他对象 -->
<alias name="user" alias="user2"/>
5.2、bean的配置
<!--
id: bean的唯一标识符,就相当于对象名
class: bean对象所对应的全限定名(包名 + 类名)
name: 也是别名,可以同时取多个别名
-->
<bean id="user6" class="com.tian.pojo.User" name="user3,user4"/>
5.3、import
一般用于团队开发使用,可以将多个配置文件导入为一个xml
假设有三个人一起开发,三个人负责不同的开发,三个类注册在不同的bean中,利用import将所有人的beans.xml合并为一个总的applicationContext.xml,使用的时候直接使用总的xml文件
-
张三 beans1.xml
-
李四 beans2.xml
-
王五 beans3.xml
-
合并为 applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <import resource="beans1.xml"/> <import resource="beans2.xml"/> <import resource="beans3.xml"/> </beans>
6、DI(依赖注入)
6.1、构造器注入
见4;
6.2、set方式注入[重点](普通注入,引用注入,map注入,list注入,set注入,null值注入,Properties 注入)
- 依赖注入:set注入!(本质)
- 依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器
- 注入:bean对象中的所有属性,由容器来注入
【环境搭建】
-
复杂类型
Address
public class Address { private String address; public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } @Override public String toString() { return "Address{" + "address='" + address + '\'' + '}'; } } -
真实测试对象
Student
public class Student { private String name; private Address address; private String[] books; private List<String> hobbys; private Map<String,String> cards; private Set<String> games; private Properties info; private String wife; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } public String[] getBooks() { return books; } public void setBooks(String[] books) { this.books = books; } public List<String> getHobbys() { return hobbys; } public void setHobbys(List<String> hobbys) { this.hobbys = hobbys; } public Map<String, String> getCards() { return cards; } public void setCards(Map<String, String> cards) { this.cards = cards; } public Set<String> getGames() { return games; } public void setGames(Set<String> games) { this.games = games; } public Properties getInfo() { return info; } public void setInfo(Properties info) { this.info = info; } public String getWife() { return wife; } public void setWife(String wife) { this.wife = wife; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", address=" + address + ", books=" + Arrays.toString(books) + ", hobbys=" + hobbys + ", cards=" + cards + ", games=" + games + ", info=" + info + ", wife='" + wife + '\'' + '}'; } } -
applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="student" class="com.tian.pojo.Student"> <!-- 第一种,普通值注入 --> <property name="name" value="天宇"/> <!-- 第二种,bean引用注入 ref --> <property name="address" ref="address"/> <!-- 数组注入 --> <property name="books"> <array> <value>红楼梦</value> <value>西游记</value> <value>水浒传</value> </array> </property> <!-- 集合注入 --> <property name="hobbys"> <list> <value>吃饭</value> <value>睡觉</value> <value>打豆豆</value> </list> </property> <!-- map注入 --> <property name="cards"> <map> <entry key="电话" value="13619126257"/> <entry key="身份证" value="612724222211551563"/> <entry key="银行卡" value="156456123465156"/> </map> </property> <!-- set注入 --> <property name="games"> <set> <value>lol</value> <value>cf</value> <value>csgo</value> </set> </property> <!-- 空值(null)注入 --> <property name="wife"> <null/> </property> <!-- Properties --> <property name="info"> <props> <prop key="学号">112</prop> <prop key="性别">男</prop> <prop key="年级">26</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean id="address" class="com.tian.pojo.Address"> <property name="address" value="北京"/> </bean> </beans> -
测试类
public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student"); System.out.println(student.toString()); } } -
结果
Student{ name='天宇', address=Address{address='北京'}, books=[ 红楼梦, 西游记, 水浒传], hobbys=[ 吃饭, 睡觉, 打豆豆 ], cards={ 电话=13619126257, 身份证=612724222211551563, 银行卡=156456123465156 }, games=[ lol, cf, csgo ], info={ 学号=112, 性别=男, 年级=26 }, wife='null' }
6.3、拓展方式注入
-
p命名空间注入 –> 可以直接通过属性注入值 ,
在我们使用前,需要导入xml约束 下方红框勾选出的 –> xmlns:p=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/p”
官方:

user实例public class User { private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- p命名空间注入,可以直接使用属性注入值 --> <bean id="user" class="com.tian.pojo.User" p:age="18" p:name="宙斯"/> </beans>tset测试
public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user = context.getBean("user", User.class); System.out.println(user); } }结果
User{name='宙斯', age=18} -
c命名空间注入 –> 通过构造器注入
nested
constructor-argelements. 必须要有构造器,没有构造器是用不了c命名空间注入在我们使用前,需要导入xml约束 下方红框勾选出的 –> xmlns:c=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/c”

user实例
public class User { private String name; private int age; public User(){ } public User(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- c命名空间注入,通过构造器注入 --> <bean id="user2" class="com.tian.pojo.User" c:age="20" c:name="塞斯"/> </beans>test测试
public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user = context.getBean("user2", User.class); System.out.println(user); } }结果
User{name='塞斯', age=20}






















 519
519











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








