 1.使用场景
1.使用场景
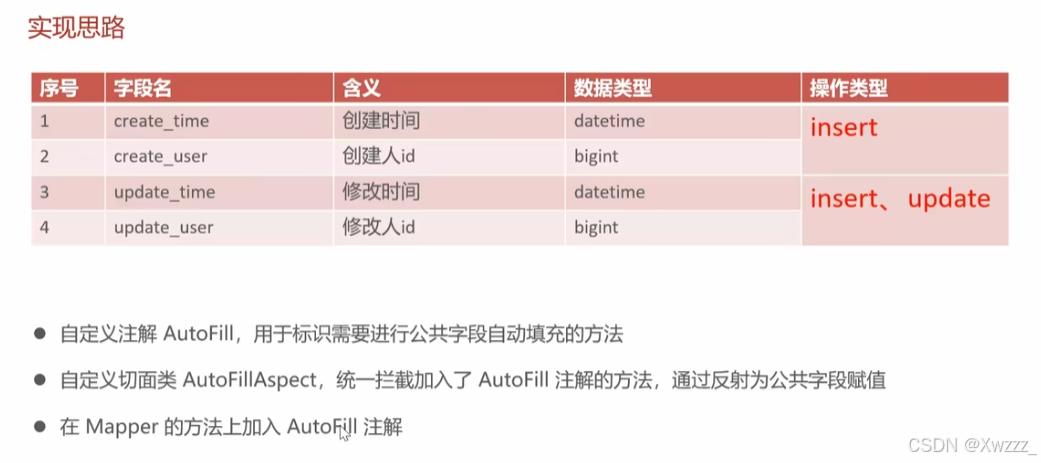
当我们有大量的表需要管理公共字段,并且希望提高开发效率和确保数据一致性时,使用这种自动填充方式是很有必要的。它可以达到一下作用
-
统一管理数据库表中的公共字段:如创建时间、修改时间、创建人ID、修改人ID等,这些字段在所有表中都会存在,需要在插入和更新时保持一致性。
-
避免重复代码:在不同的业务逻辑中频繁操作相同的字段(如每次插入记录时手动设置创建时间和创建人),使用自动填充可以避免手动填写这些字段,减少重复代码。
-
提高开发效率:当项目中有大量类似的插入或更新操作时,通过自动填充机制可以减轻手动维护字段的负担,提高开发效率和代码的可维护性。
-
确保数据的准确性:通过切面统一处理公共字段的填充,减少人为错误,确保创建时间、修改时间等字段始终准确。
2.步骤(以商城数据维护项目为例)
2.1 定义一个枚举类 OperationType,
这个类用于表示数据库操作的类型。枚举包含两个常量:
- UPDATE:表示更新操作。
- INSERT:表示插入操作。
枚举类通常用于标识某个操作是插入还是更新操作,方便在代码中进行逻辑判断或执行特定操作(如公共字段的自动填充),来让我在不同的数据库操作类型中统一处理。
package com.sky.enumeration;
/**
* 数据库操作类型
*/
public enum OperationType {
/**
* 更新操作
*/
UPDATE,
/**
* 插入操作
*/
INSERT
}
2.2 定义名为 AutoFill 的自定义注解
自定义注解用于标识某个方法需要进行公共字段的自动填充。注解包含一个刚才定义 OperationType 枚举值,用于指定该方法对应的数据库操作类型,是插入还是更新。
我下面对重要内容进行解释
- @Target(ElementType.METHOD):标注该注解只能应用在方法上。
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME):指定该注解在运行时保留,可以通过反射机制获取该注解。
- OperationType value():这个方法定义了注解的一个属性,必须设置
OperationType枚举值(INSERT或UPDATE),来表示操作类型。
package com.sky.annotation;
import com.sky.enumeration.OperationType;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 自定义注解,用于标识某个方法需要进行功能字段自动填充
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AutoFill {
// 数据库操作类型:UPDATE 或 INSERT
OperationType value();
}
这个自定义注解的主要作用是在特定的数据库操作方法上使用,通过指定操作类型(插入或更新),结合其他逻辑实现公共字段的自动填充。
2.3 定义名为 AutoFillAspect 的切面类
这个类用于处理带有 @AutoFill 注解的方法,通过定义切面,切入点,前置通知实现
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* 自定义切面,实现公共字段自动填充处理逻辑
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class AutoFillAspect {
/**
* 切入点
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.sky.mapper.*.*(..)) && @annotation(com.sky.annotation.AutoFill)")
public void autoFillPointCut() {}
/**
* 前置通知,在通知中进行公共字段的赋值
*/
@Before("autoFillPointCut()")
public void autoFill(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("开始进行公共字段自动填充...");
}
}
- @Aspect:声明该类是一个切面类,负责切入业务逻辑并执行相应操作。
- @Component:将这个类注册为Spring的组件,以便在应用程序中自动管理和注入。
- @Slf4j:启用日志记录功能,方便在切面逻辑中记录日志(当前代码中没有具体使用日志)。
- @Pointcut:定义切入点,拦截我
com.sky.mapper包下所有带有@AutoFill注解的方法。即拦截那些需要自动填充公共字段的数据库操作方法。 - @Before("autoFillPointCut()"):表示该方法会在切入点方法执行之前执行,这里切入点是那些符合
autoFillPointCut定义的带有@AutoFill注解的方法。 - JoinPoint 参数:
JoinPoint是AOP的一个接口,允许在切面中获取被拦截方法的相关信息(如方法名、参数等),便于进行逻辑处理。
那么当我们此时定义好切面后,对于我们自定义的这个auto fill这个注解,需要把它加到我们XXX Mapper的mybatis文件上面。
2.4 插入数据的Mapper方法(我这边以员工数据维护为例)
在我们特定数据库操作(Insert,Update)上使用了@AutoFill注解,指定了操作类型为OperationType.INSERT(UPDATE),意味着该方法会在插入数据或者更新数据时自动填充创建时间和创建人等公共字段。
//INSERT
@Insert("insert into employee (name, username, password, phone, sex, id_number, create_time, update_time, create_user, update_user) " +
"values (#{name}, #{username}, #{password}, #{phone}, #{sex}, #{idNumber}, #{createTime}, #{updateTime}, #{createUser}, #{updateUser})")
@AutoFill(value = OperationType.INSERT)
void insert(Employee employee);
//UPDATE
@AutoFill(value = OperationType.UPDATE)
void update(Employee employee);
这边当调用 insert(Employee employee) 方法时,SQL插入语句将会执行,并且在插入之前,通过上面自定义 @AutoFill 注解的拦截逻辑自动为 create_time 和 create_user 字段赋值。
2.5 切面类中autoFill方法逻辑完成
在上面2.3步骤中我们只是对下面方法进行Log输入,在这个步骤进一步完善通知中逻辑,下面的步骤都是在此方法中实现
@Before("autoFillPointCut()")
public void autoFill(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("开始进行公共字段自动填充...");
} 2.5.1 需要获取 @AutoFill 注解的值,以判断当前操作是插入还是更新。
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
AutoFill autoFill = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(AutoFill.class);
OperationType operationType = autoFill.value();
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature():通过JoinPoint获取方法签名。AutoFill autoFill = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(AutoFill.class):通过反射方法签名获取@AutoFill注解。OperationType operationType = autoFill.value():从注解中获取操作类型,判断是INSERT还是UPDATE。
2.5.2 获取实体对象
接下来获取当前方法的参数,因为实体对象是作为方法参数传入的。
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if (args == null || args.length == 0) {
return;
}
Object entity = args[0];
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs():获取当前方法的参数列表。通常参数的第一个就是实体对象。Object entity = args[0]:假设实体对象是第一个参数,将其提取出来进行后续的字段赋值操作。
2.5.3 准备数据
为了填充公共字段,首先需要获取当前时间和当前用户ID。通常这些信息是从上下文环境或安全机制中获取的。
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
Long currentId = BaseContext.getCurrentId();
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now():获取当前时间,用于设置createTime和updateTime。Long currentId = BaseContext.getCurrentId():通过BaseContext获取当前操作的用户ID,用于设置createUser和updateUser。
2.5.3 根据操作类型自动填充字段
如果操作类型是 INSERT,那么需要为四个字段赋值:createTime、createUser、updateTime 和 updateUser。
if (operationType == OperationType.INSERT) {
try {
Method setCreateTime = entity.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(AutoFillConstant.SET_CREATE_TIME, LocalDateTime.class);
Method setCreateUser = entity.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(AutoFillConstant.SET_CREATE_USER, Long.class);
Method setUpdateTime = entity.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(AutoFillConstant.SET_UPDATE_TIME, LocalDateTime.class);
Method setUpdateUser = entity.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(AutoFillConstant.SET_UPDATE_USER, Long.class);
setCreateTime.invoke(entity, now);
setCreateUser.invoke(entity, currentId);
setUpdateTime.invoke(entity, now);
setUpdateUser.invoke(entity, currentId);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
Method setCreateTime = entity.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(...):通过反射机制,获取实体对象的setCreateTime方法。setCreateTime.invoke(entity, now):通过反射调用setCreateTime方法,将当前时间now赋值给createTime字段。这里使用反射动态调用实体类中的set方法为指定字段赋值,从而实现灵活的字段处理。- 对
setCreateUser、setUpdateTime、setUpdateUser也执行相同操作,分别赋值给实体的createUser、updateTime和updateUser字段。
如果操作类型是 UPDATE,则只需要为 updateTime 和 updateUser 两个字段赋值。
else if (operationType == operationType.UPDATE) {
try {
Method setUpdateTime = entity.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(AutoFillConstant.SET_UPDATE_TIME, LocalDateTime.class);
Method setUpdateUser = entity.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(AutoFillConstant.SET_UPDATE_USER, Long.class);
setUpdateTime.invoke(entity, now);
setUpdateUser.invoke(entity, currentId);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
- 通过反射获取
setUpdateTime和setUpdateUser方法,并分别为updateTime和updateUser字段赋值。 - 更新操作不需要设置
createTime和createUser,因为这些字段只在插入时赋值。






















 587
587

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










