#8-1 消息:编写一个名为display_message()的函数,它打印一个句子,指出你在本章学的是什么。
#调用这个函数,确认显示的消息正确无误。
def display_message():
print('\nIn Chapter 8, I learned how to define and use functions with '
'Python.')
display_message()

'''8-2 喜欢的图书:编写一个名为favorite_book()的函数,其中包含一个名为title的形参。
这个函数打印一条消息,如One of my favorite books is Alicein in Wonderland 。
调用这个函数,并将一本图书的名称作为实参传递给它。 '''
def favorite_book(title):
print("\nOne of my favorite books is " + title.title() + ".")
favorite_book("alicein in wonderland")
#并没有因为使用函数title作为形参名而发生错误

'''8-3 T恤:编写一个名为make_shirt() 的函数,它接受一个尺码以及要印到T恤上的字样。
这个函数应打印一个句子,概要地说明T恤的尺码和字样。
使用位置实参调用这个函数来制作一件T恤;再使用关键字实参来调用这个函数。'''
def make_shirt(size, word):
print(
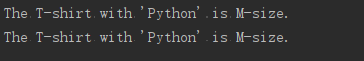
"The T-shirt with '" + word.title() + "' is " + size.title() + '-size.')
make_shirt("m", "python")
make_shirt(size="m",word="python")
'''8-4 大号T恤:修改函数make_shirt(),使其在默认情况下制作一件印有字样
“I love Python”的大号T恤。调用这个函数来制作如下T恤:一件印有默认字样的大号T恤、
一件印有默认字样的中号T恤和一件印有其他字样的T恤(尺码无关紧要)'''
def make_shirt(size='L',word='I love Python'):
#简单描述一件T恤的尺码和字样
print("The T-shirt with '"+ word.title()+"' is "+size.title()+ "-size.")
#一件印有默认字样的大号T恤(两个参数都有默认值,故不提供实参也不会出现错误)
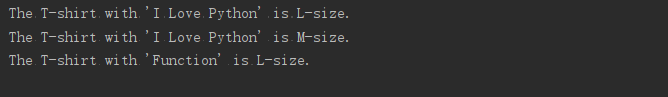
make_shirt()
#一件印有默认字样的中号T恤
make_shirt('m')
#只提供一个实参时,Python自动将其匹配到第一个有默认值的实参处
#一件印有其他字样的T恤(尺码无关紧要,假设尺码是默认的,则要将size放到形参列表的最后)
def make_shirt(word,size='L'):
#简单描述一件T恤的尺码和字样
print("The T-shirt with '"+ word.title()+"' is "+size.title()+ "-size.")
make_shirt('function')
'''8-5 城市:编写一个名为describe_city()的函数,它接受一座城市的名字以及该城市所属的国家。
这个函数应打印一个简单的句子,如Reykjavik is in Iceland.给用于存储国家的形参指定默认值。
为三座不同的城市调用这个函数,且其中至少有一座城市不属于默认国家。'''
def describe_city(city_name='Reykjavik',country='Iceland'):
print(city_name.title()+ ' is in '+country.title()+'.')
describe_city()
describe_city('Akureyri')
describe_city(city_name='Akureyri')
describe_city('Paris','France')
describe_city(country='France',city_name='Paris')

'''8-6城市名:编写一个名为city_country()的函数, 它接受城市的名称及其所属的国家。
这个函数应返回一个格式类似于下面这样的字符串:"Santiago, Chile"'''
#结合while循环
def city_country(city_name,country):
print("'" +city_name.title() + ','+ country.title() +"'")
active = True
while active:
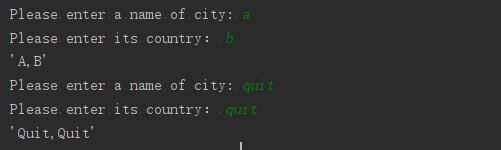
city_name = input("Please enter a name of city: " )
if city_name == "quit":
active = False
country = input('Please enter its country: ')
if country == "quit":
active = False
city_country(city_name,country)
#上述代码在输入quit后并不能直接退出,故改为用break退出循环
def city_country(city_name,country):
print("'" +city_name.title() + ','+ country.title() +"'")
while True:
city_name = input("Please enter a name of city: " )
if city_name == "quit":
break
country = input('Please enter its country: ')
if country == "quit":
break
city_country(city_name,country)
'''8-7:专辑:编写一个名为make_album()的函数, 它创建一个描述音乐专辑的字典。
这个函数应接受歌手的名字和专辑名, 并返回一个包含这两项信息的字典。
使用这个函数创建三个表示不同专辑的字典, 并打印每个返回的值, 以核实字典正确地存储了专辑的信息。
给函数make_album()添加一个可选形参, 以便能够存储专辑包含的歌曲数。
如果调用这个函数时指定了歌曲数, 就将这个值添加到表示专辑的字典中。
调用这个函数, 并至少在一次调用中指定专辑包含的歌曲数。'''
def make_album(singer_name,album_name):
"""简单描述一个音乐专辑"""
information = {}
information['singer'] = singer_name
information['album'] = album_name
return information
info = make_album('Justin Bieber','《My World》')
print(info)
#给函数make_album()添加一个可选形参,以便能够存储专辑包含的歌曲数
def make_album(singer_name,album_name,songs_number=""):
"""简单描述一个音乐专辑"""
information = {}
information['singer'] = singer_name
information['album'] = album_name
if songs_number:
information['songs number'] = songs_number
return information
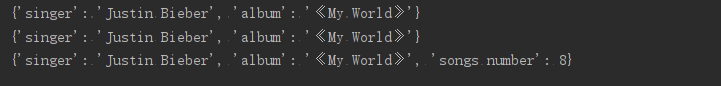
info = make_album('Justin Bieber','《My World》')
print(info)
info = make_album('Justin Bieber','《My World》',8)
print(info)
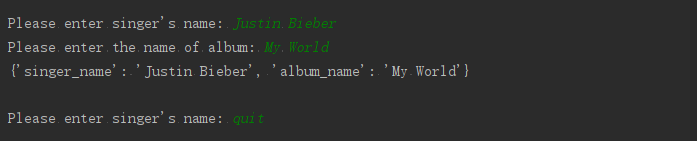
'''8-8用户的专辑:在为完成练习8-7编写的程序中,编写一个while循环, 让用户输入一个专辑的歌手和名称。
获取这些信息后, 使用它们来调用函数make_album(), 并将创建的字典打印出来。
在这个while 循环中, 务必要提供退出途径。'''
def make_album(singer_name, album_name):
album = {}
album['singer_name'] = singer_name
album['album_name'] = album_name
return album
while True:
singer_name = input("\nPlease enter singer's name: ")
if singer_name == 'quit':
break
album_name = input("Please enter the name of album: ")
if album_name == 'quit':
break
infor = make_album(singer_name, album_name)
print(infor)
#8-9魔术师:创建一个包含魔术师名字的列表,并将其传递给一个名为show_magicians()的函数,
# 这个函数打印列表中每个魔术师的名字。
def show_mgicians(magicians):
"""展示列表中每位魔术师的名字"""
for magician in magicians:
print(magician)
magicians = ['Jason Latimer','Daryl','Michael Ammar','Daryll','Criss Angel']
show_mgicians(magicians)

'''8-10 了不起的魔术师:在你为完成练习8-9而编写的程序中,编写一个名为make_great()的函数,
对魔术师列表进行修改, 在每个魔术师的名字中都加入字样“the Great”。
调用函数show_magicians( ),确认魔术师列表确实变了。'''
def make_great(magician):
print('the Great ' + magician)
def show_mgicians(magicians):
"""展示列表中每位魔术师的名字"""
for magician in magicians:
make_great(magician)
magicians = ['Jason Latimer', 'Daryl', 'Michael Ammar', 'Daryll', 'Criss Angel']
show_mgicians(magicians)
#换一下变量名称,以区分出形参与实参
def make_great(magician_name):
"""在每个魔术师的名字中都加入字样“the Great”"""
print('the Great ' + magician_name)
def show_mgicians(names):
"""展示列表中每位魔术师的名字"""
for name in names:
#以name做实参调用函数make_great(在一个函数中调用其他函数)
make_great(name)
magicians = ['Jason Latimer', 'Daryl', 'Michael Ammar', 'Daryll', 'Criss Angel']
show_mgicians(magicians)

两结果一样

'''8-11不变的魔术师:修改你为完成练习8-10而编写的程序, 在调用函数make_great()时,
向它传递魔术师列表的副本。由于不想修改原始列表,请返回修改后的列表,
并将其存储到另一个列表中。分别使用这两个列表来调用show_magicians(),
确认一个列表包含的是原来的魔术师名字, 而另一个列表包含的是添加了字样“the Great”的魔术师名字。'''
#这里只使用了一个函数
def show_mgicians(names):
"""展示列表中每位魔术师的名字"""
for name in names:
new_name = 'the Great ' + name
new_names.append(new_name)
print(names)
print(new_names)
new_names = []
magicians = ['Jason Latimer', 'Daryl', 'Michael Ammar', 'Daryll', 'Criss Angel']
show_mgicians(magicians)

#试错1
def make_great(name):
"""在每个魔术师的名字中都加入字样“the Great”"""
new_name = 'the Great ' + name
def show_mgicians(names):
"""展示列表中每位魔术师的名字"""
for name in names:
make_great(name)
#这里并不能直接用经过函数make_great而产生的变量new_name
#一个函数体中不能莫名其妙地出现一个新变量,即使这个变量是引进的函数运算所产生的也不可以
new_names.append(new_name)
print(names)
print(new_names)
new_names = []
magicians = ['Jason Latimer', 'Daryl', 'Michael Ammar', 'Daryll', 'Criss Angel']
show_mgicians(magicians)
#改正:调整函数make_great的任务
def make_great(name):
"""在每个魔术师的名字中都加入字样“the Great”,添加进新列表"""
new_name = 'the Great ' + name
#将添加到新名字列表这一任务也交给make_great函数完成
new_names.append(new_name)
def show_mgicians(names):
"""展示列表中每位魔术师的名字"""
for name in names:
make_great(name)
print(names)
print(new_names)
new_names = []
magicians = ['Jason Latimer', 'Daryl', 'Michael Ammar', 'Daryll', 'Criss Angel']
show_mgicians(magicians)

'''8-12三明治: 编写一个函数, 它接受顾客要在三明治中添加的一系列食材。
这个函数只有一个形参(它收集函数调用中提供的所有食材),并打印一条消息,
对顾客点的三明治进行概述。调用这个函数三次,每次都提供不同数量的实参。'''
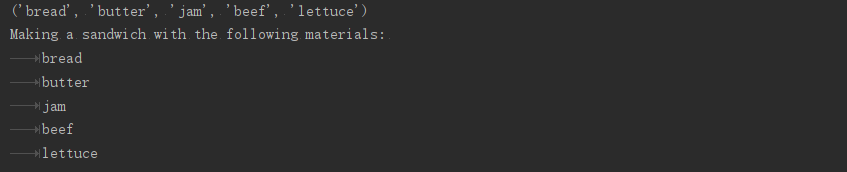
def make_sandwich(*food_materials):
"""输出顾客所点三明治的一切食材"""
#元组
print(food_materials)
print('Making a sandwich with the following materials: ')
for material in food_materials:
print('\t'+ material)
make_sandwich('bread','butter','jam','beef','lettuce')
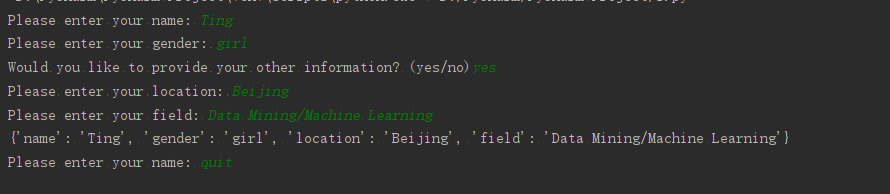
'''8-13用户简介: 复制前面的程序user_profile.py,在其中调用build_profile()
来创建有关你的简介;调用这个函数时,指定你的名和姓,以及三个描述你的键-值对。'''
def build_profile(name,gender,**info):
person_profile = {}
person_profile['name'] = name
person_profile['gender'] = gender
for key,value in info.items():
person_profile[key] = value
return person_profile
while True:
name = input('Please enter your name: ')
if name =='quit':
break
gender = input('Please enter your gender: ')
if gender =='quit':
break
repeat = input('Would you like to provide your other information? (yes/no)')
if repeat == 'yes':
address = input('Please enter your location: ')
occupation = input('Please enter your field: ')
person_information = build_profile(name,gender,
location=address,
field=occupation)
print(person_information)
'''8-14汽车:编写一个函数,将一辆汽车的信息存储在一个字典中。这个函数总是接受制造商和型号,
还接受任意数量的关键字实参。这样调用这个函数:提供必不可少的信息,以及两个名称—值对,
如颜色和选装配件。这个函数必须能够像下面这样进行调用:
car = make_car('subaru','outback',color='blue',tow_package=True)
打印返回的字典,确认正确地处理了所有信息
'''
def car_information(manufacturer,model,**info):
car_info = {}
car_info['manufacturer'] = manufacturer
car_info['model'] = model
for key,value in info.items():
car_info[key] = value
return car_info
car = car_information('Toyota','SUV-TRJ120L-GKPEKV',color='black',accessory='NQD-630')
print(car)

8-15打印模型:将示例print_models.py中的函数放在另一个名为printing_functions.py的文件中;
在print_models.py的开头编写一条import 语句, 并修改这个文件以使用导入的函数。
8-15需要用的模块(名称为:printing_functions.py)
def print_models(unprinted_designs,completed_models):
while unprinted_designs:
current_design = unprinted_designs.pop()
print("Printing model: "+ current_design)
completed_models.append(current_design)
#一个函数概述打印了哪些设计
def describe_completed_designs(completed_models):
print('\nThe following models have been printed: ')
for completed_model in completed_models:
print(completed_model)
#导入整个模块
import printing_functions
unprinted_designs = ['iphone case','robot pendant','dodecahedron']
completed_models = []
printing_functions.print_models(unprinted_designs,completed_models)
printing_functions.describe_completed_designs(completed_models)
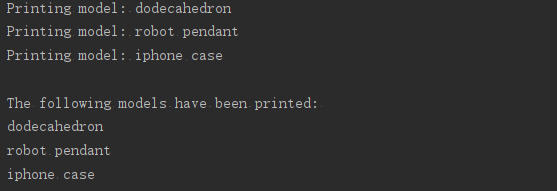
#导入特定函数print_models
from printing_functions import print_models
unprinted_designs = ['iphone case','robot pendant','dodecahedron']
completed_models = []
print_models(unprinted_designs,completed_models)
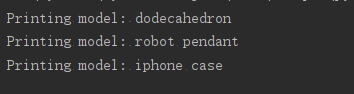
#使用as给函数指定别名
from printing_functions import print_models as p_m
unprinted_designs = ['iphone case','robot pendant','dodecahedron']
completed_models = []
p_m(unprinted_designs,completed_models)
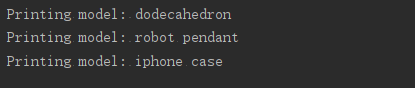
#使用as给模块指定别名
import printing_functions as p_f
unprinted_designs = ['iphone case','robot pendant','dodecahedron']
completed_models = []
p_f.print_models(unprinted_designs,completed_models)
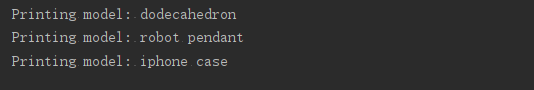
#导入模块中的所有函数
from printing_functions import *
unprinted_designs = ['iphone case','robot pendant','dodecahedron']
completed_models = []
print_models(unprinted_designs,completed_models)
describe_completed_designs(completed_models)






















 7458
7458











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








