C++ 学习 第五章
按照视频与课本,以下包含书本程序清单、复习题、习题
5.1 for 循环
//程序清单5.1
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int i;
//for(表达式initialization;表达式test-expression;表达式update-expression)
for(i=0;i < 5; i++)
{
cout << "C++ know loop"<< endl;
}
cout << "C++ knows when to stop "<< endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
C++ know loop
C++ know loop
C++ know loop
C++ know loop
C++ know loop
C++ knows when to stop
//程序清单5.2
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
cout<< "Enter the starting countdown value: ";
int limit;
cin >> limit;
int i;
for(i=limit; i; i--)
{
cout << "i = "<<i<<endl;
}
cout << "Done, now that i = " << i <<endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter the starting countdown value: 4
i = 4
i = 3
i = 2
i = 1
Done, now that i = 0
//程序清单5.3
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int x;
cout << "The expression x = 100 has the value ";
cout << (x = 100) << endl;
cout << "Now x = " << x << endl;
cout << "The expression x < 3 has the value ";
cout << (x < 3) << endl;
cout << "The expression x > 3 has the value ";
cout << (x > 3) << endl;
cout.setf(ios_base::boolalpha);
cout << "The expression x < 3 has the value ";
cout << (x < 3) << endl;
cout << "The expression x > 3 has the value ";
cout << (x > 3) << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
The expression x = 100 has the value 100
Now x = 100
The expression x < 3 has the value 0
The expression x > 3 has the value 1
The expression x < 3 has the value false
The expression x > 3 has the value true
//程序清单5.4 计算阶乘
#include <iostream>
const int ArSize = 16;
int main(void)
{
long long factorials[ArSize];
factorials[0] = factorials[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < ArSize; i++)
factorials[i] = i * factorials[i-1];
for(int i = 0; i < ArSize; i++)
std::cout << i << "! = " << factorials[i] << std::endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ g++ demo.cpp
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
0! = 1
1! = 1
2! = 2
3! = 6
4! = 24
5! = 120
6! = 720
7! = 5040
8! = 40320
9! = 362880
10! = 3628800
11! = 39916800
12! = 479001600
13! = 6227020800
14! = 87178291200
15! = 1307674368000
//程序清单5.5 修改步长
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
cout << "Enter an integer: ";
int by;
cin >> by;
cout << "Counting by " << by << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i = i + by)
cout << i << endl;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ g++ demo.cpp
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter an integer: 20
Counting by 20
0
20
40
60
80
//程序清单5.6 倒序输出
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
cout << "Enter a word:";
string word;
cin >> word;
for(int i = word.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
cout << word[i]<< endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter a word:hello
olleh
//程序清单5.7 递增递减
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int a = 20;
int b = 20;
cout << "a = " << a << ", " << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "a++ = " << a++ << ", " << "++b = " << ++b << endl;
cout << "a = " << a << ", " << "b = " << b << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
a = 20, b = 20
a++ = 20, ++b = 21
a = 21, b = 21
// 递增递减运算符和指针
//1)*++pt 2)++*pt 3)(*pt)++ 4)*pt++
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
double arr[5] = {21.1, 32.8, 23.4, 45.2, 37.4};
double *pt = arr;
// cout << *pt << endl;
cout << "*++pt = " << *++pt << endl;
cout << "++*pt = " << ++*pt << endl;
cout << "arr[1] = "<<arr[1] <<endl;
cout << "(*pt)++ = " << (*pt)++ << endl;
cout << "*pt = " << *pt << endl;
//后缀运算符比前缀要高 pt指针向后调,但是要先用完再调
cout << "*pt++ = " << *pt++ << endl;
cout << "*pt = " << *pt << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
*++pt = 32.8
++*pt = 33.8
arr[1] = 33.8
(*pt)++ = 33.8
*pt = 34.8
*pt++ = 34.8
*pt = 23.4
//程序清单5.8 循环求和
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
double number, sum = 0.0;
cout << "Calculate five numbers sum and average." << endl;
cout << "Please enter five values:" << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
cout << "Value " << i << ": " ;
cin >> number;
sum += number;
}
cout << "The sum = " << sum << endl;
cout << "Average = " << sum / 5 << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Calculate five numbers sum and average.
Please enter five values:
Value 1: 21
Value 2: 10
Value 3: 4
Value 4: 5
Value 5: 6
The sum = 46
Average = 9.2
//程序清单 5.9
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
cout << "Please enter a word:";
string word;
cin >> word;
int i, j;
char temp;
for(j = 0, i = word.size()-1; j < i; j++, i--)
{
temp = word[i];
word[i] = word[j];
word[j] = temp;
}
cout << word << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Please enter a word:slam
mals
//程序清单 5.10 程序后半部分有错误
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int arr[10] = {20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 19, 20, 18, 20, 20};
cout << "Doing it right:" << endl;
int i;
for(i = 0; arr[i] == 20; i++)
cout << "arr " << i << " is a 20." << endl;
cout << "Doing it dangerously wrong: " << endl;
for(i = 0; arr[i] = 20; i++)
cout << "arr " << i << " is a 20." << endl;
return 0;
}
..........
arr 3355 is a 20.
arr 3356 is a 20.
arr 3357 is a 20.
arr 3358 is a 20.
arr 3359 is a 20.
段错误 (核心已转储)
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$
//程序清单 5.11
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
char word[5] = "?ate";
// 比较word 与 mate 关系,不相等测试继续
for(char ch = 'a'; strcmp(word, "mate"); ch++)
{
cout << word << endl;
word[0] = ch;
}
cout << "After loop ends, word is " << word << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
?ate
aate
bate
cate
date
eate
fate
gate
hate
iate
jate
kate
late
After loop ends, word is mate
//程序清单 5.12
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //采用string类
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
string word = "?ate";
for(char ch = 'a'; word != "mate"; ch++)
{
cout << word << endl;
word[0] = ch;
}
cout << "After loop ends, word is " << word << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
?ate
aate
bate
cate
date
eate
fate
gate
hate
iate
jate
kate
late
After loop ends, word is mate

5.2 while 循环
//程序清单 5.13
#include <iostream>
const int ArSize = 20;
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
char name[ArSize];
cout << "Your first name please: ";
cin >> name;
cout << "Here is your name: " << endl;
int i = 0;
while(name[i] != '\0') //while(name[i])
{
cout << name[i] << ": " << (int)name[i] << endl;
i++;
}
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Your first name please: Muffy
Here is your name:
M: 77
u: 117
f: 102
f: 102
y: 121


//程序清单 5.14 延时一定时间
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
cout << "Enter the delay time, in seconds:";
float secs;
cin >> secs;
clock_t delay = secs * CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
clock_t start = clock();
while(clock() - start < delay)
;
cout << "done!\n";
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter the delay time, in seconds:5
done!

5.3 do while 循环
//程序清单 5.15 do while 循环演示
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int n;
cout << "Enter numbers in the range 1~10 to find my favorite number" << endl;
/*
cin >> n;
while(n != 7)
{
cin >> n;
}
*/
do
{
cin >> n;
}
while(n != 7);
cout << "Yes, 7 is my favorite." << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter numbers in the range 1~10 to find my favorite number
6
9
7
Yes, 7 is my favorite.
5.4 基于范围的for循环(C++11)

5.5 循环和文本输入
//程序清单 5.16 遇到#停下
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
char ch;
int count = 0;
cout << "Enter characters, enter # to quit:" << endl;
cin >> ch;
while(ch != '#')
{
cout << ch;
++count;
cin >> ch;
}
cout << endl;
cout << count << " characters read" << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter characters, enter # to quit:
see ken run#readlly fast
seekenrun
9 characters read
//程序清单 5.17 遇到#停下,并保留空格
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
char ch;
int count = 0;
cout << "Enter characters, enter # to quit:" << endl;
cin.get(ch);
while(ch != '#')
{
cout << ch;
++count;
cin.get(ch);
}
cout << endl;
cout << count << " characters read" << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter characters, enter # to quit:
Did you use a #2 pencil
Did you use a
14 characters read

//程序清单 5.18
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
char ch;
int count = 0;
cout << "Enter characters, enter # to quit:" << endl;
cin.get(ch);
while(cin.fail() == false)
{
cout << ch;
++count;
cin.get(ch);
}
cout << endl;
cout << count << " characters read" << endl;
return 0;
}
在Ubuntu环境下使用Ctrl + Z
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter characters, enter # to quit:
The green bird sings in the winter.
The green bird sings in the winter.
Yes, the crow files in the down.
Yes, the crow files in the down.
^Z
[1]+ 已停止 ./a.out
在Ubuntu环境下使用Ctrl + C
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter characters, enter # to quit:
The green bird sings in the winter.
The green bird sings in the winter.
36 characters read
5.6 嵌套循环和二维数组
//程序清单 5.20
#include <iostream>
const int Cities = 5;
const int Years = 4;
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
const char * cities[Cities] =
{
"Gribble City",
"Gribbletown",
"New Gribble",
"San Gribble",
"Gribble Vista"
};
int maxtemps[Years][Cities] =
{
{96, 100, 87, 101, 105},
{96, 98, 91, 107, 104},
{97, 101, 93, 108, 107},
{98, 103, 95, 109, 108}
};
cout << "City: Maximum temperature for 2008 - 2011" << endl;
for(int city = 0; city < Cities; city++)
{
cout << cities[city] << ":\t";
for(int year = 0; year < Years; year++)
cout << maxtemps[year][city] << "\t";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
City: Maximum temperature for 2008 - 2011
Gribble City: 96 96 97 98
Gribbletown: 100 98 101 103
New Gribble: 87 91 93 95
San Gribble: 101 107 108 109
Gribble Vista: 105 104 107 108
5.7 总结
5.8 复习题
1.入口:for() while()
出口: do while
2.
01234
3.
0369
12
4.
6
8
5.
k = 8
6.
int i;
for(i = 1; i < 64; i *= 2)
cout << i << ",";
cout << i << endl;
7.
use "{ ; ; ; ; }"
8.
//逗号分隔开,逗号右边为024 8进制024 = 20 表达式的右值赋给x
1) valid, x = 20
//(y = 1) , 024 最终此表达式的值为表达式右值024 没有实际意义
2) valid, (y = 1), 024 --> 024
9.
cin >> ch ---> blank char (enter tab blank) //忽略所有空白字符
cin.get(ch), ch = cin.get() //作用相同,将所有的字符并保存在ch中
5.9 编程练习

//编程练习1
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int min, max, sum = 0;
cout << "Enter the min number: ";
cin >> min;
cout << "Enter the max number: ";
cin >> max;
for(int i = min; i <= max; i++)
sum += i;
cout << "The sum = " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ g++ demo.cpp
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter the min number: 2
Enter the max number: 9
The sum = 44
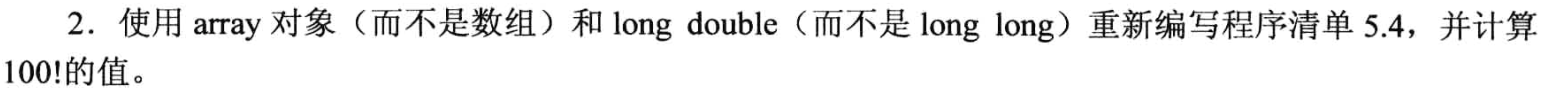
//编程练习2
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
const int ArSize = 16;
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
array<long double, ArSize> factorials;
//long long factorials[ArSize];
factorials[0] = factorials[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < ArSize; i++)
factorials[i] = i * factorials[i-1];
for(int i = 0; i < ArSize; i++)
cout << i << "! = " << factorials[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
0! = 1
1! = 1
2! = 2
3! = 6
4! = 24
5! = 120
6! = 720
7! = 5040
8! = 40320
9! = 362880
10! = 3.6288e+06
11! = 3.99168e+07
12! = 4.79002e+08
13! = 6.22702e+09
14! = 8.71783e+10
15! = 1.30767e+12

//编程练习3
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
double num, sum = 0;
do
{
cout << "Please enter a number to add: ";
cin >> num;
sum += num;
}
while(num != 0);
cout << "Input end, sum = " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Please enter a number to add: 8
Please enter a number to add: 6
Please enter a number to add: 4
Please enter a number to add: 1
Please enter a number to add: 0
Input end, sum = 19
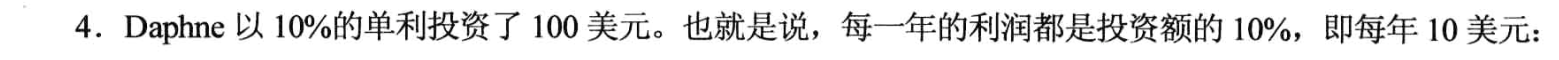

//编程练习4
#include <iostream>
const int DEPOSIT_BASE = 100;
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
double daphne_deposit = DEPOSIT_BASE;
double cleo_deposit = DEPOSIT_BASE;
int year = 0;
while(daphne_deposit >= cleo_deposit)
{
daphne_deposit += 0.1 * DEPOSIT_BASE;
cleo_deposit += 0.05 * cleo_deposit;
year++;
}
cout << "After " << year << " years, " << "Cleo has more money than Daphne!" << endl;
cout << "Daphne has " << daphne_deposit << " dollars." << endl;
cout << "Cleo has " << cleo_deposit << " dollars." << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
After 27 years, Cleo has more money than Daphne!
Daphne has 370 dollars.
Cleo has 373.346 dollars.

//编程练习5
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
const string Month[] = {"Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun", "Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec"};
int sale_num[12];
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
{
cout << "Enter the sale number of " << Month[i] << " :";
cin >> sale_num[i];
}
cout << "Input Done!" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
sum += sale_num[i];
cout << "Total sale: " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter the sale number of Jan :12
Enter the sale number of Feb :13
Enter the sale number of Mar :14
Enter the sale number of Apr :15
Enter the sale number of May :16
Enter the sale number of Jun :17
Enter the sale number of Jul :16
Enter the sale number of Aug :15
Enter the sale number of Sep :14
Enter the sale number of Oct :13
Enter the sale number of Nov :12
Enter the sale number of Dec :11
Input Done!
Total sale: 168

#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
const string Month[] = {"Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun", "Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec"};
int sale_num[3][12];
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << "Starting " << i + 1 << " year's data." << endl;
for(int j = 0; j < 12; j++)
{
cout << "Enter the sale number of " << Month[j] << " :";
cin >> sale_num[i][j];
}
}
cout << "Input Done!" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 12; j++)
sum += sale_num[i][j];
}
cout << "Three years total sale: " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Starting 1 year's data.
Enter the sale number of Jan :1
Enter the sale number of Feb :1
Enter the sale number of Mar :1
Enter the sale number of Apr :1
Enter the sale number of May :1
Enter the sale number of Jun :1
Enter the sale number of Jul :1
Enter the sale number of Aug :1
Enter the sale number of Sep :1
Enter the sale number of Oct :1
Enter the sale number of Nov :1
Enter the sale number of Dec :1
Starting 2 year's data.
Enter the sale number of Jan :2
Enter the sale number of Feb :2
Enter the sale number of Mar :2
Enter the sale number of Apr :2
Enter the sale number of May :2
Enter the sale number of Jun :2
Enter the sale number of Jul :2
Enter the sale number of Aug :2
Enter the sale number of Sep :2
Enter the sale number of Oct :2
Enter the sale number of Nov :2
Enter the sale number of Dec :2
Starting 3 year's data.
Enter the sale number of Jan :3
Enter the sale number of Feb :3
Enter the sale number of Mar :3
Enter the sale number of Apr :3
Enter the sale number of May :3
Enter the sale number of Jun :3
Enter the sale number of Jul :3
Enter the sale number of Aug :3
Enter the sale number of Sep :3
Enter the sale number of Oct :3
Enter the sale number of Nov :3
Enter the sale number of Dec :3
Input Done!
Three years total sale: 72

//编程练习7
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct car
{
string manufacturer;
int date;
};
int main(void)
{
int car_number;
car *pcar;
cout << "How many cars do you wish to catalog?";
cin >> car_number;
cin.get();
pcar = new car[car_number];
for(int i = 0; i < car_number; i++)
{
cout << "Car #" << i + 1 << ":" << endl;
cout << "Please enter the maker: ";
getline(cin, pcar[i].manufacturer);
cout << "Please enter the year made: ";
cin >> pcar[i].date;
cin.get();
}
cout << "Here is your collection:" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < car_number; i++)
cout << pcar[i].date << " " << pcar[i].manufacturer << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
How many cars do you wish to catalog?2
Car #1:
Please enter the maker: tesla
Please enter the year made: 1
Car #2:
Please enter the maker: xiaomi
Please enter the year made: 2
Here is your collection:
1 tesla
2 xiaomi

//编程练习8
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const char DONE[] = "done";
int main(void)
{
char words[20];
int counter = 0;
cout << "Enter words (to stop, type the word done):" << endl;
do
{
cin >> words;
cin.get();
counter++;
}while(strcmp(words, DONE) != 0);
cout << "You entered a total of " << counter - 1 << " words." << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter words (to stop, type the word done):
hello slam machine_learning deep_learning done
You entered a total of 4 words.

//编程练习9
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const char DONE[] = "done";
int main(void)
{
string words;
int counter = 0;
cout << "Enter words (to stop, type the word done):" << endl;
do
{
cin >> words;
cin.get();
counter++;
}while(words != DONE);
cout << "You entered a total of " << counter - 1 << " words." << endl;
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Enter words (to stop, type the word done):
hello slam C++ python
done
You entered a total of 4 words.

//编程练习10
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int row;
cout << "Please enter the number of rows: ";
cin >> row;
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < row - i - 1; j++)
cout << ".";
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
cout << "*";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
hao@hao:~/Cpp_learning$ ./a.out
Please enter the number of rows: 5
....*
...**
..***
.****
*****






















 263
263











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








