Java SPI 机制
SPI(Service Provider Interface),是JDK内置的一种服务提供发现机制,可以用来启用框架扩展和替换组件,主要是被框架开发人员使用。
文章目录
JVM 双亲委派机制
类加载器
我们平常编写的Java源代码被编译器编译成.class的字节码文件,然后类加载负责将这些字节码文件加载到JVM中去执行。JVM提供了自上而下的三层类加载器ClassLoader。
- BootstrapClassLoader(启动类加载器):最顶层的加载器,由C ++ 实现,负责加载%JAVA_HOME%/lib目录下的jar包和类或者或被 -Xbootclasspath参数指定的路径中的所有类。
- ExtensionClassLoader(扩展类加载器) :主要负责加载目录 %JRE_HOME%/lib/ext 目录下的jar包和类,或被 java.ext.dirs 系统变量所指定的路径下的jar包。
- AppClassLoader(应用程序类加载器):面向我们用户的加载器,负责加载当前应用classpath下的所有jar包和类。
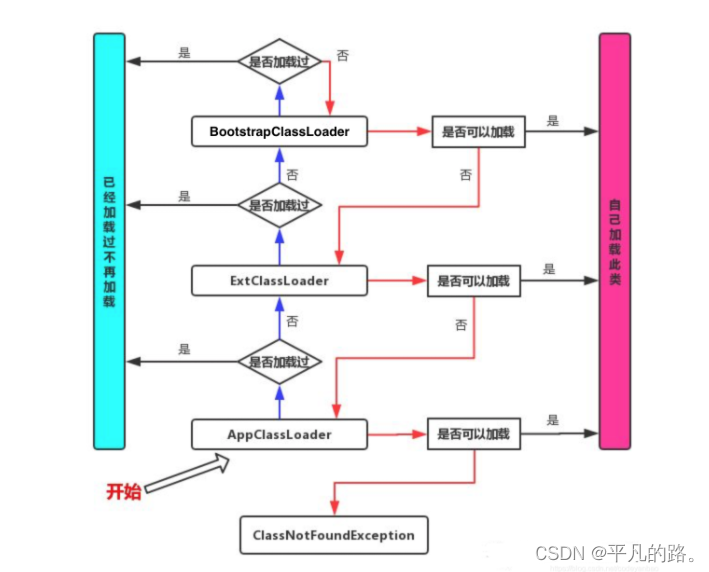
双亲委派机制
为了Java核心类不被篡改,Java提出了双亲委派的方式进行类的加载,大致流程如下:
- 首先检查AppClassLoader中是否加载了当前class,如果加载过了,就直接从JVM内存中获取,如果没有就委派给ExtensionClassLoader
- ExtensionClassLoader也和AppClassLoader同样的方式,先检查是否加载了当前class,如果加载过了,就直接从JVM内存中获取,如果没有就委派给BootstrapClassLoader
- BootstrapClassLoader先检查是否加载了当前class,如果加载过了,就直接从JVM内存中获取,如果没有就委派给ExtensionClassLoader,让ExtensionClassLoader去加载此class,如果没有就委派给AppClassLoader,AppClassLoader如果找到了此class就进行加载,否则就抛出ClassNotFoundException
源代码
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
// 首先检查当前class是否已经被加载
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
// 当前 class 没有被加载
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
// 委派给父类 递归委派 直到委派到BootstrapClassLoader
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
// BootstrapClassLoader进行类加载
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
// 如果BootstrapClassLoader没加载到此class则向下委派 让子ClassLoader 进行类加载
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// 顺序加载 先是ExtensionClassLoader 再是AppClassLoader
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
上述代码流程图
双亲委派机制的优缺点
优点
- 避免类的重复加载
- 保证了Java核心API不被篡改,如果有人想替换系统级别的类:String.java,篡改它的实现。在这种机制下这些系统的类已经被BootstrapclassLoader加载过了,所以并不会再去加载。
缺点
- 当Java核心API定义的接口,让不同厂商去实现时,如果是这种双亲委派机制来加载对应接口的实现类,是不能够加载的,因为BootstrapClassLoader只能加载Java的核心类库,不能加载应用程序或者第三方jar包中的接口实现类
上述双亲委派机制的解决方式:
- 让BootstrapClassLoader中能够获取AppClassLoader,这样就可以获取对应第三方包中Jdk接口的实现类
具体方式:获取线程上下文类加载器
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
JDK 内置 SPI
概念
SPI:服务提供发现机制,主要的作用就是用于解耦合,将接口的实现类的控制权移到程序之外,通过配置文件配置的方式实现接口实现类的改变,这样避免了硬编码,从代码中修改接口实现类。
JDK 内置 SPI 示例
不同的数据库厂商会有不同的数据库驱动实现方式,比如说MySQL、Oracle,所有我这里定义一个公共接口 MyDriver
public interface MyDriver {
/**
* 获取数据库链接
*/
void connection();
}
MySQL驱动实现
public class MySqlDataBaseDriver implements MyDriver {
@Override
public void connection() {
System.out.println("这是 MySQL 数据库驱动 ...");
}
}
Oracle驱动实现
/**
* @author 郭经伟
* @Date 2022/8/24
**/
public class OracleDataBaseDriver implements MyDriver {
@Override
public void connection() {
System.out.println("这是 Oracle 数据库驱动 ...");
}
}
使用Java 内置 SPI 机制实现不同数据库驱动实现类的加载
public class JdkSpiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// JDK Spi 机制实现
ServiceLoader<MyDriver> load = ServiceLoader.load(MyDriver.class);
Iterator<MyDriver> iterator = load.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
MyDriver driver = iterator.next();
driver.connection();
}
}
}
然后在Resource目录下创建META-INF/services目录并创建以com.gjw.jdk.spi.MyDriver为名称的文件,文件内容为MyDriver接口的实现类的全限类名
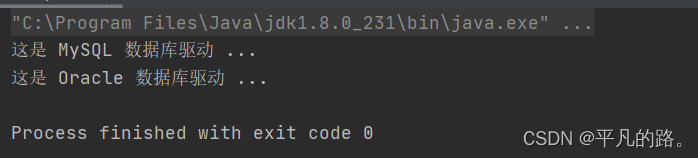
执行结果
总结一下JDK内置SPI机制的用法
- 首先定义接口和实现类。
- 在Resources目录创建META-INF/services目录,并以接口全限类名为文件名,接口实现类全限类名为文件的内容。
- 使用ServiceLoader.load()方法加载接口实现类。
JDK-SPI机制的应用
在JDBC4.0之前,我们开发有连接数据库的时候,通常会用Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”)这句先加载数据库相关的驱动,然后再进行获取连接等的操作。而JDBC4.0之后不需要用Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”)来加载驱动,直接获取连接就可以了,现在这种方式就是使用了Java的SPI扩展机制来实现。
接下来我会介绍一下数据库驱动获取的原理
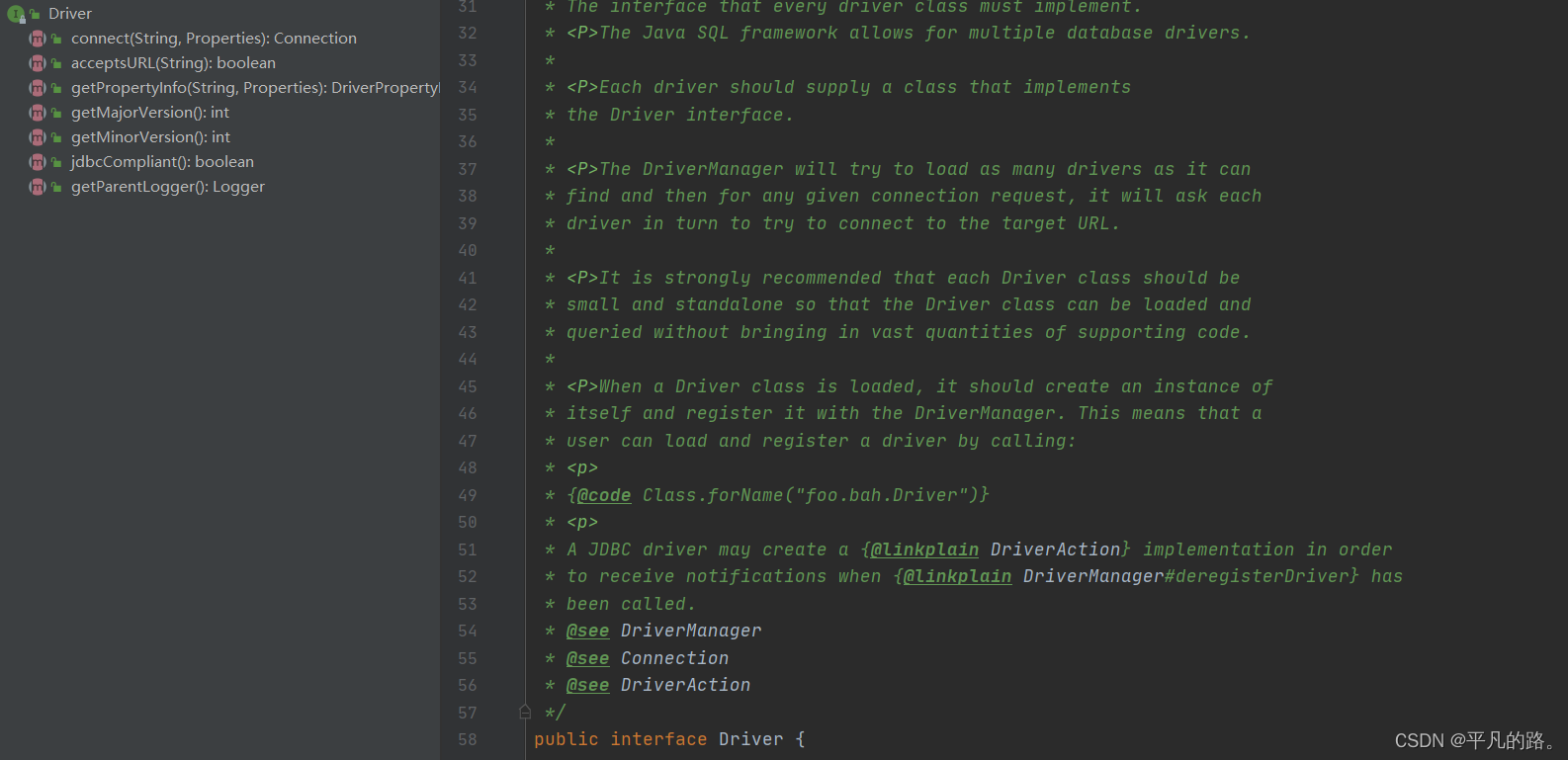
JDBC接口定义 java.sql.Driver
MySQL实现
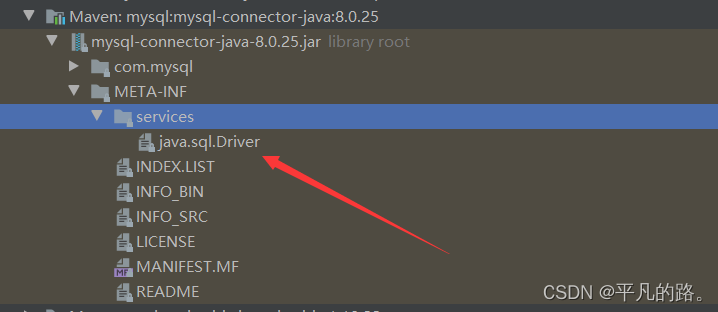
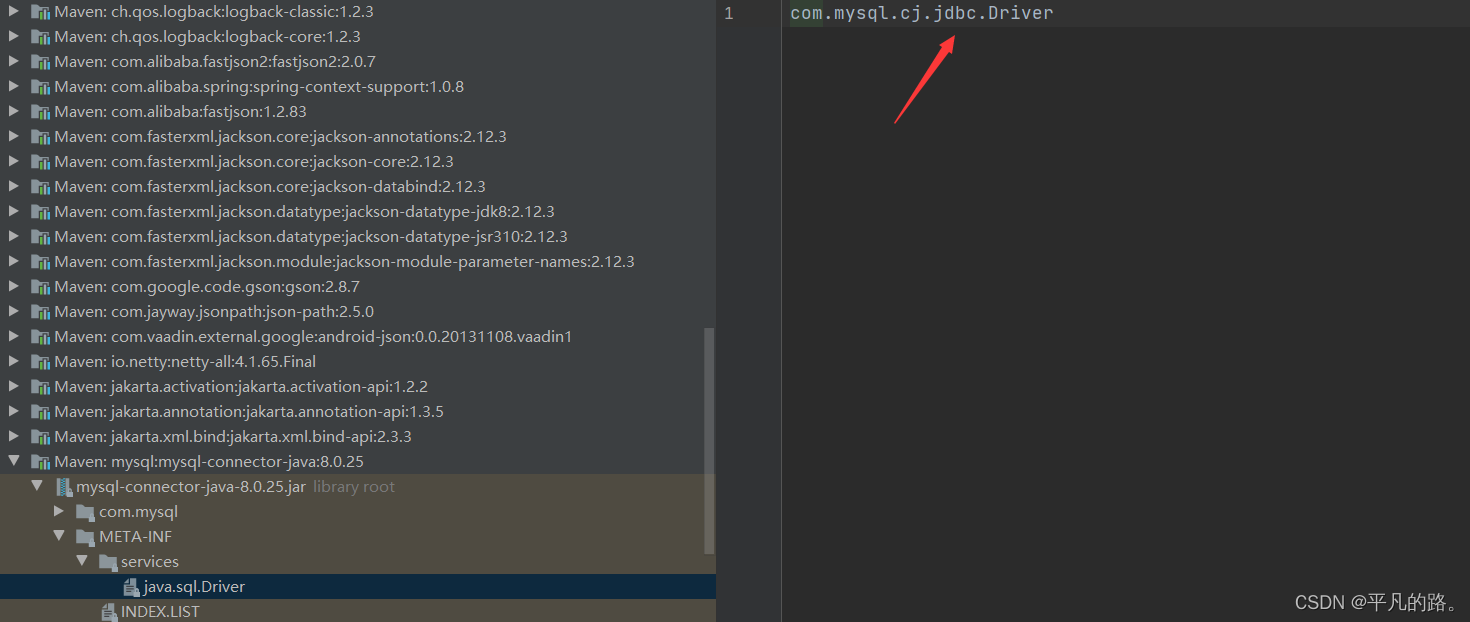
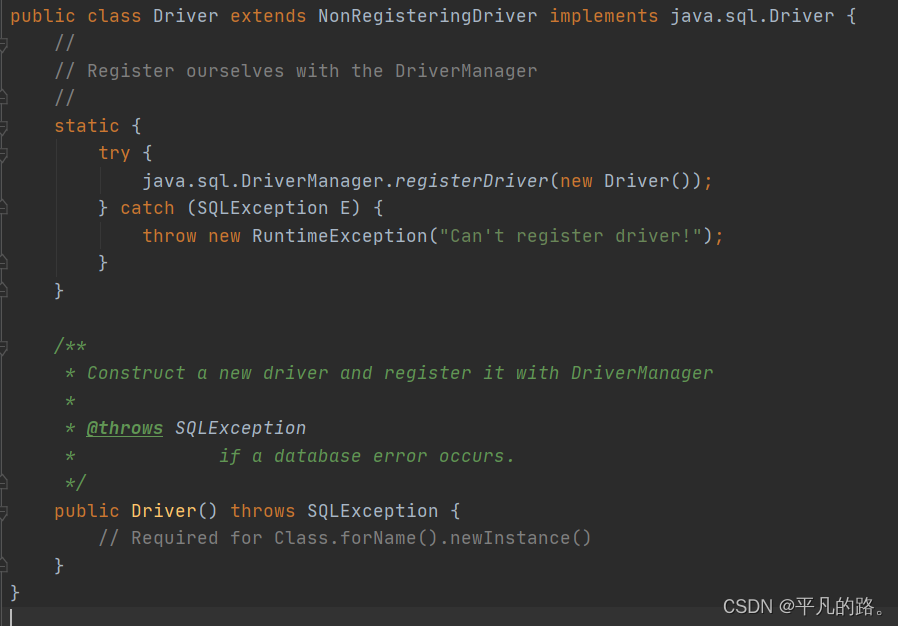
MySQL中的数据库驱动通过DriverManager来注册
DriverManager源码如下
public class DriverManager {
// List of registered JDBC drivers
private final static CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo> registeredDrivers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
private static volatile int loginTimeout = 0;
private static volatile java.io.PrintWriter logWriter = null;
private static volatile java.io.PrintStream logStream = null;
// Used in println() to synchronize logWriter
private final static Object logSync = new Object();
/* Prevent the DriverManager class from being instantiated. */
private DriverManager(){}
/**
* Load the initial JDBC drivers by checking the System property
* jdbc.properties and then use the {@code ServiceLoader} mechanism
* 加载 DriverManager.class 执行具体代码块 进行Driver初始化
*/
static {
loadInitialDrivers();
println("JDBC DriverManager initialized");
}
public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver,
DriverAction da)
throws SQLException {
/* Register the driver if it has not already been added to our list */
if(driver != null) {
// 注册Driver 就是将MySQL Driver 添加到 registeredDrivers List里面
registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver, da));
} else {
// This is for compatibility with the original DriverManager
throw new NullPointerException();
}
println("registerDriver: " + driver);
}
private static void loadInitialDrivers() {
// 加载初始化 Driver
String drivers;
try {
// AccessController.doPrivileged Java安全管理机制 赋予这段代码一定的权限去执行 返回jdbc.drivers系统环境变量
drivers = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<String>() {
public String run() {
return System.getProperty("jdbc.drivers");
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
drivers = null;
}
// If the driver is packaged as a Service Provider, load it.
// Get all the drivers through the classloader
// exposed as a java.sql.Driver.class service.
// ServiceLoader.load() replaces the sun.misc.Providers()
// SPI 机制进行 驱动加载
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
ServiceLoader<Driver> loadedDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);
Iterator<Driver> driversIterator = loadedDrivers.iterator();
/* Load these drivers, so that they can be instantiated.
* It may be the case that the driver class may not be there
* i.e. there may be a packaged driver with the service class
* as implementation of java.sql.Driver but the actual class
* may be missing. In that case a java.util.ServiceConfigurationError
* will be thrown at runtime by the VM trying to locate
* and load the service.
*
* Adding a try catch block to catch those runtime errors
* if driver not available in classpath but it's
* packaged as service and that service is there in classpath.
*/
try{
while(driversIterator.hasNext()) {
driversIterator.next();
}
} catch(Throwable t) {
// Do nothing
}
return null;
}
});
println("DriverManager.initialize: jdbc.drivers = " + drivers);
if (drivers == null || drivers.equals("")) {
return;
}
String[] driversList = drivers.split(":");
println("number of Drivers:" + driversList.length);
for (String aDriver : driversList) {
try {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: loading " + aDriver);
Class.forName(aDriver, true,
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
} catch (Exception ex) {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: load failed: " + ex);
}
}
}
}
ServiceLoader源码如下
/**
* @author Mark Reinhold
* JDK SPI 实现了Iterable接口 ServiceLoader执行load方法不会立即进行类加载和实例化,而是迭代器迭代的时候才进行懒加载和对象实例化
* @since 1.6
*/
public final class ServiceLoader<S>
implements Iterable<S>
{
private static final String PREFIX = "META-INF/services/";
// The class or interface representing the service being loaded
private final Class<S> service;
// The class loader used to locate, load, and instantiate providers
private final ClassLoader loader;
// The access control context taken when the ServiceLoader is created
private final AccessControlContext acc;
// Cached providers, in instantiation order
private LinkedHashMap<String,S> providers = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// The current lazy-lookup iterator
private LazyIterator lookupIterator;
public void reload() {
providers.clear();
lookupIterator = new LazyIterator(service, loader);
}
private ServiceLoader(Class<S> svc, ClassLoader cl) {
service = Objects.requireNonNull(svc, "Service interface cannot be null");
loader = (cl == null) ? ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() : cl;
acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null) ? AccessController.getContext() : null;
reload();
}
private Iterator<String> parse(Class<?> service, URL u)
throws ServiceConfigurationError
{
InputStream in = null;
BufferedReader r = null;
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
try {
in = u.openStream();
r = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in, "utf-8"));
int lc = 1;
while ((lc = parseLine(service, u, r, lc, names)) >= 0);
} catch (IOException x) {
fail(service, "Error reading configuration file", x);
} finally {
try {
if (r != null) r.close();
if (in != null) in.close();
} catch (IOException y) {
fail(service, "Error closing configuration file", y);
}
}
return names.iterator();
}
private class LazyIterator
implements Iterator<S>
{
Class<S> service;
ClassLoader loader;
Enumeration<URL> configs = null;
Iterator<String> pending = null;
String nextName = null;
private LazyIterator(Class<S> service, ClassLoader loader) {
this.service = service;
this.loader = loader;
}
private boolean hasNextService() {
if (nextName != null) {
return true;
}
if (configs == null) {
try {
String fullName = PREFIX + service.getName();
if (loader == null)
configs = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fullName);
else
configs = loader.getResources(fullName);
} catch (IOException x) {
fail(service, "Error locating configuration files", x);
}
}
while ((pending == null) || !pending.hasNext()) {
if (!configs.hasMoreElements()) {
return false;
}
pending = parse(service, configs.nextElement());
}
nextName = pending.next();
return true;
}
private S nextService() {
if (!hasNextService())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
String cn = nextName;
nextName = null;
Class<?> c = null;
try {
c = Class.forName(cn, false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not found");
}
if (!service.isAssignableFrom(c)) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not a subtype");
}
try {
S p = service.cast(c.newInstance());
providers.put(cn, p);
return p;
} catch (Throwable x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " could not be instantiated",
x);
}
throw new Error(); // This cannot happen
}
public boolean hasNext() {
if (acc == null) {
return hasNextService();
} else {
PrivilegedAction<Boolean> action = new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
public Boolean run() { return hasNextService(); }
};
return AccessController.doPrivileged(action, acc);
}
}
public S next() {
if (acc == null) {
return nextService();
} else {
PrivilegedAction<S> action = new PrivilegedAction<S>() {
public S run() { return nextService(); }
};
return AccessController.doPrivileged(action, acc);
}
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
public Iterator<S> iterator() {
return new Iterator<S>() {
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,S>> knownProviders
= providers.entrySet().iterator();
public boolean hasNext() {
if (knownProviders.hasNext())
return true;
return lookupIterator.hasNext();
}
public S next() {
if (knownProviders.hasNext())
return knownProviders.next().getValue();
return lookupIterator.next();
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
};
}
public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load(Class<S> service,
ClassLoader loader)
{
return new ServiceLoader<>(service, loader);
}
public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load(Class<S> service) {
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
return ServiceLoader.load(service, cl);
}
}
Spring 中的 SPI
Spring中的SPI机制主要是通过spring.factories文件来实现的,通过读取spring.factories文件中的key=value的接口和对应的接口实现类进行类加载和对象初始化。核心主要是SpringFactoriesLoader是实现的。
Spring SPI 示例
-
创建接口和其实现类
-
在Resource目录下创建META-INF目录并创建spring.factories文件
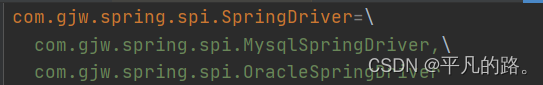
-
使用Spring-SPI机制
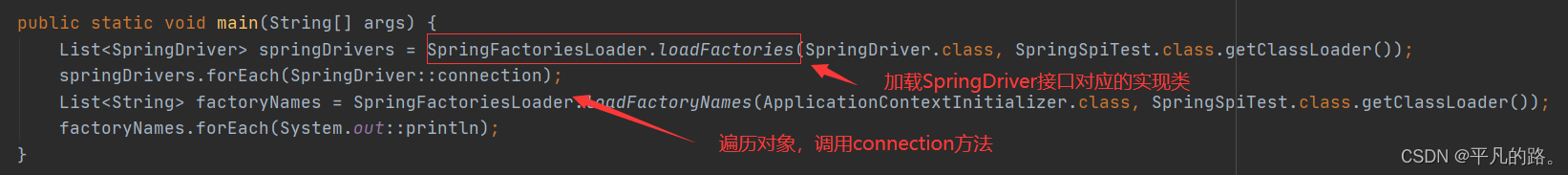

SpringFactoriesLoader源码
类结构如下:
核心方法为 loadFactories
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 加载 工厂
Assert.notNull(factoryType, "'factoryType' must not be null");
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
// 1.确定类加载器
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
// 2.核心逻辑之一,解析所有jar包中META-INF/spring.factories文件中factoryClass的实现类全限定名
List<String> factoryImplementationNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryType, classLoaderToUse);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded [" + factoryType.getName() + "] names: " + factoryImplementationNames);
}
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>(factoryImplementationNames.size());
// 3.遍历实现类的全限定名并进行实例化
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryImplementationName, factoryType, classLoaderToUse));
}
// 4.结果排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
// 返回结果
return result;
}
/**
* 根据Class对象获取所有jar包中META-INF/spring.factories文件中factoryClass的实现类全限定名
* 比如 org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=com.gjw.spring.spi.JsonPropertySourceLoader
* 并以 Map的方式返回
**/
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
// 获取 Class的全限类名
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
// loadSpringFactories获取Map
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyLis
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 获取内存中的缓存cache map
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
// 有则直接返回
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
// 获取spring.factories并解析成Properties
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
// 遍历每个 key values
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
// 存入 Map
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiabl
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}






















 90
90











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








