226.翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
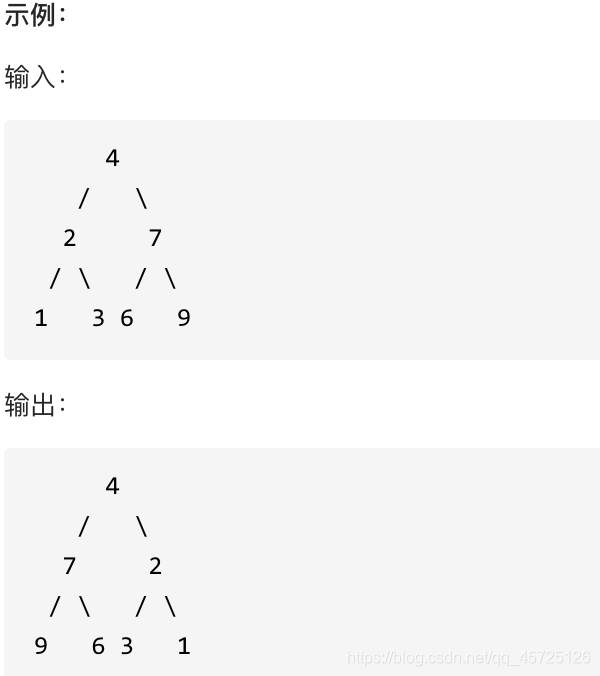
翻转二叉树其实很简单,我们每次只需要把当前结点的左右子树调换即可,通俗的说就是——左子树变右子树,右子树变左子树,那么我们如何实现呢?——两种方法:迭代和递归
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
#递归法
if not root:return None
#每次都将左右节点翻转
root.left,root.right=root.right,root.left
#然后对翻转后的左节点再进行翻转
self.invertTree(root.left)
self.invertTree(root.right)
return root
'''
迭代法
if not root:return None
st=[]
st.append(root)
while st:
node=st.pop()
node.left,node.right=node.right,node.left
if node.left:
st.append(node.left)
if node.right:
st.append(node.right)
return root
'''
101.对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。

我们判断二叉树是否对称,其实也是比较两侧节点是否相等,但是注意我们此时比较的不是左右节点!——而是外侧和里侧节点
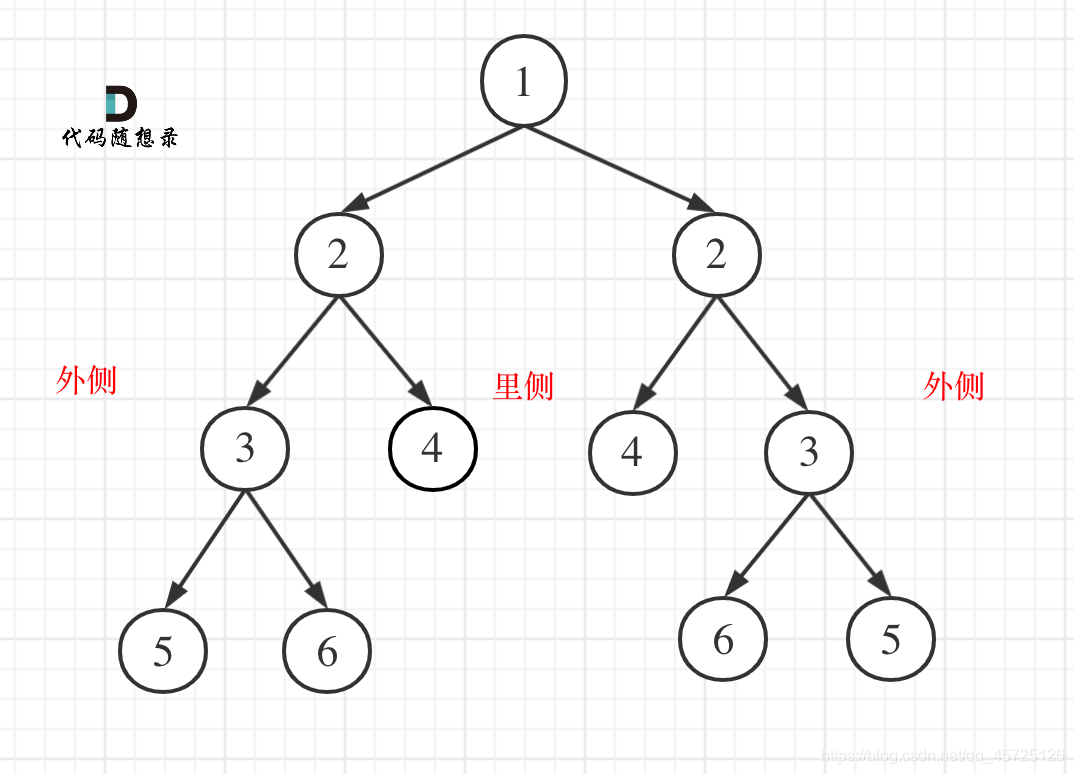
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if not root:return True
return self.theSame(root.left,root.right)
def theSame(self,left:TreeNode,right:TreeNode):
#我们首先判断这两个节点有空节点的情况
if left and not right:return False
elif not left and right:return False
elif not left and not right:return True
#然后当两个节点都不为空,判断它们的值是否相等
elif left.val!=right.val:return False
#此时经过上述的所有判断,递归到这一步代表此时两个节点都相等
#可以将它们的子节点加入递归判断了
outside=self.theSame(left.left,right.right)
inside=self.theSame(left.right,right.left)
#当外侧和里侧都相等,代表对称
res=outside and inside
return res
二叉树和N叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回最大深度3
这道题其实也是两种方法——递归与迭代,迭代就简单,和层序遍历一样,找到根节点那一层即可,递归就需要分别求出左右子树的深度,然后取两者中的最大值加1
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
#递归法
Depth=self.getDepth(root)
return Depth
def getDepth(self,root):
if not root:return 0
#分别记录左右子树的深度
left=self.getDepth(root.left)
right=self.getDepth(root.right)
#当递归完成之后,我们的结果取左右子树的最大深度加1(加上root)
Depth=1+max(left,right)
return Depth
'''
迭代法(其实就是层序遍历)
if not root:return 0
queue=collections.deque()
res=0
queue.append(root)
while queue:
size=len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
node=queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
res+=1
return res
'''
N叉树
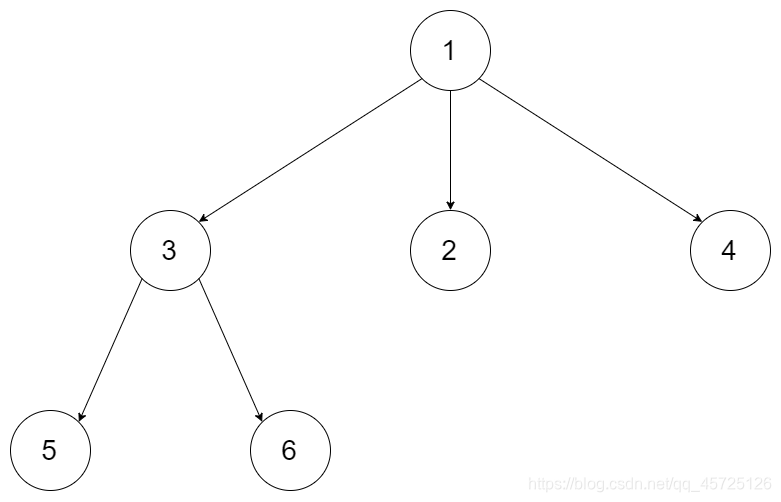
如图是一个三叉树,我们应该返回最大深度3,N叉树的特点就是用Node节点来存储,并且子树节点都是children(而不再用left,right区分)
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
import collections
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
#迭代法,和二叉树的层序遍历有一点区别
que=collections.deque()
if root:
que.append(root)
depth=0
while que:
#先记录每层的节点数,这也是这一层遍历的次数
size=len(que)
depth+=1
for i in range(size):
node=que.popleft()
#对于每一个节点,都要将其所有的children节点加入队列
for j in range(len(node.children)):
if node.children[j]:
que.append(node.children[j])
return depth
'''
def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:
递归法
return self.getDepth(root)
def getDepth(self,root):
if not root:return 0
depth=0
for i in range(len(root.children)):
depth=max(depth,self.getDepth(root.children[i]))
return depth+1
'''
二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回最小深度2
注意:很多做过二叉树最大深度的,都会遇到一个误区!举例说明
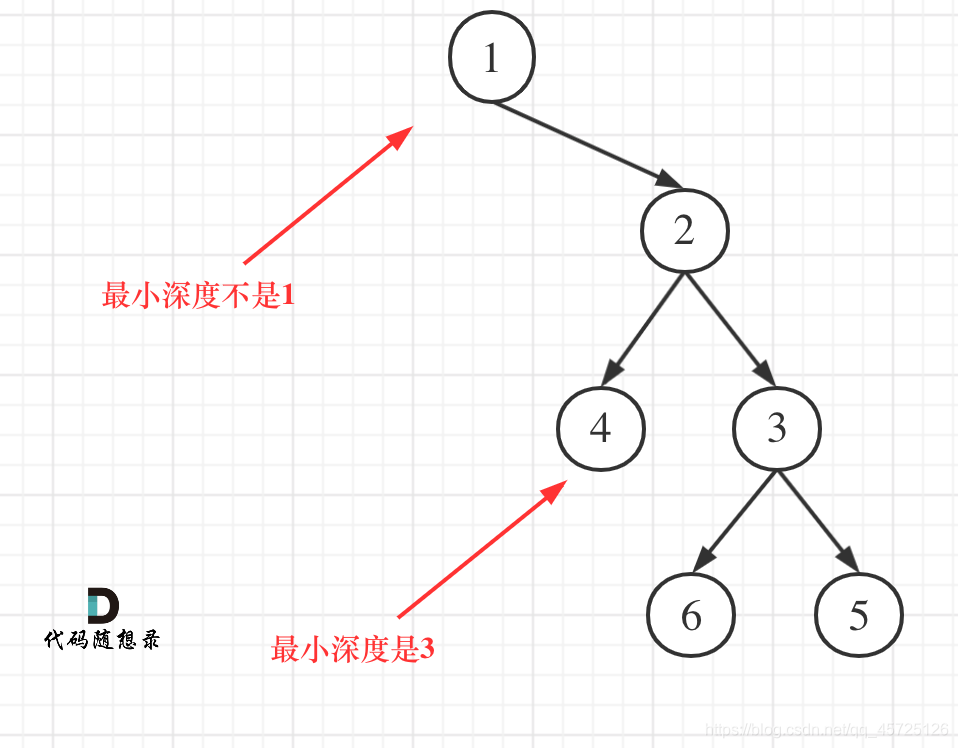
**我们找最小深度要找的时叶子节点!**如果像上述图片所示,我们还按照求最大深度的写法,分别求左右子树的最小深度加1的话,就会出错!
int leftDepth = getDepth(node.left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(node.right);
int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return result;//错误写法
正确的判断应该是,首先判断左右子树只有一个为空的情况,然后再判断两者都不为空或者同时为空,此时就是返回左右子树的最小深度加1
int leftDepth=getDepth(node.left)
int rightDepth=getDepth(node.right)
if not root.left and root.right:
return 1+rightDepth
elif root.left and not root.right:
return 1+leftDepth
return 1+min(leftDepth,rightDepth)
完整代码(迭代+递归)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
import collections
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
#递归法
return self.getDepth(root)
def getDepth(self,root):
if not root:return 0
left=self.getDepth(root.left)
right=self.getDepth(root.right)
#当左子树不为空但右子树为空时,最小深度应该是右子树深度加1
if root.left and not root.right:
return 1+left
#右子树同理
elif root.right and not root.left:
return 1+right
#当左右子树都不为空或者同时为空时,就取两者中的最小值即可
return 1+min(left,right)
'''
迭代法
if not root:return 0
st=collections.deque()
st.append(root)
res=0
while st:
res+=1
for _ in range(len(st)):
node=st.popleft()
#这里判断当前节点是否为叶子节点
if not node.left and not node.right:
return res
if node.left:
st.append(node.left)
if node.right:
st.append(node.right)
return res
'''
完全二叉树的节点个数
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例: 示例 1: 输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6] 输出:6
示例 2: 输入:root = [] 输出:0
示例 3: 输入:root = [1] 输出:1
提示:
树中节点的数目范围是[0, 5 * 10^4]
0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 10^4
题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
思路
其实这道题就是要遍历二叉树,每遍历一个节点就给节点数加1即可,那么遍历整颗二叉树也可以用迭代法和递归法来解决
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
#迭代法
if not root:return 0
st=[root]
res=0
while st:
for _ in range(len(st)):
node=st.pop()
res+=1
if node.right:
st.append(node.right)
if node.left:
st.append(node.left)
return res
'''
递归法
if not root:return 0
res=0
if root:res+=1
left=self.countNodes(root.left)
right=self.countNodes(root.right)
return left+right+1
'''
判断二叉树是否平衡
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
示例 1:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]——返回True

示例 2:
给定二叉树 [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]——返回False

以上两个例子说明,我们不仅要分别判断左右子树是否平衡,最后还要将左子树和右子树放在一起判断最大高度差
思路
如何判断当前传入节点为根节点的二叉树是否是平衡二叉树呢,当然是左子树高度和右子树高度相差。
分别求出左右子树的高度,然后如果差值小于等于1,则返回当前二叉树的高度,否则则返回-1,表示已经不是二叉树了。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
res=self.getDepth(root)
return True if res!=-1 else False
def getDepth(self,root):
if not root:return 0
leftDepth=self.getDepth(root.left)
if leftDepth==-1:return -1
rightDepth=self.getDepth(root.right)
if rightDepth==-1:return -1
res=0
if abs(rightDepth-leftDepth)>1:
res=-1
else:
res=max(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1
return res




















 36万+
36万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








