springBoot 声明式事务,设置声明式事务的隔离级别
之前使用的是 @Transactional 最近迷上 声明式事务了 TransactionTemplate
-
propagation_required:spring的默认传播机制,如果上下文有事物则加入当前事务,如果不存在事物则新建事物执行。
-
propagation_supports:如果上下文中存在事务则加入当前事务,如果没有则以非事务的方式运行。
-
propagation_mandatory:该传播级别要求上下文必须存在事务,否者抛出异常。
-
propagation_requires_new:该传播级别每次都会创建新的事物,并同时将上下文中的事务挂起,新事物执行完成后,会恢复上下文事物。(外层的事务不会影响内层的事务提交和回滚)
-
propagation_not_supported:如果上下文存在事物则挂起当前事物,并以非事物的方式执行当前逻辑,执行完成后恢复上下文事物
-
propagation_never:该传播级别要求上下文中不能存在事务,否则抛出异常
-
propagation_nested:嵌套事务,如果上下文中存在事务则嵌套执行,不存在则新建事物 (save point 概念)(外层事务会影响内层的事务提交和回滚)
说一下用的最多的两个传播机制
propagation_required(默认传播机制)
package com.app.service;
import com.app.entity.Test;
import com.app.mapper.TestMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate;
/**
* @author supermarketss@163.com
* @date 2024-01-19 - 14:08
*/
@Service
public class TestService1 {
@Autowired
private TestMapper testMapper;
/**
* 这里的@Lazy主要解决循环依赖的问题
*/
@Autowired
@Lazy
private TestService1 thisService;
@Autowired
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
public void a() {
TransactionTemplate transaction = new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager);
transaction.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW);
transaction.execute(status -> {
Test test = new Test();
test.setId(1);
test.setName("张三");
testMapper.insert(test);
//默认,如果方法没有事务则加入当前事务
thisService.b();
return null;
});
}
public void b() {
Test test = new Test();
test.setId(2);
test.setName("王五");
testMapper.insert(test);
int a = 1 / 0;
}
}
这种情况下b方法出现异常,a方法也会一块回滚的
propagation_requires_new(创建新的事务挂起当前事务)
package com.app.service;
import cn.hutool.extra.spring.SpringUtil;
import com.app.entity.Test;
import com.app.mapper.TestMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate;
/**
* @author supermarketss@163.com
* @date 2024-01-27 - 22:24
*/
@Service
public class TestService2 implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
private TestMapper testMapper;
@Autowired
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
//spring启动完成后执行
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
TransactionTemplate transaction = new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager);
transaction.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED);
transaction.execute(status -> {
SpringUtil.getBean(TestService2.class).b();
Test test = new Test();
test.setId(1);
test.setName("张三");
testMapper.insert(test);
int a = 1 / 0;
return null;
});
}
public void b() {
//PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 如果上下文有事务会暂时挂起,并且开启一个新的事务执行,独立于原来的事务
//所以,即使a方法出现异常,b方法也不会回滚
TransactionTemplate transaction = new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager);
transaction.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW);
transaction.execute(status -> {
Test test = new Test();
test.setId(2);
test.setName("王五");
testMapper.insert(test);
return null;
});
}
}
外层事务不会影响,内层的事务提交与回滚的
@Transactional 多线程事务异常
这里需要在说一下mysql的事务隔离级别了 可重复读:开启事务后,即使其他事务数据已经提交了,原本的事务读取到的还是原来的数据。
问题复现 (先事务+后加锁 )
package com.app.service;
import cn.hutool.extra.spring.SpringUtil;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author supermarketss@163.com
* @date 2024-01-27 - 22:24
*/
@Service
public class TestService3 implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
//spring启动完成后执行
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
new Thread(() ->{
SpringUtil.getBean(TestService3.class).b();
}).start();
}
}
@Transactional
public void b() {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("test:sub:lock");
lock.lock(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
try {
//获取库存
//扣减库存
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
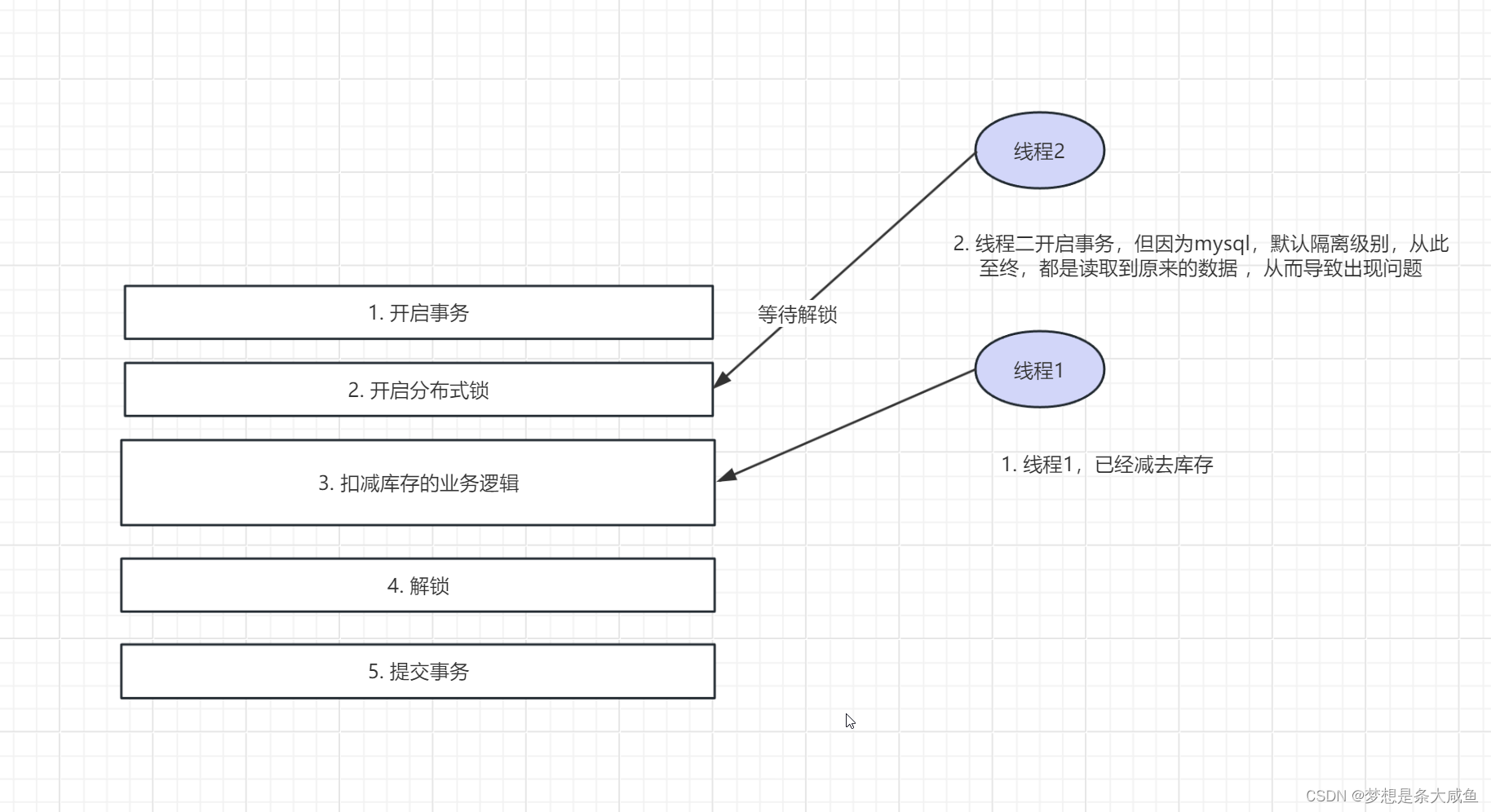
因为先开启的事务,后添加的锁,在多线程的情况下,一个线程进入开启事务并抢到锁,并开始执行扣库存的逻辑,第二个线程也进来,开启事务,但是锁被其他线程拿到需要等待,此时就出现问题了。第二个线程因为已经开启事务,即使第一个线程提交第二个线程拿到的也是原来的数据(mysql模式隔离级别,可重复读)
解决问题(先加锁 + 后加事务)
package com.app.service;
import cn.hutool.extra.spring.SpringUtil;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author supermarketss@163.com
* @date 2024-01-27 - 22:24
*/
@Service
public class TestService4 implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
//spring启动完成后执行
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
SpringUtil.getBean(TestService4.class).b();
}).start();
}
}
public void b() {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("test:sub:lock");
lock.lock(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
try {
transactionTemplate.execute(status -> {
//获取库存
//扣减库存
return null;
});
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
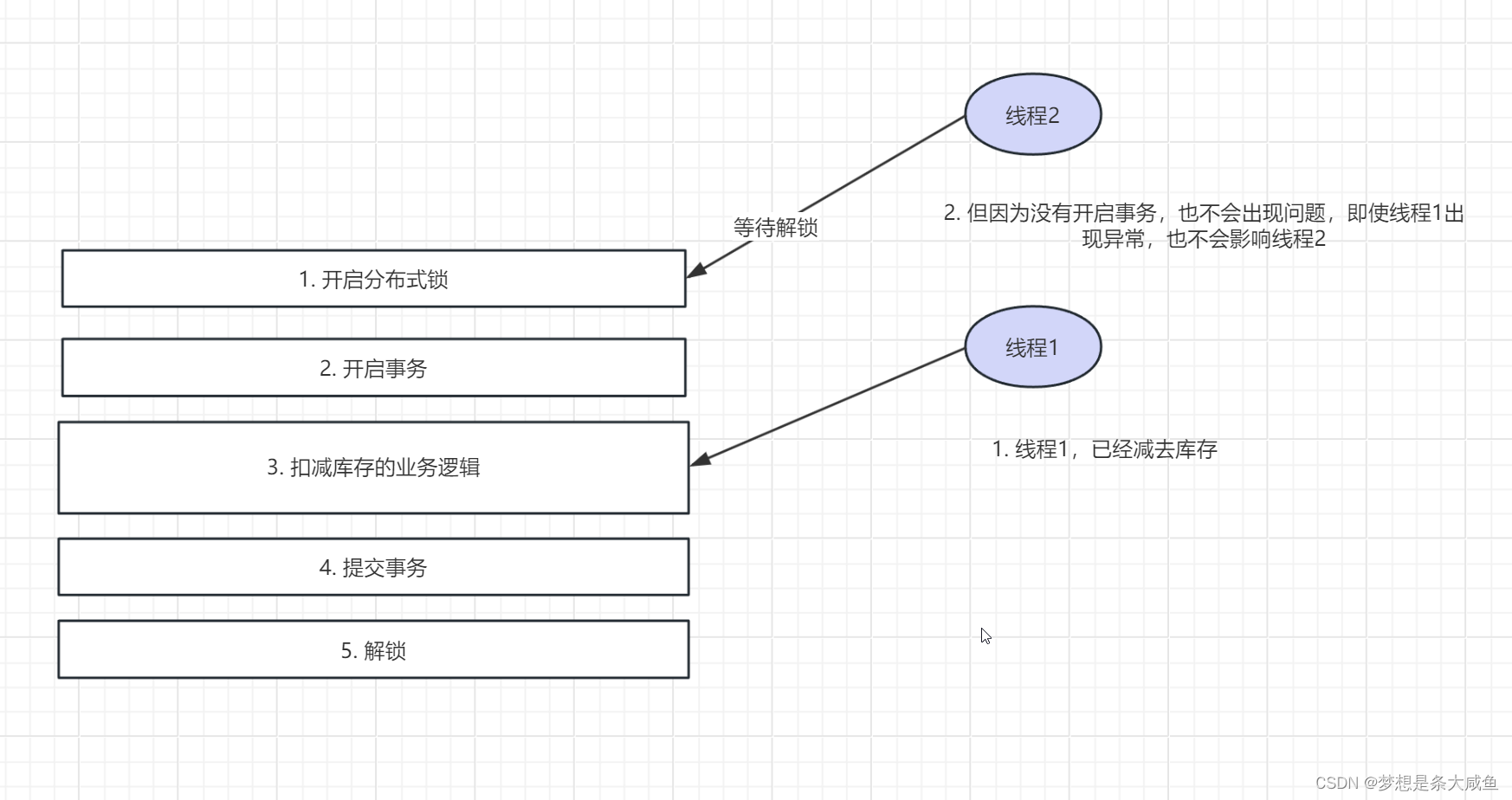
在多线程的情况下,线程1先加锁,在开启事务,在执行业务逻辑,此时第二个线程到来,因为第一个线程已经获取到锁,第二个线程需要等待,等待第一个线程整个业务逻辑执行完成并提交后,第二个线程才能拿到锁
参考
原创 | CRUD更要知道的Spring事务传播机制 (qq.com)
Spring的嵌套事务(Propagation.NESTED)到底是个啥 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)







 本文详细介绍了SpringBoot中声明式事务的使用,特别是TransactionTemplate的几种传播行为(如propagation_required、propagation_supports等),以及如何处理事务隔离级别,以确保多线程和嵌套事务的正确性。
本文详细介绍了SpringBoot中声明式事务的使用,特别是TransactionTemplate的几种传播行为(如propagation_required、propagation_supports等),以及如何处理事务隔离级别,以确保多线程和嵌套事务的正确性。














 340
340











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








