开篇
总所周知,jdbc是Java DataBase Connectivity(Java语言连接数据库),有一套标准的连接数据库规范规范,其中java连接mysql的驱动名称就叫做mysql-connector-java。
简单的连接和使用
如果是连接高版本的mysql,需要在jdbc-url后面加一些如下内容
?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&generateSimpleParameterMetadata=true
generateSimpleParameterMetadata=true,这个是用来获取元数据需要的一个参数,做一个简单说明,大概的元数据分为
- 由Connection对象的getMetaData()方法获取的是DatabaseMetaData对象。
- 由PreparedStatement对象的getParameterMetaData ()方法获取的是ParameterMetaData对象。
- 由ResultSet对象的getMetaData()方法获取的是ResultSetMetaData对象。
后面的使用再举例说明
一般来说,需要加载所需要的驱动、获取连接、创建对应执行sql是statement,如果有查询返回值则获取结果集resultset。
static String url;
static String user;
static String password;
static String driver;
static public Connection connection;
static {
//使用Properties文件用来存放配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
//加载配置文件
String file1 = JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResource("jdbc.properties").getFile();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream(file1));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
url=properties.getProperty("url");
user=properties.getProperty("user");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
}
public static void closeResource(Connection connection, Statement statement){
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void closeResource(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet){
closeResource(connection,statement);
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
关闭资源的时候需要从下到上依次关闭。
一个简单的查询案例
sql表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`;
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` int(0) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`d_id` int(0) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of employee
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (1, 'ye', 1);
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (2, 'zs', 2);
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (3, 'ls', 3);
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (4, 'ww', 1);
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
测试案例
@Test
public void test01() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from employee");
while (resultSet.next()){
Object object1 = resultSet.getObject(1);
Object object2 = resultSet.getObject(2);
Object object3 = resultSet.getObject(3);
System.out.println(object1+" "+object2+" "+object3);
}
closeResource(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
测试结果
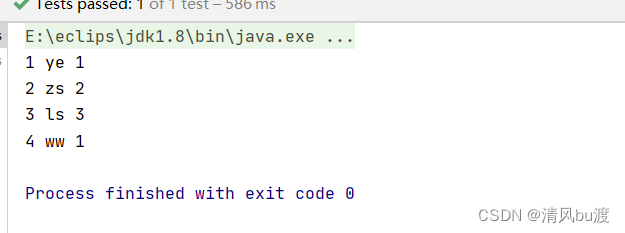
如果这样写显然不太灵活,很多地方就写死了这里查询就仅仅限制了只有三条数据的时候,这时候就需要用到元数据信息了
这里举一个简单例子 metaData 类的简单应用,代码如下
@Test
public void test02() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from employee");
//这个就是查询后的数据元数据信息
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
//获取一共有多少条数据
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
List<String> colunNames=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=1;i<=columnCount;i++){
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
colunNames.add(columnName);
String columnTypeName = metaData.getColumnTypeName(i);
System.out.println(columnName+" "+columnTypeName);
}
System.out.println(colunNames);
}
结果,这样就获取到了数据库的信息和字段类型。
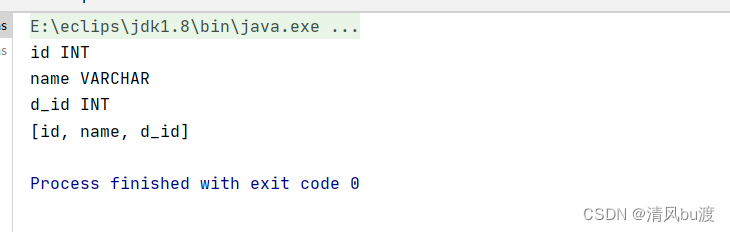
如果我想自己封装一个简单的orm对象关系映射的工具类该如何解决?
这里就不做过多解析了,关键还是metaData元数据信息类的使用和对象类的反射的应用,我下面给一个我的实现例子。
public static <T> List<T> excuteQuery(String sql, Class<T> t, Object... s) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
int i = 1;
for (Object o : s) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i, o);
i++;
}
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
ArrayList<T> ts = new ArrayList<T>();
while (resultSet.next()) {
ts.add(ClassUtil.fillBean(resultSet, t));
}
closeResource(connection, preparedStatement, resultSet);
return ts;
}
fillBean工具类的方法
public static <T> T fillBean(ResultSet resultSet,Class<T> tClass) throws SQLException {
//新建tClass对象
T t=null;
try {
Constructor<T> constructor = tClass.getConstructor();
t = constructor.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (NoSuchMethodException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//获取java对象中的fileds对象
Field[] declaredFields = tClass.getDeclaredFields();
Method method=null;
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
String fileName;
Class<?> type;
String methodName;
for (Field f:declaredFields){
fileName = f.getName();
type=f.getType();
methodName= StringUtil.setterName(fileName);
try {
method=tClass.getMethod(methodName,type);
method.invoke(t,type.cast(resultSet.getObject(fileName)));
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
System.err.println("没有找到"+fileName+"属性的setter方法");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return t;
}
其实这样写还是有很多的不足,需要考虑的数据库类型和字段类型的映射其实没有做好,还有很多需要优化的东西,当然这仅仅是提供以一个简单的思路而已。






















 5192
5192











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








