以下是一个使用贝叶斯优化的示例函数的Matlab代码:
```matlab
function [xopt,fopt] = bayesopt_fun(f,x0,lb,ub,opts)
% BAYESOPT_FUN: Bayesian optimization of a function
% [XOPT,FOPT] = BAYESOPT_FUN(F,X0,LB,UB,OPTS) finds the minimum of a
% function F using Bayesian optimization. X0 is the initial guess,
% LB and UB are the lower and upper bounds of the variables, and OPTS
% is an options structure created using BAYESOPT_OPTIONS. The function
% F should take a vector of variables as input and return a scalar
% output.
%
% Example usage:
% f = @(x) sin(3*x) + x.^2 - 0.7*x;
% opts = bayesopt_options('AcquisitionFunctionName','expected-improvement-plus');
% [xopt,fopt] = bayesopt_fun(f,0,0,1,opts);
%
% See also BAYESOPT_OPTIONS.
% Check inputs
narginchk(4,5);
if nargin < 5, opts = bayesopt_options(); end
assert(isa(f,'function_handle'),'F must be a function handle');
assert(isvector(x0) && isnumeric(x0),'X0 must be a numeric vector');
assert(isvector(lb) && isnumeric(lb),'LB must be a numeric vector');
assert(isvector(ub) && isnumeric(ub),'UB must be a numeric vector');
assert(all(size(x0)==size(lb)) && all(size(x0)==size(ub)), ...
'X0, LB, and UB must have the same size');
opts = bayesopt_options(opts); % ensure opts has all fields
% Initialize
X = x0(:); % column vector
Y = f(X);
n = numel(X);
Xbest = X;
Ybest = Y;
fmin = min(Y);
fmax = max(Y);
% Loop over iterations
for i = 1:opts.MaxIterations
% Train surrogate model
model = fitrgp(X,Y,'Basis','linear','FitMethod','exact', ...
'PredictMethod','exact','Standardize',true, ...
'KernelFunction',opts.KernelFunction,'KernelParameters',opts.KernelParameters);
% Find next point to evaluate
if strcmp(opts.AcquisitionFunctionName,'expected-improvement-plus')
% Use expected improvement with small positive improvement threshold
impThreshold = 0.01*(fmax-fmin);
acqFcn = @(x) expected_improvement_plus(x,model,fmin,impThreshold);
else
% Use acquisition function specified in options
acqFcn = str2func(opts.AcquisitionFunctionName);
end
xnext = bayesopt_acq(acqFcn,model,lb,ub,opts.AcquisitionSamples);
% Evaluate function at next point
ynext = f(xnext);
% Update data
X = [X; xnext(:)];
Y = [Y; ynext];
if ynext < Ybest
Xbest = xnext;
Ybest = ynext;
end
fmin = min(Y);
fmax = max(Y);
% Check stopping criterion
if i >= opts.MaxIterations || (i > 1 && abs(Y(end)-Y(end-1))/Ybest <= opts.TolFun)
break;
end
end
% Return best point found
xopt = Xbest;
fopt = Ybest;
end
function EI = expected_improvement_plus(X,model,fmin,impThreshold)
% EXPECTED_IMPROVEMENT_PLUS: Expected improvement with small positive improvement threshold
% EI = EXPECTED_IMPROVEMENT_PLUS(X,MODEL,FMIN,IMPTHRESHOLD) computes
% the expected improvement (EI) of a surrogate model at the point X.
% The input MODEL is a regression model, FMIN is the current minimum
% value of the function being modeled, and IMPTHRESHOLD is a small
% positive improvement threshold.
%
% The expected improvement is defined as:
% EI = E[max(FMIN - Y, 0)]
% where Y is the predicted value of the surrogate model at X.
% The expected value is taken over the posterior distribution of Y.
%
% However, if the predicted value Y is within IMPTHRESHOLD of FMIN,
% then EI is set to IMPTHRESHOLD instead. This is done to encourage
% exploration of the search space, even if the expected improvement
% is very small.
%
% See also BAYESOPT_ACQ.
% Check inputs
narginchk(4,4);
% Compute predicted value and variance at X
[Y,~,sigma] = predict(model,X);
% Compute expected improvement
z = (fmin - Y - impThreshold)/sigma;
EI = (fmin - Y - impThreshold)*normcdf(z) + sigma*normpdf(z);
EI(sigma==0) = 0; % avoid division by zero
% Check if improvement is small
if Y >= fmin - impThreshold
EI = impThreshold;
end
end
function opts = bayesopt_options(varargin)
% BAYESOPT_OPTIONS: Create options structure for Bayesian optimization
% OPTS = BAYESOPT_OPTIONS() creates an options structure with default
% values for all parameters.
%
% OPTS = BAYESOPT_OPTIONS(P1,V1,P2,V2,...) creates an options structure
% with parameter names and values specified in pairs. Any unspecified
% parameters will take on their default values.
%
% OPTS = BAYESOPT_OPTIONS(OLDOPTS,P1,V1,P2,V2,...) creates a copy of
% the OLDOPTS structure, with any parameters specified in pairs
% overwriting the corresponding values.
%
% Available parameters:
% MaxIterations - Maximum number of iterations (default 100)
% TolFun - Tolerance on function value improvement (default 1e-6)
% KernelFunction - Name of kernel function for Gaussian process
% regression (default 'squaredexponential')
% KernelParameters - Parameters of kernel function (default [])
% AcquisitionFunctionName - Name of acquisition function for deciding
% which point to evaluate next (default
% 'expected-improvement-plus')
% AcquisitionSamples - Number of samples to use when evaluating the
% acquisition function (default 1000)
%
% See also BAYESOPT_FUN, BAYESOPT_ACQ.
% Define default options
opts = struct('MaxIterations',100,'TolFun',1e-6, ...
'KernelFunction','squaredexponential','KernelParameters',[], ...
'AcquisitionFunctionName','expected-improvement-plus','AcquisitionSamples',1000);
% Overwrite default options with user-specified options
if nargin > 0
if isstruct(varargin{1})
% Copy old options structure and overwrite fields with new values
oldopts = varargin{1};
for i = 2:2:nargin
fieldname = validatestring(varargin{i},fieldnames(opts));
oldopts.(fieldname) = varargin{i+1};
end
opts = oldopts;
else
% Overwrite fields of default options with new values
for i = 1:2:nargin
fieldname = validatestring(varargin{i},fieldnames(opts));
opts.(fieldname) = varargin{i+1};
end
end
end
end
function xnext = bayesopt_acq(acqFcn,model,lb,ub,nSamples)
% BAYESOPT_ACQ: Find next point to evaluate using an acquisition function
% XNEXT = BAYESOPT_ACQ(ACQFCN,MODEL,LB,UB,NSAMPLES) finds the next point
% to evaluate using the acquisition function ACQFCN and the regression
% model MODEL. LB and UB are the lower and upper bounds of the variables,
% and NSAMPLES is the number of random samples to use when maximizing
% the acquisition function.
%
% The input ACQFCN should be a function handle that takes a regression
% model and a set of input points as inputs, and returns a vector of
% acquisition function values. The set of input points is a matrix with
% one row per point and one column per variable.
%
% The output XNEXT is a vector containing the next point to evaluate.
%
% See also BAYESOPT_FUN, EXPECTED_IMPROVEMENT_PLUS.
% Check inputs
narginchk(4,5);
assert(isa(acqFcn,'function_handle'),'ACQFCN must be a function handle');
assert(isa(model,'RegressionGP'),'MODEL must be a regressionGP object');
assert(isvector(lb) && isnumeric(lb),'LB must be a numeric vector');
assert(isvector(ub) && isnumeric(ub),'UB must be a numeric vector');
assert(all(size(lb)==size(ub)),'LB and UB must have the same size');
if nargin < 5, nSamples = 1000; end
% Generate random samples
X = bsxfun(@plus,lb,bsxfun(@times,rand(nSamples,numel(lb)),ub-lb));
% Evaluate acquisition function
acq = acqFcn(model,X);
% Find maximum of acquisition function
[~,imax] = max(acq);
xnext = X(imax,:);
end
```
该示例代码实现了一个使用贝叶斯优化的函数优化器。该优化器使用高斯过程回归模型来近似目标函数,并使用期望改进加上(EI+)作为获取函数。您可以将此代码用作自己的优化问题的起点,并根据需要进行修改。

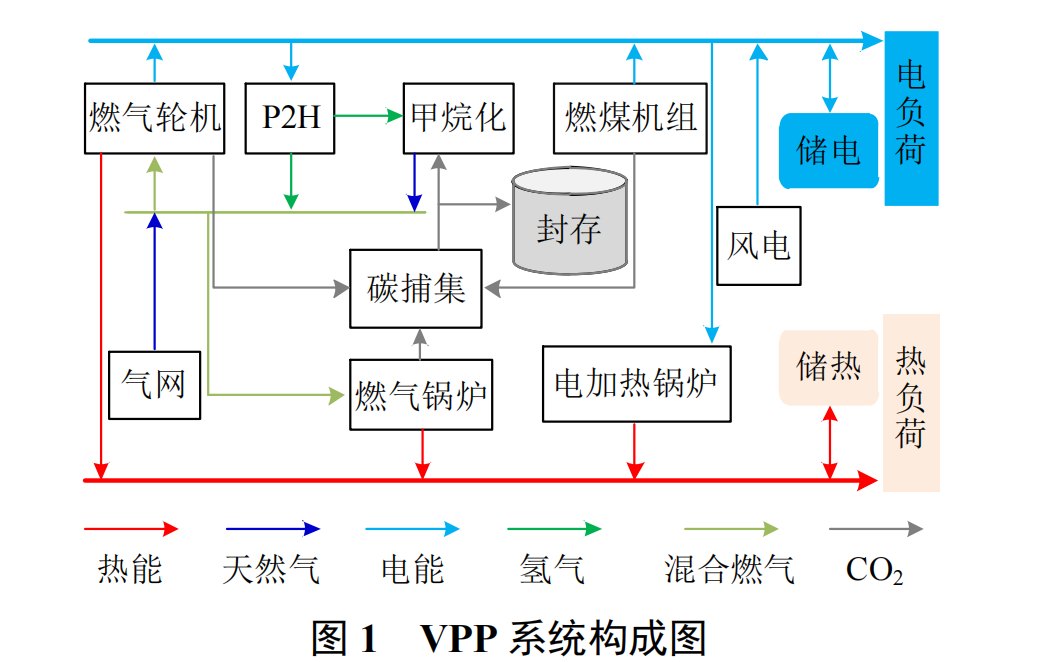
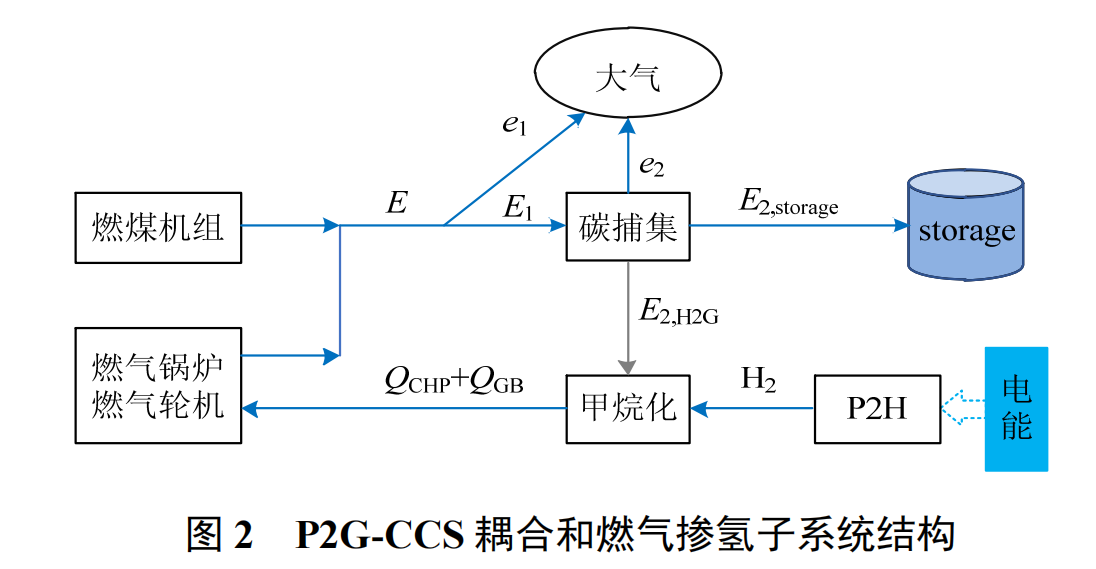







































 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








