文章目录
java基础-File类与IO流
java.io.File类
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Date;
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//File file = new File("D:/a.txt");
File file = new File("D:\\a.txt");
//File file = new File("D:"+File.separator+"a.txt");//File.separator:盘符分隔的方式
boolean exists = file.exists();
System.out.println(exists);
System.out.println(file.length());//获取文件的字节长度
System.out.println(file.getName());//获取文件名字:a.txt
System.out.println(file.getPath());//获取文件地址:D:\a.txt
long l = file.lastModified();//最后修改时间:毫秒数
System.out.println(new Date(l).toLocaleString());
File file1 = new File("../../a.txt");
//构建路径(相对路径):怎么写怎么输出
System.out.println(file1.getPath());//..\..\a.txt
//获取绝对地址
System.out.println(file1.getAbsolutePath());//D:\JavaData\Hello\..\..\a.txt
//规范路径getCanonicalPath()有异常需要抛出
System.out.println(file1.getCanonicalPath());//D:\a.txt
File file2 = new File("D:/c.tst");
//新建一个文件
boolean newFile = file2.createNewFile();
System.out.println(newFile);//如果新建的文件不存在 新建成功输出true
boolean newFile1 = file2.createNewFile();
System.out.println(newFile1);//新建的文件已存在 创建失败输出false
//删除文件,删除内容不经过回收站(慎用)
System.out.println(file2.delete());
File file3 = new File("D:/AA");
//file3.mkdir();//创建文件夹
file3.mkdirs();//可创建多层目录
//file3.delete();//删除文件夹
File file4 = new File("D:\\AA\\b.tst");
file4.setWritable(false);//禁止写入权限
//返回的是文件的名字,字符串类型的数组
String[] list = file4.list();
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());//小写转大写
System.out.println(s);
}
File[] files = file4.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
if (f.isFile()) {
System.out.println(f.getName() + " this is 文件");
}
if (f.isDirectory()){
System.out.println(f.getName() + " this is 文件夹");
}
}
}
}
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Date;
public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("E:\\阿里下载");
listFiles(file);
}
static void listFiles(File file){
//列出当前目录内所有文件或者文件夹
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
if (f.isFile()) {//如果是文件输出 名字 字节长度 日期:最后修改时间
System.out.println(f.getName()+"\t"+f.length()+"\t"+new Date(f.lastModified()).toLocaleString());
}else{//当是文件夹时 继续迭代找到当前文件夹内的目录或者文件
System.out.println("this is 文件夹:" + f.getName());
listFiles(f);
}
}
}
}
io流
- 作用:实现数据传输
i:input 输入流
o:output 输出流 - io分类:
- 按照流向分:输入流、输出流
- 按照传输的数据:字节流、字符流
- 按照处理单元不同:
- 节点流(直接对到数据上的流)
- 字节流的节点流:inputStream、outputStream
- 字符流的节点流:Reader、Writer
- 处理流(对节点流再次进行处理)
BufferedInputStream 、BufferedOutputStream
BufferedRead、BufferedlWriter
- 节点流(直接对到数据上的流)
字节流
所有的数据都可以采用字节流进行传输
字节输入流:InputStream
1. 抽象类,通过子类FileInputStream实现功能
2. 创建字节输入流对象
1. File file = new File("D:/a.txt");
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
2. InputStream is1 = new FileInputStream("D:/a.txt");
3. 读取数据
输入流对象.read();//获取对应的编码值
当读到-1时,文件内的资源已经读取完毕
4. 注意:一次读取一个字节,不能一次读取一个汉字,可以使用字节数组完成
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建输入流对象
File file = new File("D:/a.txt");
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStream is1 = new FileInputStream("D:/a.txt");
//读取数据
/*while (true){
//一次只能读取一个字节数据 -128~127
int read = is.read();
if (read==-1){
break;
}
System.out.println((char) read);
}*/
/*int len = is.read();
while (len!=-1){
System.out.println((char) len);
len = is.read();
}*/
/*int l = 0;
while((l = is.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) l);
}*/
/*byte[] b = new byte[8];
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
int read = is.read(b);//将数据读取到数组内,返回读取的有效数据个数
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
System.out.println(read);*/
byte[] a = new byte[4];
/* int len = is.read(a);
while (len!=-1){
String s = new String(a,0,len);
System.out.println(s);
len = is.read(a);
}*/
int len = 0;
while((len=is.read(a))!=-1){
String s = new String(a,0,len);
System.out.println(s);
}
//关闭输入流
is.close();
}
}
字节输出流:OutputStream
1. 抽象类,需要借助子类实现功能
可以将数据写到磁盘上,还可以进行网络传输
2. FileOutputStream()直接作用到文件上,是一个节点流
3. 使用FileOutputStream写出数据时,会将原有数据清空,保留写出的数据
4. 使用FileOutputStream写出数据时,如果目标文件不存在,直接创建一个文件,只能是一级目录
5. 写出字节数组
write(数组,开始下标,数量);
6. 在原有数据后进行追加
append : true可以进行追加
FileOutputStream("路径" , booLean append) ;
7. 写出字符串
byte[] b =字符串对象.getBytes();
import java.io.*;
public class OutStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象方式1
File file = new File("D:/a.txt");
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
//创建字节输出流对象方式2
OutputStream os1 = new FileOutputStream("D:/a.txt");
//可追加数据
//OutputStream os1 = new FileOutputStream("D:/a.txt",true);
//写出数据
os1.write(90);
String s = "ABCD";
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
os1.write(bytes);//写出字节数组
//写出字节数组部分数据write(字节数组名,开始下标,写出个数)
os1.write(bytes,0,2);
//关闭资源
os1.close();
}
}
使用字节流完成文件复制
import java.io.*;
public class CopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
//新建输入和输出流对象
is = new FileInputStream("D:/a.txt");
os=new FileOutputStream("E:/a.txt");
// 读取数据
//新建字节数组
byte[] b = new byte[20];
int len = 0;
//循环读取数据
while ((len = is.read(b))!=-1){
// 写出的是读进来的数据
os.write(b,0,len);
}
System.out.printf("", "复制完毕");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关流
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
字符流
-
字符输出流:
Writer 抽象类,需要子类FileWriter来实现功能
一次输出一个字符
注意:- 字符输出流内部有一个缓冲区,写出数据时先将数据写到缓冲区内
- 将数据写到磁盘中(一般都写上)
- 字符输出流对象.flush();
- 关闭资源也会将缓冲区的数据刷出到磁盘上
-
字符输入流:
Reader 抽象类,通过子类FileReader来实现功能注意:
- 使用字符输入流读取数据时,存储数据的文件编码类型要与代码编辑器类型一致
- 字符输入流每次读取一个字符数据,如果没有数据了返回-1
- 字符输入流每次读取一个字符数组时,返回数组内有效数据的个数;如果已经读取完毕,则返回-1
字符输出流
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
public class WriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建输出流对象
Writer writer = new FileWriter("E:/a.txt");
Writer writer1 = new FileWriter(new File("E:/a.txt"));
// 输出数据
writer.write(97);//字符流有缓冲区,先写入缓冲区需要flush刷出缓冲区写入磁盘
writer.write("你好世界");
char[] ch = {'你','好','世','界'};
writer.write(ch);//写出所有内容
writer.write(ch,1,2);//'好','世'
writer.flush();
// 关闭流
writer.close();
}
}

字符输入流

import java.io.*;
public class ReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字符输入流对象
Reader reader = new FileReader("E:/a.txt");
//Reader reader1 = new FileReader(new File(""));
//读取数据
int read = reader.read();
System.out.println((char) read);//a
int read1 = reader.read();
System.out.println((char)read1);//你
int read2 = reader.read();
System.out.println((char)read2);//好
/*while (true){
int read3 = reader.read();
System.out.println((char) read3+"--->"+read3);
if (read3==-1){
break;
}
}*/
int len = 0;
while ((len=reader.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)len+"--->"+len);
}
//关流
reader.close();
}
}
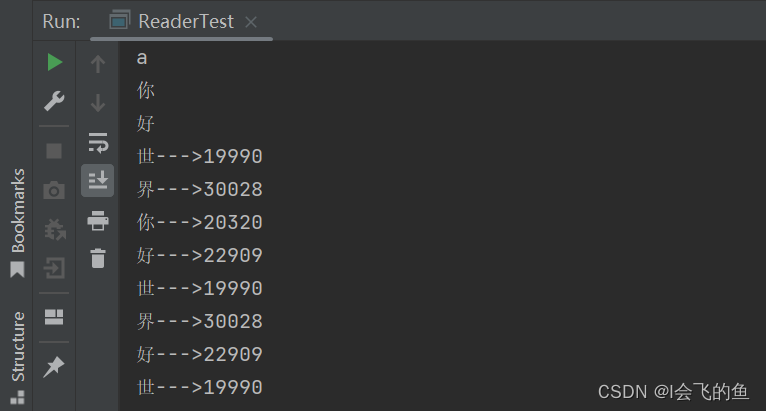
import java.io.*;
public class ReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字符输入流对象
Reader reader = new FileReader("E:/a.txt");
//新建字符数组
char[] c = new char[20];
//第一次读
/* int len = reader.read(c);
while (len != -1){
String s = new String(c, 0, len);
//输出数据
System.out.println(s);
//继续读
len = reader.read(c);
}*/
int len = 0;
while((len= reader.read(c))!=-1){
String s = new String(c, 0, len);
System.out.println(s);
}
//关流
reader.close();
}
}
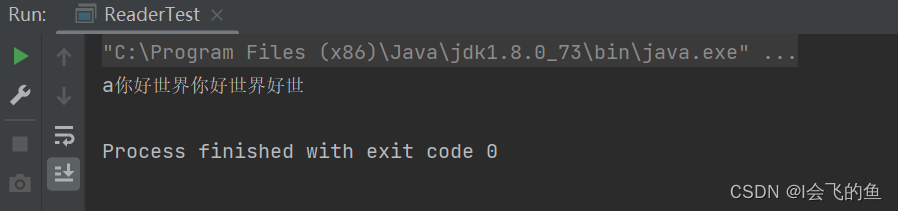
copy纯文本
import java.io.*;
public class CopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Reader reader = null;
Writer writer = null;
try {
// 创建输入输出流对象
reader = new FileReader("E:/作文.txt");
writer = new FileWriter("D:/作文.txt");
// 读取数据
char[] chars = new char[20];
int len = 0;
//将数据读到字符数组内
while((len = reader.read(chars))!=-1){
// 将读取进来的数据进行展示
System.out.println(new String(chars, 0, len));
// 将字符数组的数据进行写出
writer.write(chars,0,len);
}
writer.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 关闭资源
if (reader != null){
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (writer != null) {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
缓冲流
字节缓冲流
字节输入缓冲流:BufferedInputStream
底层采用8192的(byte)字节数组,存储数据
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class BufferStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
//节点流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("E:a.txt");
//处理流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
}
}
字节输出缓冲流:BufferedOutputStream
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:/a.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
字节缓冲输入输出流copy文件
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 创建输入输出流对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/a.txt"));
// 读取数据
// 创建字节数组,提高读取的速度
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024*20];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
// 从0开始有多少有效数据就写出多少
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
System.out.println("copy完毕");
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("用时:" + (endTime - startTime));
// 关闭资源
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
字符缓冲流
缓冲字符输入流:BufferedReader
底层有一个char类型的数组,存储缓冲的数据:8192
readLine(); 一次读取一行数据,当没有数据时返回null
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ButterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 新建字符缓冲输入流 缓冲流嵌套节点流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:/a.txt"));
String s = br.readLine();
System.out.println(s);
// 外层关闭内层自动关闭
br.close();
}
}
缓冲字符输出流:BufferedWriter
底层有一个char类型的数组,存储缓冲的数据:8192
import java.io.*;
public class ButterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:/b.txt"));
bw.write("会当凌绝顶");
//换行
// bw.write("\n");
bw.newLine();//新建一行
bw.write("一览众山小");
bw.close();
}
}
转换流
- 将字节流转换为字符流
- InputStreamReader
- OutputStreamWriter
import java.io.*;
public class TestInputStreamReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader reader = new FileReader("E:/a.txt");
int read = reader.read();
// 当前idea是UTF-8编码,读取GBK编码,出现乱码
System.out.println((char) read);
reader.close();
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class TestInputStreamReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 使用GBK编码方式读取GBK编码文件
InputStreamReader gbk = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("E:/a.txt"), "GBK");
int read = gbk.read();
System.out.println((char) read);
gbk.close();
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class TestInputStreamReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// new Scanner(System.in);
// 自己写键盘输入类
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
System.out.println("请输入");
// int read = inputStreamReader.read();
// System.out.println((char) read);
String s = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
// System.out.println(111);
// 自己写输出,通过把字节流变字符流
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(System.out);
outputStreamWriter.write("你好");
outputStreamWriter.flush();
outputStreamWriter.close();
// 向指定文件写入
FileOutputStream stream = new FileOutputStream("E:/c.txt");
OutputStreamWriter gbk = new OutputStreamWriter(stream, "GBK");
gbk.write(97);
gbk.close();
数据流
- 可以保留数据的原始特性 int
- 以二进制的形式存储数据,(人看不懂)
- 只有字节流没有字符流
import java.io.*;
public class DataStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 新建数据流对象
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:/d.txt"));
// 写出数据
dos.writeInt(10);
dos.writeBoolean(false);
dos.writeUTF("你好");
// 关闭资源
dos.close();
// 新建数据输入流对象来读取数据
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/d.txt"));
// 读取
int i = dis.readInt();
boolean b = dis.readBoolean();
String s = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(i);//10
System.out.println(b);//false
System.out.println(s);//你好
// 关闭流
dis.close();
}
}
对象流
-
进行对象的存取
-
对象输出流:ObjectOutputStream
-
对象输入流:ObjectInputStream
-
注意:
-
如果有属性不想序列化,可以选择在属性前+transient(短暂的)
-
static 修饰的属性 ,不会参与序列化
-
在进行序列化 或者 反序列化,序列化的版本必须一致
-
在进行反序列化时,对象类的class文件,不能消失 ,必须存在
-
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L;
- 插件方式
序列化
-
如果将一个对象进行存储或网络传输,那么要将此对象进行序列化
-
如何实现序列化?:implements Serializable
-
会将对象数据采用二进制的形式存到磁盘上
反序列化
- 将对象从磁盘或者网络中读取出来
序列化方式1
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
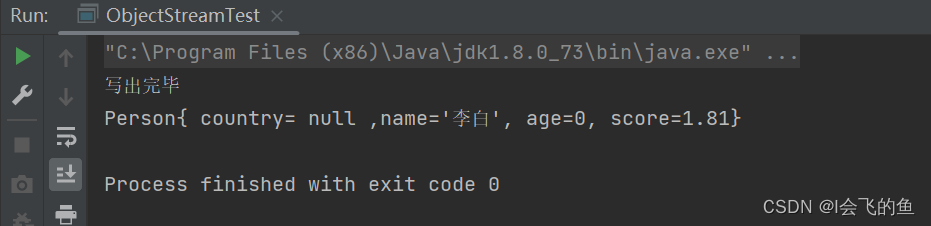
public class ObjectStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建对象
Person p = new Person("李白", 18, 1.81);
/*p.setCountry("China");
System.out.println(p);*/
// 创建对象输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:/obj.txt"));
// 写出对象
oos.writeObject(p);
// 关闭流
System.out.println("写出完毕");
oos.close();
// 创建对象输入流
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/obj.txt"));
// 读取对象
Object o = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
// 关闭资源
ois.close();
}
}
//如何实现序列化?:implements Serializable
//对象序列化实现接口
class Person implements Serializable {
String name;
int age;
double score;
static String country;
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public Person(String name, int age, double score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" + " country= " + country +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
序列化方式2
- 使用Externalizable接口也可以进行序列化和反序列化操作
- 使用此接口任意属性都可以序列化
//序列化时会调用此方法
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {}
//反序列化时调用
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {}
import java.io.*;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:/obj2.txt"));
Student s1 = new Student("李白",18 , 99);
s1.setCountry("China");
oos.writeObject(s1);
System.out.println("写出成功");
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/obj2.txt"));
Object o = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
}
}
class Student implements Externalizable {
String name;
transient int age;
static String country;
double score;
public void setCountry(String country) {
Student.country = country;
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, double score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" + " country= " +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(name);
out.writeUTF(country);
out.writeInt(age);
out.writeDouble(score);
}
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 怎么写怎么读
name = in.readUTF();
country = in.readUTF();
age = in.readInt();
score = in.readDouble();
}
}
打印流与Scanner
打印流
- System.out 默认输出到控制台,可以通过System.setOut(打印流);改变流向
- System.err 默认输出到控制台,可以通过System.setErr(打印流);改变流向
输出到控制台
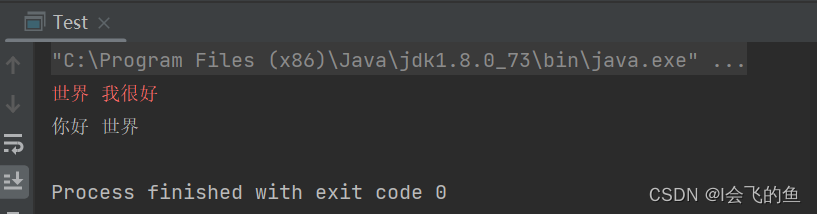
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 打印流
System.out.println("你好 世界");//正常输出
System.err.println("世界 我很好");//错误输出,位置不定,红色
}
}
输出到文件中
// 创建一个打印流
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("E:/p.txt");
ps.println("会当凌绝顶");
ps.println("一览众山小");
ps.close();

import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
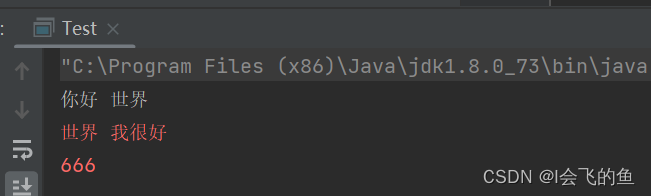
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// 打印流
System.out.println("你好 世界");//正常输出
System.err.println("世界 我很好");//错误输出,位置不定,红色
// 创建一个打印流
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("E:/p.txt");
ps.println("会当凌绝顶");
ps.println("一览众山小");
// 通过System.setOut(打印流);改变流向
System.setOut(ps);
System.out.println("望岳");
System.out.println("杜甫");
System.err.println("666");
ps.close();
}
}

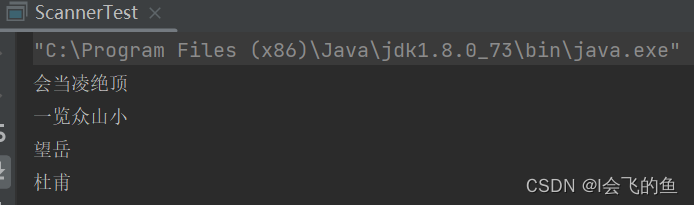
Scanner
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
Scanner s = new Scanner(new File("E:/p.txt"));
while(s.hasNextLine()){
String s1 = s.nextLine();
System.out.println(s1);
}
s.close();
}
}
jdk1.7关闭流新特性
import java.io.*;
public class TestCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedInputStream bis =null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
// 新建流对象:缓冲字节流
// 输入流
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/p.txt"));
// 输出流
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/pp.txt"));
// 对数据读,写
byte[] b = new byte[1024*10];//1字节*10=1kb
int len = 0;
while((len= bis.read(b))!=-1){
bos.write(b,0,len);
}
bos.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 关闭流
if (bis!=null){
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (bos!=null){
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
try(
需要关闭资源的对象
){
}catch(){
}
- 只要实现了AutoCloseable接口就可以使用try-with-resourse 新特性(jdk1.7提出)
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class TestCopy2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/p.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:/pp2.txt"));
){
byte[] b = new byte[1024*10];
int len = 0;
while((len = bis.read(b))!=-1){
bos.write(b,0,len);
}
bos.flush();
System.out.println("写出完毕");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








