sql函数
单行函数
1、显示系统时间(注:日期+时间))
select now()
2、查询员工号、姓名、工资,以及工资提高百分之100%后的结果(new salary))
select employee_id,last_name,salary*1.2 "new salary" from employees;
3、将员工的姓名按首字母排序,并写出姓名的长度
select length(last_name) 长度,SUBSTR(last_name,1,1) 首字母,last_name from employee order by last_name
4、做一个查询,产生下面的结果
select concat(last_name,'earns',salary,' monthly but wants ',salary*3) as "Dream salary" from employees;
如果只想查询一个,那么就加个where条件
5、使用case-when 按照下面的条件
select job_id as job,
CASE 'AD_PRES' THEN 'A'
CASE 'ST_MAN' THEN 'B'
CASE 'IT_PROD' THEN 'C'
END AS Grace
FROM employees
分组函数
group by 搭配having使用
select count(1),clientNo from employees group by clientNo having count(*) >4;
案列2:查询每个工种有奖金的员工的最高工资>12000
1、查询每个工种有奖金的员工的最高工资
select max(salary),job_id from employees where commisson_pct is not null
group by job_id
2、查询最高工资>12000
select max(salary),job_id from employees where commisson_pct is not null
group by job_id having max(salary) > 12000;
案例3、查询领导编号>102的每个领导手下的最低工资>5000的领导编号是那个,以及其最低工资
1、查询每个领导手下的员工固定最低工资
select min(salary),manager_id from employees group by manager_id;
2、添加筛选条件:编号 > 102
select min(salary),manager_id from employees where managet_id > 102 group by manager_id ;
3、最低工资(min(salary>5000))
select min(salary),manager_id from employees where managet_id > 102 group by manager_id having min(salary) > 5000;
案例4:按员工姓名的长度分组,查询每一组的员工个数,刷选员工个数>5 有那些
select length(last_name) len_name,count(last_name) c from employees group by length(last_name) having c > 5;
案列5:查询那个部门的员工个数> 2
select count(*),department_id from employees group by department_id having count(*) > 2;
查询每个部门每个工种的员工的平均工资
select avg(salary) ,department_id,job_id from employees
group by job_id,department_id;
案例6:查询每个部门每个工种的员工的平均工资,并且按平均工资的高低显示
select avg(salary),departmen_id,job_id from employees group by department_id,job_id
order by avg(salary) desc;
连接查询
含义: 又称多表查询,当查询的字段来自多个表时,就会用到连接查询
子查询
出现在其他语句内部的select 语句,称为子查询或内查询
内部嵌套其他select语句的查询,成为外查询或主查询
select first_name from employees where department_id in(select department_id from departments where location_id = 1700)
特点:
1、子查询放在小括号内
2、子查询一般放在条件条件的右侧
3、标量子查询,一般搭配单行操作符使用
in 、any/some、all
| 操作符 含义 | |
|---|---|
| IN/NOT IN | 等于列表中得任意一个 |
| ANY/SOME | 和子查询返回的某一个值比较 |
| ALL | 和子查询返回的所有值比较 |
按子查询出现的位置:
select 后面
from
where 或 having后面
exits后面(相关子查询)
按功能按结果集的行列数不同
标量子查询(按结果集只有一行一列)
列子查询(结果集只有一列多行)
行子查询 (结果集有一行多列)
表子查询 (结果集一般为多行多列)
标量子查询:
案例1: 谁的工资比Abel高
select salary from employeees where last_name = 'Abel'
查询员工的信息,满足salary>1的结果
select * from employees where salary > (
select salary from employeees where last_name = 'Abel'
)
案例2:返回job_id与141号员工相同,salary 比143号员工多的员工 姓名,job_id和工资
select job_id from employees where employees_id = 141
select salary from employees where employees_id = 143
select last_name,job_id,salary from employees where job_id = (
select job_id from employees where employees_id = 141 )and salary > (
select salary from employees where employees_id = 143
)
 **案例
**案例
列子查询:(多行子查询–单例多行)
**案列3:返回公司工资最少的员工信息 **
select job_id from employees where salary =
案例1:返回location_id是1400或1700的部门中的所有员工姓名
select last_name from employees where department_id in (select distinct department_id from departments where location_id IN (1400,1700));
案例2:返回其他工种比job_id 为IT_PROD工种任一工资低的员工的员工号、姓名、工资和job_id
1、查询job_id 为’IT_PROD’部门任一工资
select distinct salary from employees where job_id = 'IT_PROD'
2、查询员工号、姓名、job_id 、以及salary ,salary<1的任意一个
select last_name,employees_id,job_id,salary from employees where salary < ANY (
select distinct salary from employees where job_id = 'IT_PROD'
) and job_id <> 'ID_CODE';
案例3、返回其他部门中比job_id 为IT_PROD 部门所有工资都低的员工
select last_name,employee_id,job_id,salary
from employees
where salary < ALL(
select distinct salary from employees where job_id = 'IT_PROD'
)
行子查询
案例:查询员工编号最小并且工资最高的员工信息
1、查询最小的员工编号
select min(employee_id) from employees
2、查询工资最高的员工
select max(salary) from employees;
3、查询员工信息
select * from employees where employee_id = (
select min(employee_id) from employees
) and salary = (select max(employee_id) from employees)
二、select后面
里面仅仅支持标量子查询
案例:查询每个部门的员工个数
select d.* ,(
select count(*) from employees e where e.department_id = d.`department_id`
)个数
from departments d;
案例2:查询员工号=102的部门名
select (
select department_name
from departments d
INNER JOIN employees e
on d.partment_id = e.department_id
where e.employee_id = 102
)部门名
三、from后面
将子查询结果充当一张表,必须起别名
案例:查询每个部门的平均工资
1、查询每个部门的平均工资
select avg(salary),department_id from employees group by department_id
select * from job_graces;
2、连接1的结果集和job_graces表,筛选条件平均工资between lowest_sal and highest_sal
select ag_dep.*,g.`grade_level`
from (
select avg(salary),department_id from employees group by department_id
) ag_dep
INNER JOIN job_graces g
on ag_dep.ag BETWEEN lowest_sal and highest_sal;
四、exists后面(相关子查询)
语法:
exists(完整的查询语句)
select exists(select employee_id from employees where salary = 300000);
案例1:查询有部门员工名和部门名
select department_name
from departments
where
select department_name
from departments
where exists(
select *
from employees e
where d.`department_id` and e.`department_id`
);
案例 2、查询工资比公司平均工资高
1、查询平均工资
select avg(salary) from employees
2、查询工资>1的员工号,姓名和工资
select last_name ,employee_id,salary
from employees
where salary > (
select avg(salary) from employees
)
案例3、查询各部门中工资比本部门平均工资高的员工号、姓名和工资
1、查询各部门中平均工资
select avg(salary) from employees group by department_id
2、查询比本部门中平均工资高的员工号、姓名和工资
select last_name,employee_id,salary
from employees
join in (
select avg(salary) ag,department_id from employees group by department_id
) avg_ag on avg_ag.deaprtment_id = department_id where salary > avg_ag.ag;
案例4 查询管理者是king的员工姓名和工资
select employee_id
from employees
where last_name = "K_ing"
select salary ,last_name
from employees
where manager_id in (
select employee_id
from employees
where last_name = "K_ing"
)
案例5 查询工资最高的员工的姓名,要求first_anem 和last_name显示为一列 姓.名
select concat(first_name,last_name) from employees where salary = (
select max(salary) from employees
)
分页查询
查询顺序
select *
from
join on
group by
having
order by
limit offset(起始条数) size(显示数)
select * from employees limit 0,5;
select * from employees limit 5;
select 查询列表
from 表
limit
一、查询 所有学员的邮箱的用户名(注:邮箱中 @前面的字符)
select substr(email,1,instr(email,'@')-1) 用户名 from stuinfo
外连接: select * from 表1 join 表2 on
左连接:left join
右连接:right join
练习:
五、查询每个专业的男生人数和女生人数
方式一:
select count(*) 个数,sex,majorid
from student
group by sex,majorid;
方式二:
select majorid,
(select count(*) from student where sex = '男' and majorid = s.majorid) 男,
(select count(*) from student where sex = '女' and majorid = s.majorid)
女,
from student s
group by majorid
联合查询
将多条查询的语句的结果合并成一个结果
部门编号大于90或者邮箱中包含a的员工信息
select * from employees where email like '%a%' or department_id > 90;
select * from employees where email like '%a%'
union
select * from employees where department_id > 90;
语法:
查询语句1
union
查询语句2
union
…
DML 数据操作语言
插入insert
修改update
删除delete
方式一:
insert into 表明 (列名,列明) values ('','');
支持插入多行
支持子查询
方式二:
insert into 表名 set id = '',name = ''
update 表名 set 列名 = 列值,列名 = 列值,列名 = 列值 where
还可以
update 表1 别名 inner | left |right join 表2 别名 on 连接条件 set 列= 值
delete from 表名 where 筛选条件
多表删除
truncate table 表名
DDL 数据定义语言
库和表的管理
一、库的管理
创建、修改、删除
二、表的管理
创建、修改、删除
创建:create
修改: alter
删除:drop
1、库的管理
create datebase [if not exists] 表名
表的管理:
1、
alter table book change column publishdate pubDate DATETIME;
2、改表表字段长度:
alter table book modify column last_name varchar(50);
alter table book modify column pubdate timestamp;
3、添加列
alter table author add column annual double;
4、删除列
alter table author drop column annual;
5、修改表名
alter table author rename to book_author;
desc book; --查看都有那些列
6、扩容表字段
alter table author modify name varcher2(10);
表的删除
drop table if exists book_author;
show tables
通用的写法
drop datebases if exists 旧库名;
create datebases 新库名;
drop table if exists 旧表名
create table 表名();
表的复制
1、仅仅复制表的结构
create table copy like author;
2、复制表的结构+数据
create copy2
select * from author;
3、只复制部分数据
create table copy3
select id,au_name
from author
where nation = '中国'
仅仅复制某些字段
create table copy4
select id,au_name
from author
where 1 = 2
或者
create table copy4
select id,au_name
from author
where 0;
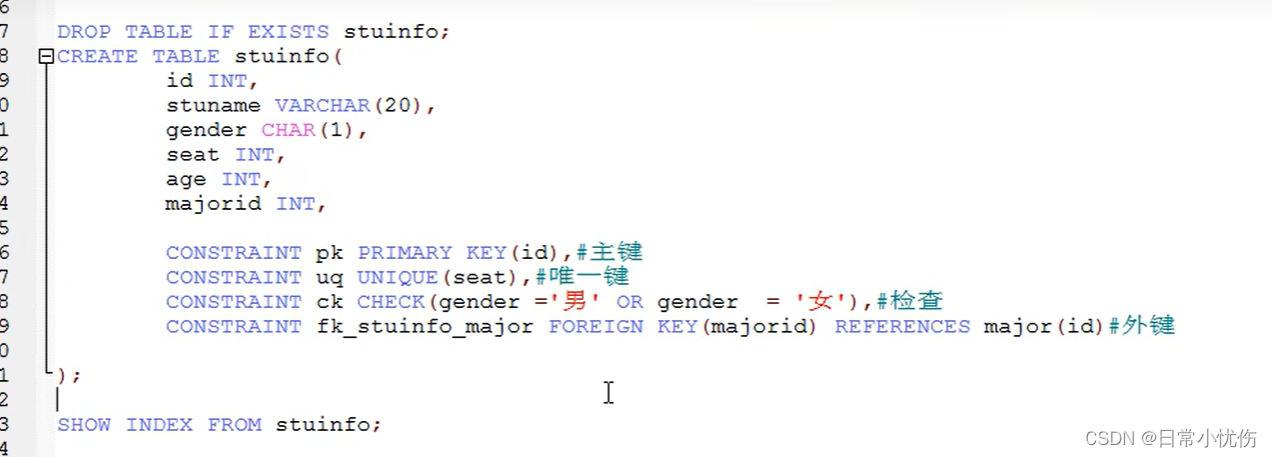
主键和唯一的大对比
主键不可以为空,允许同时设置多个
唯一可以为空,允许同时设置多个
TCL 事务
隐式事务
隐式事务:事务没有明显的开启和结束的标记
eg: insert update delete语句
delete from 表 where id = 1;
显示事务:事务具有明显的开启和结束的标志 (使用之前一定要先关掉事务)
前提: 必须线设置自动提交功能的禁用
set autocommit = 0;
MySQL数据库
批量插入
Oracle数据库
Oracle清数据库表
select 'truncate table' || table_name || ';' from user_tables where table_name like 'NL';
Oracle快照恢复数据库
select * from NL_ACCT as of timestamp timestamp'2024-07-17 16:31:00' where
Oracle如何实现批量插入
INSERT INTO SELECT语句允许我们从另一个表或子查询中选择数据,并将其插入到指定表中。
-- 新建表
create table table_name as select * from source_table where condition
-- 批量插入表
insert into target_table select * from table_name;
INSERT ALL
INTO 表名 (表字段) values (数据1)
INTO 表名 (表字段) values (数据2)
SELECT * FROM DUAL
INSERT ALL
INTO NL_ACCT_INT_DETAIL (INTERNAL_KEY,INT_ACCRUED,CLIENT_NO) VALUES (12,'23.15','123456781')
INTO NL_ACCT_INT_DETAIL (INTERNAL_KEY,INT_ACCRUED,CLIENT_NO) VALUES (123,'24.15','123456782')
SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
insert into 表名 select * from 表名
insert into NL_ACCT_DEMO select * from NL_ACCT;
Oracle数据库中截取一段字符串并转换成数字
如果要截取身份证号,例如(只截取身份证号的一段)
select * from dual;
select substr(document_id,7,4) from dual; --substr是字符串
substr是截取字符串 如果需要转换成数字类型number
select * from RB_ACCT where TO_NUMBER(REGEXP_SUBSTR(document_id,^\d{6}{\d{4}},1,1,NULL,1)) between 1970 and 2000;
--这里用到了正则表达式:
^ 表示字符串的开始
\d+ 表示一个或多个数字字符
S 表示字符串的结束
\d{6} 匹配前6个字符 {\d{4}} 输出后四个字符
1,1:表示从当前字符输出,循环一遍
NULL
1:
这里查询一个较为复杂的场景:
截取身份证的出生日期且出生日期在1970-2000年之间的人群,判断当前的数据是否满足条件,并且身份证号对应唯一客户号,且没有限制 返回前25行
select * from
(select a.client_no,a.document_id,a.acct_name ROWNUM r
from RB_ACCT a
where a.acct_status = 'A'
and not exists
(select 1 from RB_RESTRAINTS b where a.internal_key = b.internal_key AND b.RESTRAINTS_STATUS = 'A')
and a.document_id is not null
AND length(a.document_id) = 18
AND REGEXP_LIKE(SUBSTR(a.document_id,7,4),'^\d+S')
AND REGEXP_SUBSTR(a.document_id,'^\d{6}{\d{4}}',1,1,NULL,1) BETWEEN 1970 AND 2000
GROUP BY a.client_no ,a.document_id ,a.acct_name having count(*) = 1)
r < 25;
Oracle中分页
Oracle中的分页ROWNUM、使用OFFSET和FETCH、使用ROW_NUMBER() OVER()
在Oracle中ROWNUM是一个伪劣,由于他返回的是一个行号,所以被用在select 查询中where条件里面作为筛选条件
select * from (select a.*,ROWNUM r from RB_ACCT a where ROWNUM <= 30) where r < 20;
这个sql的意思是:在RB_ACCT中查找到30条数据 并返回前面20条数据
OFFSET和FETCH是Oracle 12c引入的语法,它们可以更方便地实现分页查询。使用OFFSET和FETCH进行分页查询的方法是在SELECT语句中加入OFFSET和FETCH子句,例如:
SELECT *
FROM my_table
ORDER BY my_column
OFFSET 20 ROWS FETCH NEXT 10 ROWS ONLY;
上述查询语句的意思是对my_table表按照my_column列进行排序,然后取出从第21条记录开始的10条记录作为结果返回。使用OFFSET和FETCH进行分页查询的优点是简单方便,缺点是只有在Oracle 12c及以上版本中才能使用。
ROW_NUMBER() OVER()是Oracle中一种用于计算行号的函数。使用ROW_NUMBER() OVER()进行分页查询的方法是在SELECT语句中加入ROW_NUMBER() OVER()函数,并在WHERE子句中指定ROW_NUMBER() OVER()的取值范围,例如:
SELECT *
FROM (
SELECT a.*, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY my_column) r
FROM my_table a
)
WHERE r BETWEEN 21 AND 30;
上述查询语句的意思是对my_table表按照my_column列进行排序,然后取出第21到第30条记录作为结果返回。使用ROW_NUMBER() OVER()进行分页查询的优点是灵活性高,可以实现各种不同的分页方式,缺点是语法较为复杂。
Oracle分区
哈希分区(散列分区表)hash
说明:这类分区是在列值上使用散列算法,以确定将行放入那个分区中
Oracle分区优缺点:
优点:
- 可用性强
- 维护方便
- 均衡I/O
- 改善查询性能
缺点: - Hash分区







 本文详细介绍了SQL中的各种函数(如显示系统时间、计算百分比、排序等)、分组函数的使用、连接查询、子查询的不同类型,以及DML(数据操作语言)如插入、更新、删除,DDL(数据定义语言)如表结构管理,主键概念,TCL事务管理和Oracle数据库清理操作。
本文详细介绍了SQL中的各种函数(如显示系统时间、计算百分比、排序等)、分组函数的使用、连接查询、子查询的不同类型,以及DML(数据操作语言)如插入、更新、删除,DDL(数据定义语言)如表结构管理,主键概念,TCL事务管理和Oracle数据库清理操作。














 4470
4470

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








