多线程文件复制
一、TestCode
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#define THREADS_COUNT 3
#define THREADS_BUFF_SIZE 1*1024
struct thread_block
{
int infd; ///源文件句柄
int outfd;//目的文件句柄
size_t start;///文件的写入起始位置
size_t end; ///文件写入的终止位置
};
void usage()
{
printf("copy %%src %%dst\n");
}
///获取文件大小
size_t get_filesize(int fd)
{
struct stat st;
fstat(fd,&st);
return st.st_size;
}
void *thread_copy_fn(void *arg);
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc < 3)
{
usage();
return -1;
}
///打开文件
int infd = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
int outfd = open(argv[2],O_CREAT|O_WRONLY,0644);
// 0644也就是-文件所有者有读写权限,组有读权限,其他用户有读权限
if(infd == -1|| -1 ==outfd)
{
printf("error while open file \n");
return -1;
}
size_t file_size = get_filesize(infd);
size_t thread_size = THREADS_COUNT;
struct thread_block *blocks = (struct thread_block *)
malloc(sizeof(struct thread_block )* thread_size);
size_t percent = file_size / thread_size;
printf("filesize = %d\t percent_blocks = %d\n",\
file_size,percent);
int i = 0;
//init-thread-block
for(; i < thread_size;++i)
{
blocks[i].infd = infd;
blocks[i].outfd = outfd;
blocks[i].start = i * percent;
blocks[i].end = blocks[i].start + percent;
}
//the last thread
blocks[i].end = file_size;
pthread_t ptid[thread_size];
///创建线程
for(i = 0 ; i < thread_size; ++i)
{
pthread_create(&ptid[i],NULL,thread_copy_fn,&(blocks[i]));
}
///线程Join
for(i = 0 ; i < thread_size; ++i)
{
pthread_join(ptid[i],NULL);
}
///释放资源
free(blocks);
close(infd);
close(outfd);
printf("Copy Successfully \n");
return 0;
}
void *thread_copy_fn(void *arg)
{
struct thread_block *block = (struct thread_block *)arg;
char buf[THREADS_BUFF_SIZE];
int ret;
size_t count = block->start;
printf("In Thread\t%ld\nstart = %ld\t end = %ld\n",\
pthread_self(),block->start,block->end);
///lseek到同样的位置
ret = lseek(block->infd,block->start,SEEK_SET);
ret = lseek(block->outfd,block->start,SEEK_SET);
int bytes_read;
int bytes_write;
while(count < block->end)
{
bytes_read = read(block->infd,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(bytes_read >0)
{
printf("thread = %ld\t read = %ld\t count %d\n",\
pthread_self(),bytes_read,count);
count += bytes_read;
//read()返回-1,同时errno为EINTR,表示读的过程中遇到了中断
if((bytes_read == -1)&&(errno !=EINTR))
break;
char *ptr_write = buf;
while((bytes_write = write(block->outfd,ptr_write,bytes_read))!=0)
{
//write()会返回-1,同时errno为EINTR,表示在写的过程中遇到了中断
if((bytes_write == -1)&&(errno!=EINTR))
break;
if(bytes_write == bytes_read)
break;
else if(bytes_write > 0)
{
ptr_write += bytes_write;
bytes_read -= bytes_write;
}
printf("thread = %ld\t write = %ld\t read %d\n",\
pthread_self(),bytes_write,bytes_read);
}//end-write;
///error while write
if(bytes_write == -1)
break;
}
}
printf("#####Thread exit %ld#####\n",pthread_self());
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
二、知识点介绍
2.1. 文件的打开和关闭
2.1.1 open()函数 , open()函数的作用是打开文件, 其调用格式为:
int open(char *filename, int access);
该函数表示按access的要求打开名为filename的文件, 返回值为文件描述字
open()函数打开成功, 返回值就是文件描述字的值(非负值), 否则返回-1。
2.1.2 close()函数 , close()函数的作用是关闭由open()函数打开的文件, 其调用格式为:
int close(int handle);
该函数关闭文件描述字handle相连的文件。
2.2.读写函数
2.2.1 read()函数 ,read()函数的调用格式为:
int read(int handle, void *buf, int count);
read()函数从handle(文件描述字)相连的文件中, 读取count个字节放到buf所指的缓冲区中, 返回值为实际所读字节数, 返回-1表示出错。返回0 表示文件结束。
2.2.2 write()函数
write()函数的调用格式为:
int write(int handle, void *buf, int count);
write()函数把count个字节从buf指向的缓冲区写入与handle相连的文件中,返回值为实际写入的字节数
2.3.随机定位函数
lseek()函数 ,lseek()函数的调用格式为:
int lseek(int handle, long offset, int fromwhere);
该函数对与handle相连的文件位置指针进行定位, 功能和用法与fseek() 函数相同。
2.4 Linux struct stat介绍
struct stat这个结构体是用来描述一个linux系统文件系统中的文件属性的结构。讲文件传递给定义即可,通过结构体的方式访问里面的成员变量如大小、创建时间、、、、、。
eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
struct stat buf;
int result;
result = stat ("./test", &buf);
if (result != 0)
{
perror ("Failed ^_^");
}
else
{
//! 文件的大小,字节为单位
cout << "size of the file in bytes: " << buf.st_size << endl;
//! 文件创建的时间
cout << "time of creation of the file: " << ctime (&buf.st_ctime) << endl;
//! 最近一次修改的时间
cout << "time of last modification of the file: " << ctime (&buf.st_mtime) << endl;
//! 最近一次访问的时间
cout << "time of last access of the file: " << ctime (&buf.st_atime) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
测试结果:
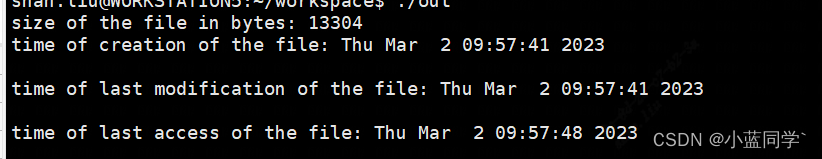
作者:流星
参考连接:http://blog.sina.com.cn/staratsky






















 270
270











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








