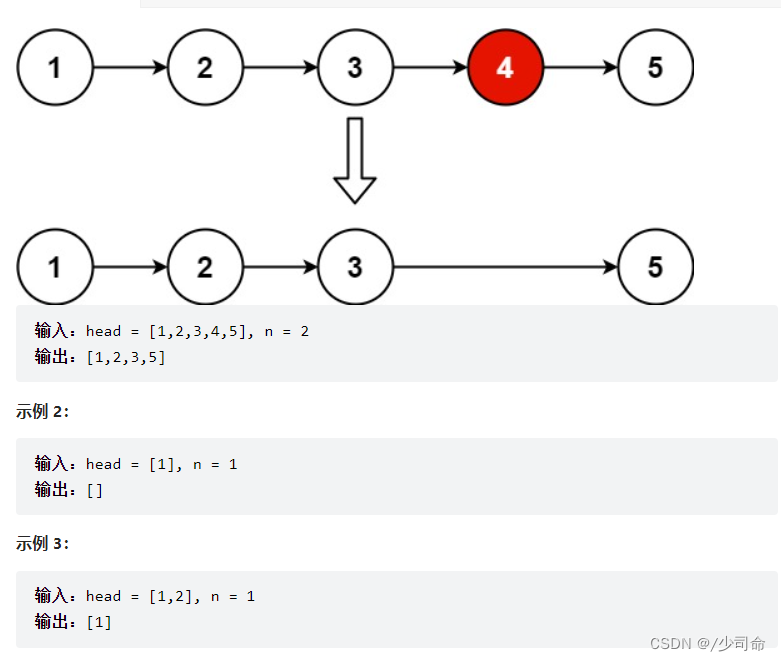
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0,head);
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
stack.pop();
}
ListNode prev = stack.peek();
prev.next = prev.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
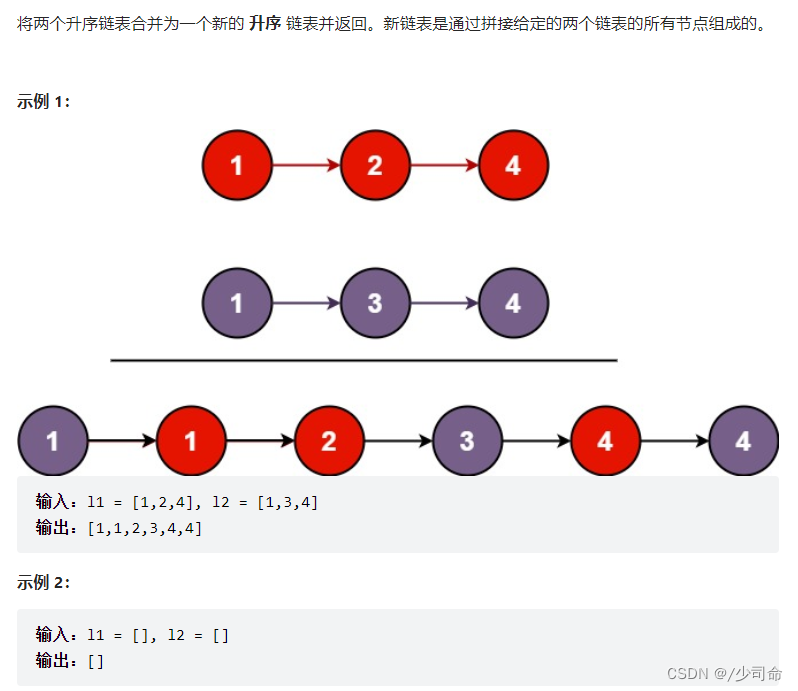
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null){
return list1;
}
if (list1.val < list2.val){
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}else {
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
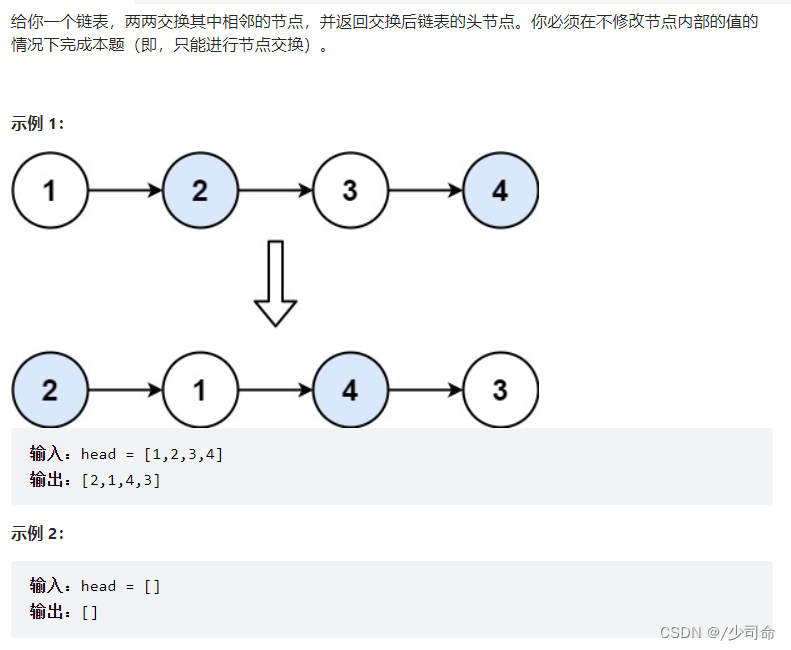
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0);
newHead.next = head;
ListNode tmp = newHead;
while (tmp.next != null && tmp.next.next != null){
ListNode node1 = tmp.next;
ListNode node2 = tmp.next.next;
tmp.next = node2;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
tmp = node1;
}
return newHead.next;
}
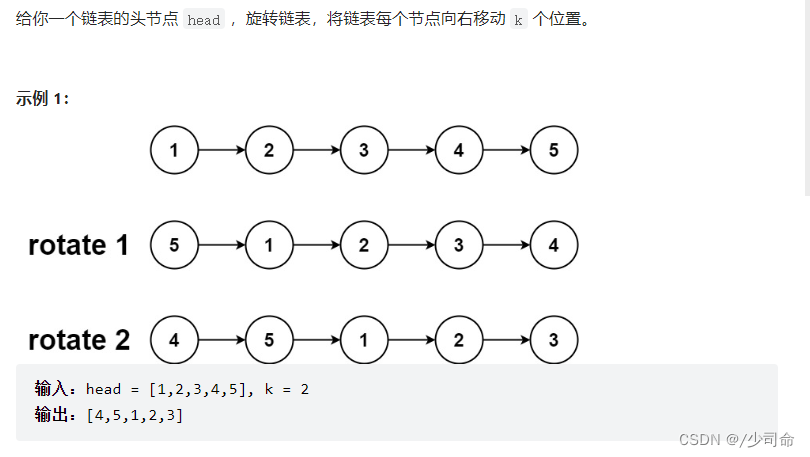
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null || k == 0){
return head;
}
int count = 1;
ListNode tmp = head;
while (tmp.next != null){
count++;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
k %= count;
if (k == 0){
return head;
}
//首尾相连
tmp.next = head;
for (int i = 0;









 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 1670
1670

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










