every() 方法用于检测数组所有元素是否都符合指定条件(通过函数提供)。
every() 方法使用指定函数检测数组中的所有元素:
如果数组中检测到有一个元素不满足,则整个表达式返回 false ,且剩余的元素不会再进行检测。
如果所有元素都满足条件,则返回 true。
注意: every() 不会对空数组进行检测。
注意: every() 不会改变原始数组。
isEvery:function(){
let a = [2,3,5,7,9]
let status = a.every(function(currentValue,index,arr){
console.log(currentValue) // 必须。当前元素的值
console.log(index) // 可选。当前元素的索引值
console.log(arr) // 可选。当前元素属于的数组对象
return currentValue >= 1 // 判断数组中是否所有值都大于等于1
})
console.log(status)
}
// currentValue:2
// index:0
// arr:2,3,5,7,9,
// currentValue:3
// index:1
// arr:2,3,5,7,9,
// currentValue:5
// index:2
// arr:2,3,5,7,9,
// currentValue:7
// index:3
// arr:2,3,5,7,9,
// currentValue:9
// index:4
// arr:2,3,5,7,9,
// status:true
every()参数说明
function(currentValue, index,arr){
// currentValue 必须。当前元素的值
// index 可选。当前元素的索引值
// arr 可选。当前元素属于的数组对象
// 布尔值。如果所有元素都通过检测返回 true,否则返回 false。
}
some()定义和用法
some() 方法用于检测数组中的元素是否满足指定条件(函数提供)。
some() 方法会依次执行数组的每个元素:
如果有一个元素满足条件,则表达式返回true , 剩余的元素不会再执行检测。
如果没有满足条件的元素,则返回false。
注意: some() 不会对空数组进行检测。
注意: some() 不会改变原始数组。
————————————————
isSome:function(){
let a = [2,3,5,7,9]
let status = a.some(function(currentValue,index,arr){
console.log(currentValue) // 必须。当前元素的值
console.log(index) // 可选。当前元素的索引值
console.log(arr) // 可选。当前元素属于的数组对象
return currentValue >= 1 // 判断数组中是否有值大于等于1
})
console.log(status)
}
// currentValue:2
// index:0
// arr:2,3,5,7,9
// true
some()参数说明
function(currentValue, index,arr){
// currentValue 必须。当前元素的值
// index 可选。当前元素的索引值
// arr 可选。当前元素属于的数组对象
// 布尔值。如果所有元素都通过检测返回 true,否则返回 false。
}every()和some()的主要区别
every()会对数组中的每一个元素,即currentValue进行匹配,只有全部满足条件才会返回true,而some()中,只需有一个currentValue满足条件即可返回true,后面的currentValue不会再进行比较
every()和some()的应用场景
如下图,有一个表格,运用every()和some()来判断选中的表格状态,当选中其中一条数据时,判断他的当前状态,当选择多条数据时判断他的当前状态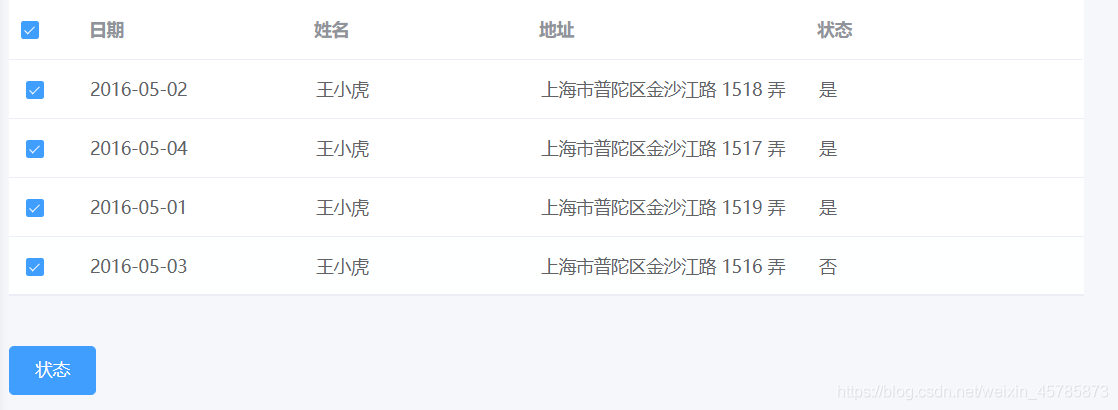
vue代码片段
data() {
return {
statusDes:''
}
},
methods:{
handleSelectionChange:function(val){
const statusList = [] //定义数组,保存每一项状态
val.forEach((item) =>{
// 遍历选择的项,把状态保存到数组
statusList.push(item.status)
})
// every()会遍历每一个状态,当全部满足条件时,才返回true
this.statusDes = statusList.every(this.isAllQuery)
// some()会遍历状态,只要一个满足,就返回true
// this.statusDes = statusList.some(this.isAllQuery)
},
// 过滤状态,即当状态显示:”是“时,返回true
isAllQuery(status){
return status === '是'
},
changes:function(){
if(this.statusDes){
this.$alert('是', '成功状态', { confirmButtonText: '确定', type: 'success' })
}else {
this.$alert('否', '失败状态', { confirmButtonText: '确定', type: 'warning' })
}
},
isTrue(value){
return value >=1
}
}
结果分析
every()全选,发现状态不同时:
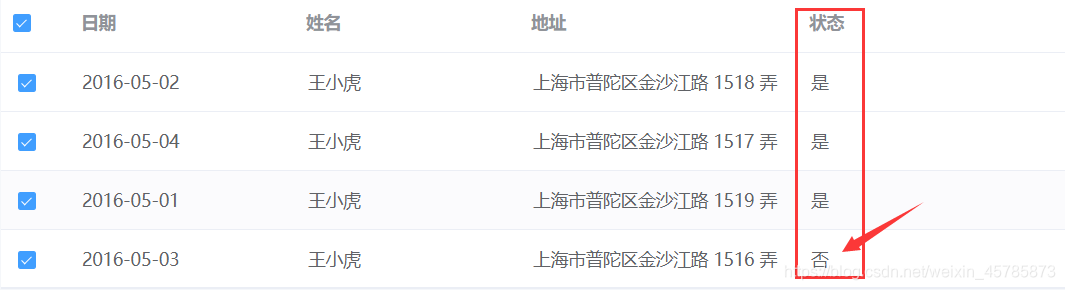

some()全选,发现状态不同时:





















 745
745











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








