使用java实现一棵二叉树,并使用他完成二叉树的层次遍历,两种中序遍历(递归 &非递归)
1、二叉树基本结构
public class BinaryTree {
BinaryTree left;
BinaryTree right;
Integer val;
public BinaryTree getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(BinaryTree left) {
this.left = left;
}
public BinaryTree getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(BinaryTree right) {
this.right = right;
}
public Integer getVal() {
return val;
}
public void setVal(Integer val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
2、二叉树层次遍历
首先将二叉树根节点放入到队列中,当队列不为空时,依次出队,并将出队的节点的左右孩子入队,再将该节点加入到结果集中
/**
* 二叉树层次遍历
* @param root
* @return
*/
public List<BinaryTree> levelOrder(BinaryTree root){
Queue<BinaryTree> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<BinaryTree> list = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
BinaryTree head = queue.poll();
if(head.getLeft() != null){
queue.offer(head.getLeft());
}
if(head.getRight() != null){
queue.offer(head.getRight());
}
list.add(head);
}
return list;
}
3、递归中序遍历
/**
* 二叉树递归中序遍历
* @param root
*/
public void midOrderRecur(BinaryTree root){
if (root == null){
return;
}
midOrderRecur(root.left);
System.out.print(root.getVal());
midOrderRecur(root.right);
}
4、非递归中序遍历
/**
* 二叉树中序遍历
* @param root
*/
public void midOrder(BinaryTree root){
BinaryTree current = root;
LinkedList<BinaryTree> list = new LinkedList<>();
while(current != null || !list.isEmpty()){
while(current != null){
list.addFirst(current);
current = current.left;
}
if(!list.isEmpty()){
current = list.removeFirst();
System.out.print(current.getVal());
current = current.right;
}
}
}
5、全部代码以及测试
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class BinaryTree {
BinaryTree left;
BinaryTree right;
Integer val;
/**
* 二叉树层次遍历
* @param root
* @return
*/
public List<BinaryTree> levelOrder(BinaryTree root){
Queue<BinaryTree> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<BinaryTree> list = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
BinaryTree head = queue.poll();
if(head.getLeft() != null){
queue.offer(head.getLeft());
}
if(head.getRight() != null){
queue.offer(head.getRight());
}
list.add(head);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 二叉树递归中序遍历
* @param root
*/
public void midOrderRecur(BinaryTree root){
if (root == null){
return;
}
midOrderRecur(root.left);
System.out.print(root.getVal());
midOrderRecur(root.right);
}
/**
* 二叉树中序遍历
* @param root
*/
public void midOrder(BinaryTree root){
BinaryTree current = root;
LinkedList<BinaryTree> list = new LinkedList<>();
while(current != null || !list.isEmpty()){
while(current != null){
list.addFirst(current);
current = current.left;
}
if(!list.isEmpty()){
current = list.removeFirst();
System.out.print(current.getVal());
current = current.right;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree node1 = new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree node2 = new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree node3 = new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree node4 = new BinaryTree();
node1.setVal(1);
node2.setVal(5);
node3.setVal(3);
node4.setVal(4);
node1.setLeft(node2);
node1.setRight(node3);
node2.setLeft(node4);
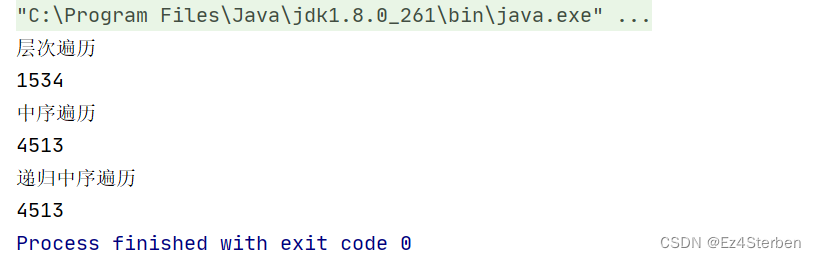
System.out.println("层次遍历");
List<BinaryTree> binaryTreeList = node1.levelOrder(node1);
for(BinaryTree binaryTree : binaryTreeList){
System.out.print(binaryTree.getVal());
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
node1.midOrder(node1);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("递归中序遍历");
node1.midOrderRecur(node1);
}
public BinaryTree getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(BinaryTree left) {
this.left = left;
}
public BinaryTree getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(BinaryTree right) {
this.right = right;
}
public Integer getVal() {
return val;
}
public void setVal(Integer val) {
this.val = val;
}
}






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








