一、为什么用SpringBoot
SpringBoot优点
-
创建独立Spring应用
-
内嵌web服务器
-
自动starter依赖,简化构建配置
-
自动配置Spring以及第三方功能
-
提供生产级别的监控、健康检查及外部化配置
-
无代码生成、无需编写XML
SpringBoot缺点
-
人称版本帝,迭代快,需要时刻关注变化
-
封装太深,内部原理复杂,不容易精通
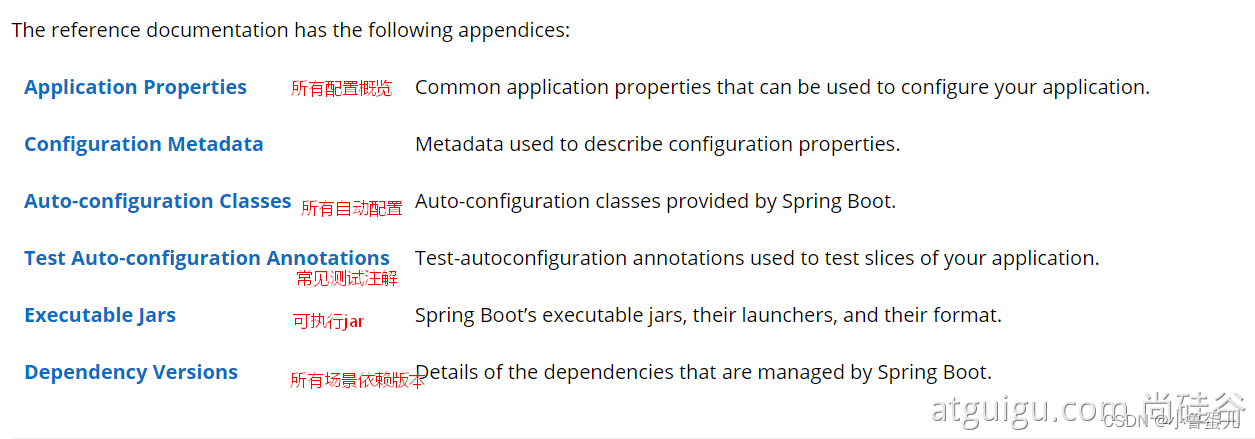
官网文档架构

二、入门
-
maven配置
给maven 的settings.xml配置文件的profiles标签添加
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>2、Spring Boot HelloWorld
实现功能:浏览发送/hello请求,响应 Hello,Spring Boot 2
引入依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>创建主程序类
/**
* 主程序类
* @SpringBootApplication:这是一个SpringBoot应用
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);
}
}编写业务
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(){
return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!";
}
}测试
直接运行main方法
简化配置
server.port=8888简化部署
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>把项目打成jar包,直接在目标服务器执行即可。
三、了解自动配置原理
-
依赖管理
1)父项目做依赖管理
依赖管理
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
它的父项目
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
几乎声明了所有开发中常用的依赖的版本号,自动版本仲裁机制2)开发导入starter场景启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>spring-boot-starter-web:帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件;
-
见到很多 spring-boot-starter-* : *就某种场景,Spring Boot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starters(启动器),只需要在项目里面引入这些starter,相关场景的所有依赖都会导入进来。要用什么功能就导入什么场景的启动器
-
SpringBoot所有支持的场景:支持场景
-
见到的 *-spring-boot-starter: 第三方为我们提供的简化开发的场景启动器。
-
所有场景启动器最底层的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>3)无需关注版本号,自动版本仲裁
-
引入依赖默认都可以不写版本
-
引入非版本仲裁的jar,要写版本号。
4)可以修改默认版本号
1、查看spring-boot-dependencies里面规定当前依赖的版本 用的 key。
2、在当前项目里面重写配置
<properties>
<mysql.version>5.1.43</mysql.version>
</properties>2、自动配置
1)自动配好Tomcat,引入了Tomcat依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>2)自动配好SpringMVC
-
引入SpringMVC全套组件
-
自动配好SpringMVC常用组件(功能)
3)自动配好Web常见功能,如:字符编码问题
SpringBoot帮我们配置好了所有web开发的常见场景
4)默认的包结构
-
主程序所在包及其下面的所有子包里面的组件都会被默认扫描进来,无需以前的包扫描配置
-
想要改变扫描路径,@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.atguigu")或者@ComponentScan 指定扫描路径
@SpringBootApplication
等同于
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.boot")5)各种配置拥有默认值
-
默认配置最终都是映射到某个类上,如:MultipartProperties
-
配置文件的值最终会绑定每个类上,这个类会在容器中创建对象
6)按需加载所有自动配置项
-
非常多的starter
-
引入了哪些场景这个场景的自动配置才会开启
-
SpringBoot所有的自动配置功能都在 spring-boot-autoconfigure 包里面
3、容器功能
3.1 组件添加
@Configuration
Full模式与Lite模式
-
配置类组件之间无依赖关系用Lite模式加速容器启动过程,减少判断
-
配置类组件之间有依赖关系,方法会被调用得到之前单实例组件,用Full模式
#############################Configuration使用示例######################################################
/**
* 1、配置类里面使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实例的
* 2、配置类本身也是组件
* 3、proxyBeanMethods:代理bean的方法
* Full(proxyBeanMethods = true)、【保证每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是单实例的】
* Lite(proxyBeanMethods = false)【每个@Bean方法被调用多少次返回的组件都是新创建的】
* 组件依赖必须使用Full模式默认。其他默认是Lite模式
*
*
*
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类 == 配置文件
public class MyConfig {
/**
* Full:外部无论对配置类中的这个组件注册方法调用多少次获取的都是之前注册容器中的单实例对象
* @return
*/
@Bean //给容器中添加组件。以方法名作为组件的id。返回类型就是组件类型。返回的值,就是组件在容器中的实例
public User user01(){
User zhangsan = new User("zhangsan", 18);
//user组件依赖了Pet组件
zhangsan.setPet(tomcatPet());
return zhangsan;
}
@Bean("tom")
public Pet tomcatPet(){
return new Pet("tomcat");
}
}
################################@Configuration测试代码如下########################################
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.boot")
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、返回我们IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
//2、查看容器里面的组件
String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
//3、从容器中获取组件
Pet tom01 = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
Pet tom02 = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
System.out.println("组件:"+(tom01 == tom02));
//4、com.atguigu.boot.config.MyConfig$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$51f1e1ca@1654a892
MyConfig bean = run.getBean(MyConfig.class);
System.out.println(bean);
//如果@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true)代理对象调用方法。SpringBoot总会检查这个组件是否在容器中有。
//保持组件单实例
User user = bean.user01();
User user1 = bean.user01();
System.out.println(user == user1);
User user01 = run.getBean("user01", User.class);
Pet tom = run.getBean("tom", Pet.class);
System.out.println("用户的宠物:"+(user01.getPet() == tom));
}
}@Bean、@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository
@ComponentScan、@Import
* @Import({User.class, DBHelper.class})
* 给容器中自动创建出这两个类型的组件、默认组件的名字就是全类名
*/
@Import({User.class, DBHelper.class})
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类 == 配置文件
public class MyConfig {
}@Conditional
@Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用)
作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
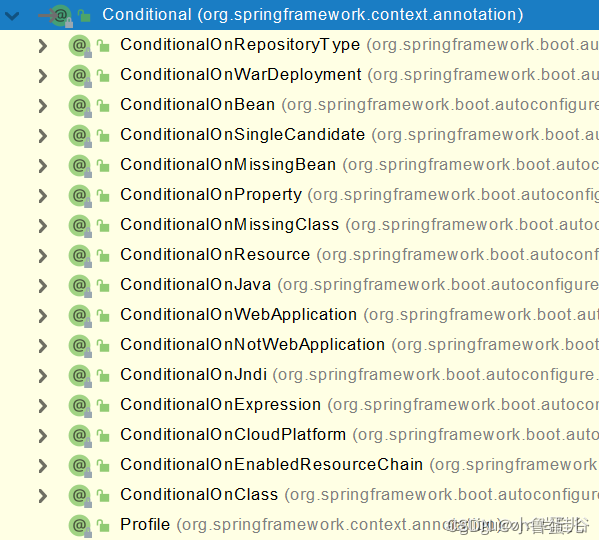
| @Conditional扩展注解 | 作用(判断是否满足当前指定条件) |
| @ConditionalOnJava | 系统的java版本是否符合要求 |
| @ConditionalOnBean | 容器中存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | 容器中不存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnExpression | 满足SpEL表达式指定 |
| @ConditionalOnClass | 系统中有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnBean | 容器中存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | 容器中不存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnExpression | 满足SpEL表达式指定 |
| @ConditionalOnClass | 系统中有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnBean | 容器中存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | 容器中不存在指定Bean; |
=====================测试条件装配==========================
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类 == 配置文件
//@ConditionalOnBean(name = "tom")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "tom")
public class MyConfig {
@Bean //给容器中添加组件。以方法名作为组件的id。返回类型就是组件类型。返回的值,就是组件在容器中的实例
public User user01(){
User zhangsan = new User("zhangsan", 18);
//user组件依赖了Pet组件
zhangsan.setPet(tomcatPet());
return zhangsan;
}
@Bean("tom22")
public Pet tomcatPet(){
return new Pet("tomcat");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、返回我们IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
//2、查看容器里面的组件
String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
boolean tom = run.containsBean("tom");
System.out.println("容器中Tom组件:"+tom);
boolean user01 = run.containsBean("user01");
System.out.println("容器中user01组件:"+user01);
boolean tom22 = run.containsBean("tom22");
System.out.println("容器中tom22组件:"+tom22);
}自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效;
我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效;
我们可以通过启用 debug=true属性;来让控制台打印自动配置报告,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置类生效;
=========================
AUTO-CONFIGURATION REPORT
=========================
Positive matches:(自动配置类启用的)
-----------------
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnClass found required class 'org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet'; @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class (OnClassCondition)
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication (required) found StandardServletEnvironment (OnWebApplicationCondition)
Negative matches:(没有启动,没有匹配成功的自动配置类)
-----------------
ActiveMQAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required classes 'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory', 'org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory' (OnClassCondition)
AopAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required classes 'org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect', 'org.aspectj.lang.reflect.Advice' (OnClassCondition)3.2 原生配置文件引入
@ImportResource
======================beans.xml=========================
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="haha" class="com.atguigu.boot.bean.User">
<property name="name" value="zhangsan"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="hehe" class="com.atguigu.boot.bean.Pet">
<property name="name" value="tomcat"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
@ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml")
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {}
======================测试=================
boolean haha = run.containsBean("haha");
boolean hehe = run.containsBean("hehe");
System.out.println("haha:"+haha);//true
System.out.println("hehe:"+hehe);//true3.3 配置绑定
如何使用Java读取到properties文件中的内容,并且把它封装到JavaBean中,以供随时使用;
public class getProperties {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
Properties pps = new Properties();
pps.load(new FileInputStream("a.properties"));
Enumeration enum1 = pps.propertyNames();//得到配置文件的名字
while(enum1.hasMoreElements()) {
String strKey = (String) enum1.nextElement();
String strValue = pps.getProperty(strKey);
System.out.println(strKey + "=" + strValue);
//封装到JavaBean。
}
}
}@Component + @ConfigurationProperties
/**
* 只有在容器中的组件,才会拥有SpringBoot提供的强大功能
*/
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Integer price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}@EnableConfigurationProperties + @ConfigurationProperties
==============================配置类====================================
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)
// 开启 Car 的配置绑定功能,开启后 Car 类中就可以不用写 @Component
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
}
==============================Car类=======================================
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
}4、自动配置原理入门
4.1 引导加载自动配置类
@SpringBootApplication:标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类,SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
}1)@SpringBootConfiguration:Spring Boot的配置类,标注在某个类上,表示这是一个Spring Boot的配置类;
-
@Configuration:配置类上来标注这个注解;
配置类 ----- 配置文件;配置类也是容器中的一个组件;@Component
2)@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能;
以前我们需要配置的东西,Spring Boot帮我们自动配置;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能;这样自动配置才能生效;
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
}@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包,将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication标注的类)的所在包及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器;
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) //给容器中导入一个组件
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}
// 利用Registrar给容器中导入一系列组件,将指定的一个包下的所有组件导入进来@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):
可以查看selectImports()方法的内容;
-
利用getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);给容器中批量导入一些组件
-
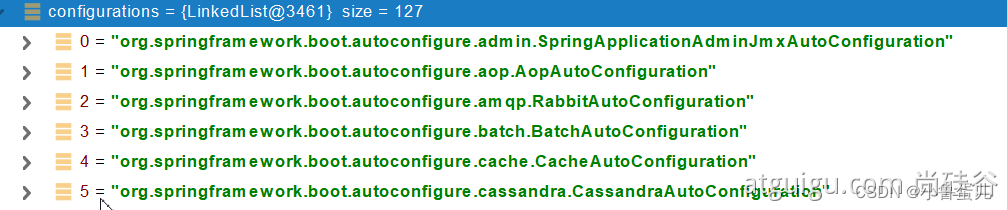
调用List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)获取到所有需要导入到容器中的配置类
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()
扫描所有jar包类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories
把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象
从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中
将类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中;
文件里面写死了spring-boot一启动就要给容器中加载的所有配置类
spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar/META-INF/spring.factories
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
每一个这样的 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能;
4.2 按需开启自动配置项
虽然我们127个场景的所有自动配置启动的时候默认全部加载。xxxxAutoConfiguration
按照条件装配规则(@Conditional),最终会按需配置。
以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理;
//表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
//将配置文件中对应的值和HttpProperties绑定起来,并把HttpEncodingProperties加入到ioc容器中
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpProperties.class)
//Spring底层@Conditional注解,根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效;
//判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET)
//判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter,SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;
//如果有,当前配置类生效
@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class)
//判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.http.encoding.enabled;如果不存在,判断也是成立的
//即使我们配置文件中不配置spring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
//他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了
private final HttpProperties.Encoding properties;
//只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Bean
//容器中没有这个组件,SpringBoot添加默认的组件
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class)
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http")
public class HttpProperties {
public static class Encoding {
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
private Charset charset = DEFAULT_CHARSET;
private Boolean force;
private Boolean forceRequest;
private Boolean forceResponse;
private Map<Locale, Charset> mapping;
}
}所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装着;配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效?
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
4.3 修改默认配置
@Bean //@Bean标注的方法传入了对象参数,这个参数的值就会从容器中找。
//容器中有这个MultipartResolver组件,但是名字不为 multipartResolve
//则给容器中添加该组件
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
//SpringMVC multipartResolver。防止有些用户配置的文件上传解析器名字不符合规范
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
给容器中加入了文件上传解析器;SpringBoot默认会在底层配好所有的组件,但是如果用户自己配置了以用户的优先。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
}总结:
-
SpringBoot先加载所有的自动配置类 xxxxxAutoConfiguration
-
每个自动配置类按照条件进行生效,给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从xxxProperties类中获取某些属性,我们可以在配置文件中指定这些属性的值,xxxProperties和配置文件进行了绑定
-
生效的配置类就会给容器中装配很多组件
-
只要容器中有这些组件,相当于这些功能就有了
-
定制化配置
-
用户直接自己@Bean替换底层的组件
-
用户去看这个组件是获取的配置文件什么值就去修改。
xxxxxAutoConfiguration ---> 组件 ---> xxxxProperties里面拿值 ----> application.properties
四、开发小技巧
1、Lombok
简化JavaBean开发
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
idea中搜索安装lombok插件
===============================简化JavaBean开发===================================
@NoArgsConstructor
//@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
public User(String name,Integer age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
================================简化日志开发===================================
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(@RequestParam("name") String name){
log.info("请求进来了....");
return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!"+"你好:"+name;
}
}2、dev-tools
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>项目或者页面修改以后:Ctrl+F9;
3、Spring Initailizr(项目初始化向导)
选择我们需要的开发场景

自动依赖引入
自动创建项目结构

自动编写好主配置类
参考文章:






















 3896
3896











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








