map的使用
简介:map是C++的STL中最常用的容器之一,他对于算法题的在算法题与工程项目中的贡献难以替代,本文旨在快速让读者入门map的使用,附带英文解说。
map/multimap的基本概念(它们都是同一个头文件)

注意:Python里面的字典就是这么造出来的.
insert函数仔细看,里面的参数是pair,然后通过输出可以看出,元素按照对组的key值进行排序,也就是first值。
multimap除了允许重复的key值以外其他的和map一样
Note: This is how the dictionary in Python is made
If you look at the insert function carefully, the parameters in it are "pair". Then you can see from the output that the elements are sorted according to the key value of the group, that is the "first" value.
multimap is the same as map except for duplicate key values
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
/* map container construction and assignment*/
void PrintMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
// Create map container
// Default construction
map<int, int>m;
m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 10));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 120));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 100));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 400));
cout << "m: " << endl;
PrintMap(m);
cout << endl;
// Copy construction
map<int, int>m2(m);
cout << "m2: " << endl;
PrintMap(m2);
cout << endl;
// Assignment
map<int, int>m3;
m3 = m2;
cout << "m3: " << endl;
PrintMap(m3);
}
void test02()
{
multimap<int, string>mm;
mm.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "刘备"));
mm.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "小明"));
mm.insert(pair<int, string>(5, "宋神宗"));
mm.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "李斯"));
mm.insert(pair<int, string>(8, "曹操"));
mm.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "路飞"));
cout << "mm: " << endl;
for (multimap<int, string>::iterator it = mm.begin(); it != mm.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
cout << endl << "---------------------" << endl;
test02();
return 0;
}
运行结果:

map大小和交换

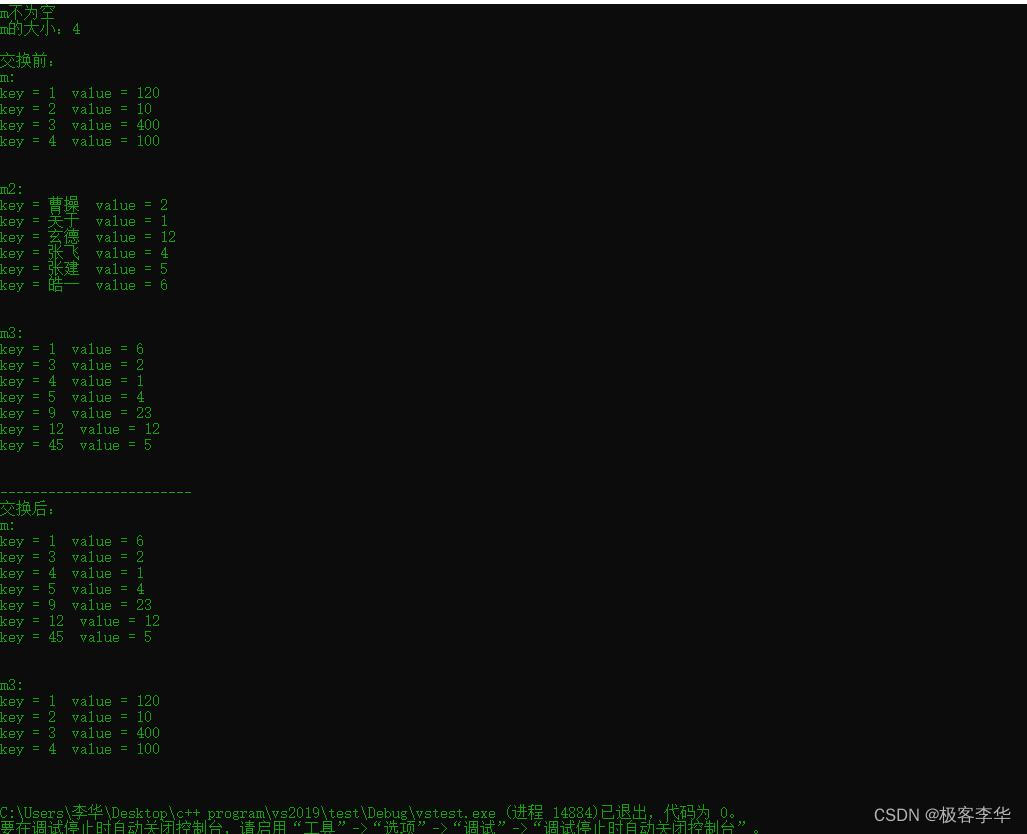
注意:swap函数目前来看只支持相同数据类型的集合之间的交换
Note: at present, swap function only supports exchange between sets of the same data type
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
/* map container size and swap*/
void PrintMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void PrintMap(map<string, int>& m)
{
for (map<string, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
// Create map container
map<int, int>m;
m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 10));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 120));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 100));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 400));
if (m.empty())
{
cout << "m为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "m不为空" << endl;
cout << "m的大小:" << m.size() << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "交换前: " << endl;
cout << "m: " << endl;
PrintMap(m);
cout << endl;
map<string, int>m2;
m2.insert(pair<string, int>("玄德", 12));
m2.insert(pair<string, int>("玄德", 23));
m2.insert(pair<string, int>("张飞", 4));
m2.insert(pair<string, int>("关于", 1));
m2.insert(pair<string, int>("曹操", 2));
m2.insert(pair<string, int>("张建", 5));
m2.insert(pair<string, int>("皓一", 6));
// string 字符串如果是中文的话,应该是按照汉字的编码表来排序的,但是汉字的编码表不止一张,这些之后再讨论
cout << "m2: " << endl;
PrintMap(m2);
cout << endl;
map<int, int>m3;
m3.insert(pair<int, int>(12, 12));
m3.insert(pair<int, int>(9, 23));
m3.insert(pair<int, int>(5, 4));
m3.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 1));
m3.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 2));
m3.insert(pair<int, int>(45, 5));
m3.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 6));
cout << "m3: " << endl;
PrintMap(m3);
cout << endl;
cout << "------------------------" << endl;
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
// m.swap(m2); // 这里可以看见, swap函数只支持相同类型的map容器之间的交换
m.swap(m3);
cout << "m: " << endl;
PrintMap(m);
cout << endl;
cout << "m3: " << endl;
PrintMap(m3);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
map插入和删除

注意:第三种插入方式太长不建议使用,第四种方式虽然看起来简短但是也不建议使用,这个括号[]的目的不是用来设置元素的,用于设置元素的话,容易导致混乱,后面的一个例子会说明。
[]主要是用来访问的,当我们确定这个key的值的时候我们就可以通过key来访问,key对应的值。
Note: the third insertion method is too long and is not recommend. Although the fourth insertion method looks short, it is not recommended. The purpose of this [] is not to set
elements. If it is used to set elements, it will easily lead to confusion. A later example will illustrate.
When we determine the value of the key, we can access the corresponding value of the key through the key.
第一种情况:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
/* map container insertion and deletion*/
void PrintMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
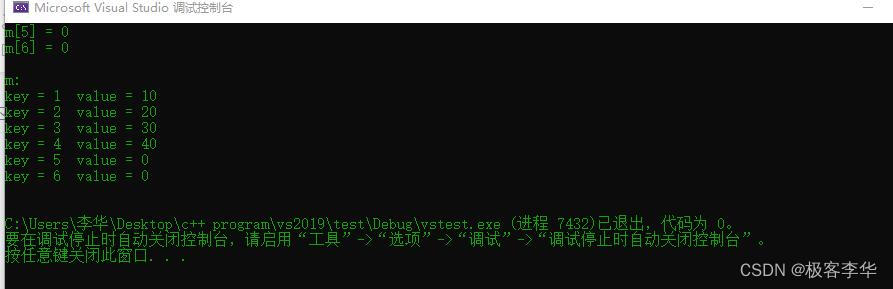
void test01()
{
// Create map container
map<int, int>m;
// insert
// The first method
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
// The second method
m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
// The third method
m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30));
// The fourth mathod
m[4] = 40;
cout << "m[5] = ";
cout << m[5] << endl;
cout << "m[6] = ";
cout << m[6] << endl;
// 这两处位置就体现了一个问题,明明在插入的时候没有插入m[5], m[6]但是在打印的时候这两个却可以打印出来
// 而且后面的PrintMap也将这个两个打印出来了
// 这里要说明的是如果没有插入m[n],是可以输出这个m[n]的,但是它的值为0
cout << endl << "m: " << endl;
PrintMap(m);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
第二种情况:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
/* map container insertion and deletion*/
void PrintMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
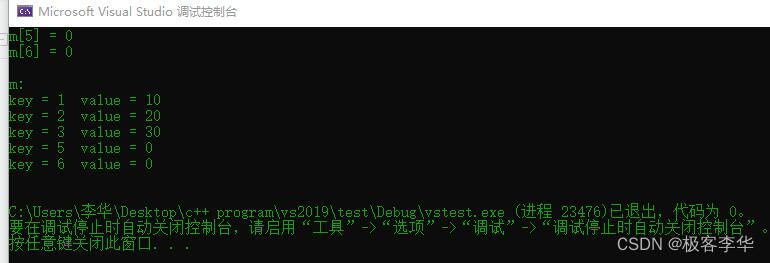
void test01()
{
// Create map container
map<int, int>m;
// insert
// The first method
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
// The second method
m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
// The third method
m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30));
// The fourth mathod
// m[4] = 40; 把这里的m[4]给注释了之后,在这个容器中就没有了这个值,然后打印的时候就不会出现这个值
// 及时是PrintMap的打印,这一体现出了map容器的元素的存储在空间上也不是连续的
cout << "m[5] = ";
cout << m[5] << endl;
cout << "m[6] = ";
cout << m[6] << endl;
// 这两处位置就体现了一个问题,明明在插入的时候没有插入m[5], m[6]但是在打印的时候这两个却可以打印出来
// 而且后面的PrintMap也将这个两个打印出来了
// 这里要说明的是如果没有插入m[n],是可以输出这个m[n]的,但是它的值为0
cout << endl << "m: " << endl;
PrintMap(m);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
/* map container insertion and deletion*/
void PrintMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
// Create map container
map<int, int>m;
// insert
// The first method
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
// The second method
m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
// The third method
m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30));
// The fourth mathod
m[4] = 40;
// []不建议插入,用途 可以利用key访问到value
// cout << m[4]<< endl;
cout << endl << "m: " << endl;
PrintMap(m);
cout << endl;
// erase
m.erase(m.begin()); // Through iterator
cout << endl << "m: " << endl;
PrintMap(m);
cout << endl;
m.erase(3); // Through value
cout << endl << "m: " << endl;
PrintMap(m);
cout << endl;
m.erase(m.begin(), m.end()); // 等价于m.clear();
cout << endl << "m: " << endl;
PrintMap(m);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
运行结果:

map查找和统计

注意:find返回的迭代器,不是具体位置,将find的结果打印出来的话就是这个值。
在map中count就只有0或者1,multimap允许重复key值里面有多种结果。
Note: the iterator returned by find function is not the specific location. If the result of find function is printed out, it is this value.
In map, count is only 0 or 1, and multimap allows mulitimap results in repeated key values.
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
/* map container find and count*/
void PrintMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
// Create map container
map<int, int>m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 10));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));
m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30));
m[4] = 40;
m[4] = 40;
m[4] = 40;
m[4] = 40;
map<int, int>::iterator pos = m.find(2);
if (pos != m.end())
{
cout << "找到这个元素 key = " << pos->first << " value = "<< pos->second <<endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到这个元素" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
int num = m.count(4);
// num = 1, map 不允许插入重复的元素
cout << "num = " << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
运行结果:

总结:

map容器排序
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
/* map sort*/
class Mycmp // 这个就是仿函数
{
public:
bool operator()(int m1, int m2) const
{
// 降序
return m1 > m2;
}
};
void PrintMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
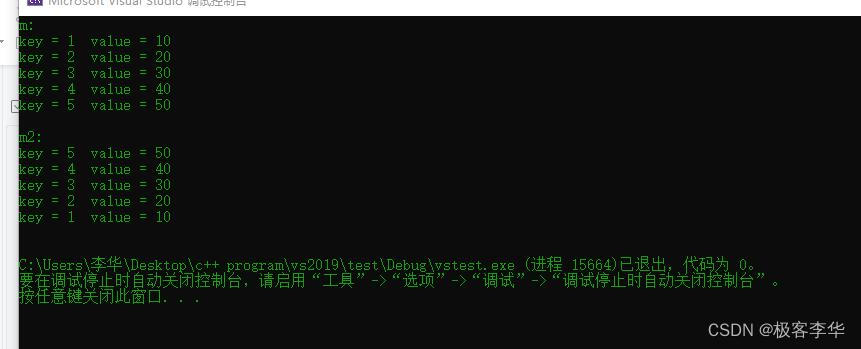
void test01()
{
// Create map container
map<int, int>m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 10));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 30));
m.insert(make_pair(4, 40));
m.insert(make_pair(5, 50));
cout << "m: " << endl;
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
map<int, int, Mycmp>m2; // 仿函数必须在定义的时候使用,已经定义好了的,排序规则不可 // 改变
m2.insert(make_pair(1, 10));
m2.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
m2.insert(make_pair(3, 30));
m2.insert(make_pair(4, 40));
m2.insert(make_pair(5, 50));
cout << "m2: " << endl;
for (map<int, int, Mycmp>::iterator it = m2.begin(); it != m2.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
如果大家觉得有用的话,可以关注我下面的微信公众号,极客李华,我会在里面更新更多行业资讯,企业面试内容,编程资源,如何写出可以让大厂面试官眼前一亮的简历等内容,让大家更好学习编程,我的抖音,B站也叫极客李华。大家喜欢也可以关注一下
如果大家觉得有用的话,可以关注我下面的微信公众号,极客李华,我会在里面更新更多行业资讯,企业面试内容,编程资源,如何写出可以让大厂面试官眼前一亮的简历等内容,让大家更好学习编程,我的抖音,B站也叫极客李华。大家喜欢也可以关注一下
























 3043
3043











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










