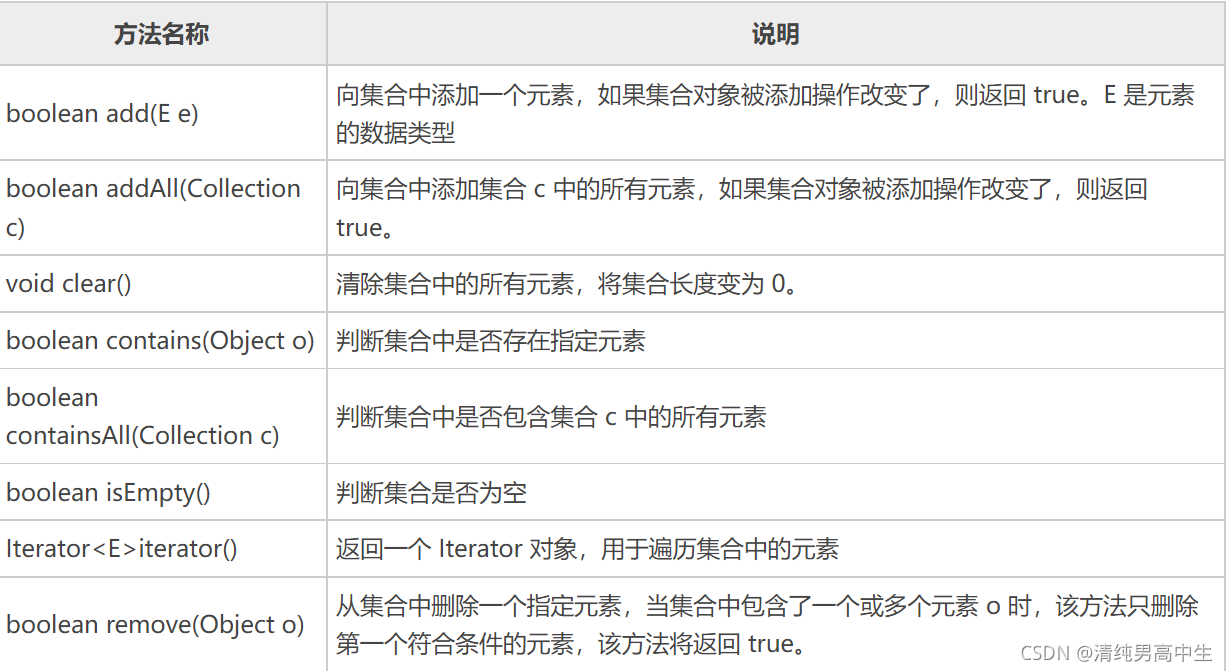
Collection接口
接口方法:

ArrayList:
底层基于数组实现,实现了长度可变的数组,其最大特点是内存空间连续,优点是遍历元素和随机访问效率比较高;
1,ArrayList特点:
①数据是插入有序的
②数据是可以重复的
③可以存储null
④底层数据结构是数组
⑤可以动态扩容的,默认容量是10
⑥扩容是按照原大小的1.5倍进行扩容
2,基本方法应用:
ArrayList <Integer> a = new ArrayList <Integer>();
a.add(1);
a.add(2);
a.add(3);
ArrayList <Integer> b = new ArrayList <Integer>();
b.add(3);
b.add(4);
b.add(5);
//并集:获取两个集合中所有元素
a.addAll(b);
//交集:获取两个集合中相同的元素
a.retainAll(b);
//差集:a与b的差集,即我有你没有的
a.removeAll(b);
3,ArrayList的源码实现
(1),继承关系:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
ArrayList继承自AbstractList,AbstractList类是抽象类实现自List接口,对接口中通用的方法做了实现,子类可以不用实现,子类如果有特殊需求可以重写对应方法
ArrayList实现接口List、RandomAccess、Cloneable、Serializable
List接口是ArrayList、Linkedlist的接口,定义了集合中大部分方法
RandomAccess接口表明当前类可以随机访问
Cloneable接口表明当前类是可以被克隆
Serializable接口表明当前类是可以支持序列化和反序列化
(2),构造函数:
//通过初始容量参数来实例化ArrayList
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
//参数校验
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);
//创建指定大小的数组实例
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
//无参构造函数
public ArrayList() {
super();
//给定空的数组
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
//通过集合实例来实例化ArrayList
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
//完成数据拷贝
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
(4),属性信息:
/存储元素位置
private transient Object[] elementData;
//存储元素个数
private int size;
//父类提供的属性 记录集合数据变更版本值(新增、修改、删除) ,和业务无关
private int modcount 修改版本号
//通过elementData属性了解:ArrayList底层数据存储在数组中
(5),默认值或默认属性:
//默认的数组初始容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
//空数组实例
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
(6)底层数据结构:
数组
(7),扩容机制:
//扩容大小
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
Arraylist集合扩容时按照1.5倍进行扩容
(8),常用方法研究:
add(E e)
1、如果存储数组为空,获取默认的大小值是10
2、如果需要大小超过数组大小、考虑扩容,按照原数组大小的1.5倍扩容
3、通过创建新数组,将元素组大小拷贝到新数组中
4、将新增元素插入最后的size位置并对size进行加1操作
public boolean add(E e){
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//将新增元素插入elementData数组中
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//当数组为空时,获取当前容量值
if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
//当无参构造的实例时,第一次会进入该方法
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
//数据空间不足,考虑扩容
if (minCapacity > elementData.length )
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//扩容大小
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//扩容范围的限制
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
//创建新的指定大小的集合,将原有数据拷贝到新数组中
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
public void add(int index, E element)
//添加数据;在指定位置添加数据,需要保证index合法,并将index之后的数据后移一位,然后插入新值
get(int index)
public E get(int index) {
//检查下标的合法性 0<= index <size
rangeCheck(index);
//通过下标指定位置来获取数据
return elementData(index);
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
remove(Object o) 删除
remove(int index) 删除
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
//元素为空时
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
//不为空
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//将index后续的数据前移一位
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
4,ArrayList和数组区别:
1、ArrayList底层封装数组,提供了丰富API操作
2、存储数据:ArrayList存储的是自定义对象,基本包装类型 数组可以存放自定义类型,包装类型、基类类型(int)
3、ArrayList是可以自动扩容的 ,数组不能自动扩容
5,ArrayList应用场景:
在查询操作的时间复杂度O(1),对于数据操作时间复杂度是O(n),ArrayList的适用于多查询、修改较少的业务场景
迭代器:
1,迭代器是行为型设计模式
提供了一种方法来遍历一个聚合的容器(集合)中的各个元素,而不用暴露其内部的表示。对于容器的访问而不需要关注容器内部的实现细节,可以使用迭代器,需要具备功能:
1、能够便利的访问一个聚合容器
2、不需要了解聚合容器的内部结构
3、能够提供多种不同的遍历方式
2,在Java中需要使用的迭代器遍历的容器需要实现Iterable接口,
Iterable接口中声明如下:
public interface Iterable<T> {
Iterator<T> iterator();
}
该接口中声明了iterator()方法,要使用迭代器类需要实现Iterable接口,即实现iterator方法,返回的是Iterator实现类
Iterator本身是一个接口,该接口声明如下:
//迭代器返回实例Iterator的实现类
public interface Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext(); //判断集合中是否还有下一个元素 true:集合还有元素 false:集合中没有元素
E next();//返回当前的一个元素,每调用一次集合元素会移动一位 (注意:hasNext和next需要依次循环调用)
void remove(); //删除容器元素
}
迭代器访问容器Demo:
ArrayList <Integer> a = new ArrayList <Integer>();
a.add(1);
a.add(2);
a.add(3);
//获取迭代器实例
Iterator <Integer> iterator1 = a.iterator();
//首先判断容器是否还有元素hasNext
while (iterator1.hasNext()) {
//获取当前的元素next()
Integer value = iterator1.next();
System.out.println(value);
}
3,在ArrayList中迭代器的遍历该如何实现?
ArrayList集合中使用数组作为存储数据结构,迭代器来遍历ArrayList本质上来遍历数组,
arraylist中存储数据个数size ,假如当前索引index
hasnext(); => index<size;
next(); =>elementData[index] ;index++;
ArrayList中迭代器的源码实现:
// iterator()是Iterable接口提供的方法,而ArrayList是Iterable接口实现类,因此具有iterator方法
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
//Itr类是Iterator接口的实现类
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // 返回下一个元素的位置
int lastRet = -1; // 上一个位置,即cursor前一个位置
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
//判断索引位置不是size,即还没有到尾部
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
//校验modCount属性
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
//校验modCount属性
checkForComodification();
try {
//调用的是ArrayList中提供的删除方法
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
4,自定义的集合中实现迭代器的要点:
1、自定义集合必须实现Iterable接口
2、自定义一个迭代器的内部类,该类实现Iterator接口
3、迭代器的内部类分别实现 hasNext()、next()、remove()方法
4、自定义集合类中iterator()方法中实现创建迭代器的内部类实例
5,ConcurrentModificationException异常排查
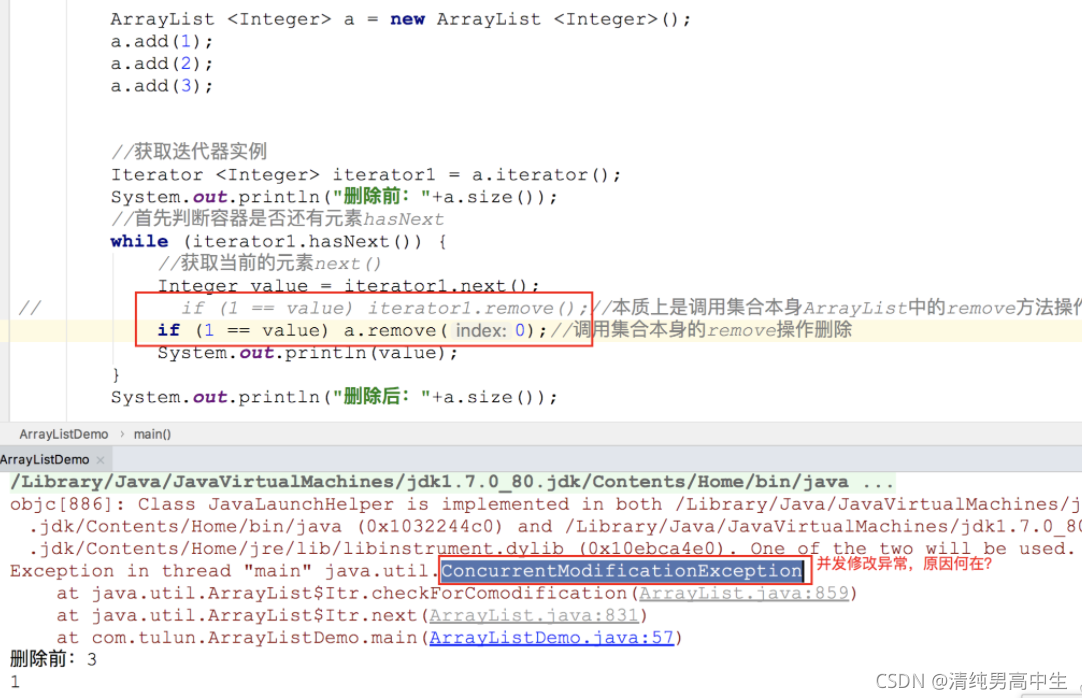
调用集合本身的remove操作(集合变更)会发生ConcurrentModificationException异常,而调用迭代器中的remove操作不会发生异常,根本原因在于迭代器中的变量expectedModCount和集合中的modcount的值不一致引起的,
expectModCount是迭代器的内部属性,在迭代器实例化时将当前的集合的modcount值赋值给expectModCount,后续当中的next操作和remove操作都会检测expectModCount和modcount是否一致,当调用迭代器的remove操作,会引起modcount值发生改变,这个改变在迭代器的remove方法中同步给expectModCount让其保持一致,不会抛出异常,而直接调用集合本身的remove操作会引起modcount的修改,而修改是不会同步给expectModCount,会导致expectModCount和ModCount值不一致抛出异常。
主要是考虑线程并发问题,一个线程对集合进行遍历的同时,另一个线程对集合做修改,集合对modcount等版本号做判断,如果不同,说明存在线程并发操作集合的问题,会直接抛出异常,不在进行后续处理,这个也是Fast-fair机制:快速失败机制。
6,ListIterator迭代器特点
ListIterator迭代器是Iterator的子接口,只适用于List接口下的实现类
具有Itreator接口的方法,能够实现集合从前往后遍历还具有其他特点:
1、可以对集合实现从后往前遍历
2、提供特有方法:获取当前索引位置、修改集合元素、对集合添加元素
public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext();
E next();
boolean hasPrevious();//判断前一个是否存在
E previous();//获取前一个值
int nextIndex();
int previousIndex();
void remove();
void set(E e);
void add(E e);
}
利用ListIterator实现反向输出:
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList=new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(8);
arrayList.add(9);
ListIterator<Integer> listIterator=arrayList.listIterator(arrayList.size());
//将arrayList移动到最后一位,直接开始是从第一位开始的,hasPrevious判断为flase
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(listIterator.previous());
}
LinkedList接口:
底层基于双向链表实现,其最大特点是内存空间不连续,其中元素允许为null,优点是增加元素和删除元素效率比较高;
LinkedList类是双向列表,列表中的每个节点都包含了对前一个和后一个元素的引用.
1,LinkedList接口特点:
1、数据插入有序
2、数据可重复
3、可以存储null
4、底层数据结构是链表
2,特有方法:
LinkedList是List接口的试下实现类,具有List接口提供的所有方法
还提供了一些额外方法,LinkedList实现了Deque接口,提供方法如下:
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> {
void addFirst(E e); //将元素添加在队列第一个位置
void addLast(E e); //将元素添加到最后位置
boolean offerFirst(E e); //将元素添加在队列第一个位置
boolean offerLast(E e);//将元素添加到最后位置
E removeFirst(); //删第一个
E removeLast(); //删最后一个
E pollFirst(); //删除
E pollLast(); //删除
E getFirst();
E getLast();
E peekFirst(); //获取第一个
E peekLast(); //获取最后一个
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);
boolean add(E e);
boolean offer(E e);
E remove();
E poll();
E element();
E peek();
void push(E e);
E pop();
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean contains(Object o);
public int size();
Iterator<E> iterator();
Iterator<E> descendingIterator();
}
3,LinkedList接口的源码实现:
(1)继承关系:
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
继承自AbstractSequentialList,该类对通用方法做了实现,linkedlist可以直接继承使用
实现接口:List、Deque、Cloneable、Serializable
Deque接口是队列的接口,提供了队列相应的方法
(2),构造函数
//无参构造函数
public LinkedList() {
}
//有参构造 通过Collection集合实现类来实例化LinkedList
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
(3),属性:
//集合中数据个数
transient int size = 0;
//头结点
transient Node<E> first;
//尾节点
transient Node<E> last;
//Node的声明如下:
private static class Node<E> {
E item; //存储元素
Node<E> next; //下一个
Node<E> prev; //上一份元素位置
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
通过Node可知:LinkedList底层实现的数据结构是双向链表
(4),常用方法:
//插入节点
public boolean add(E e) {
//调用尾插法插入数据
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
//集合插入第一个节点时,first和last都为null,就将当前节点作为头节点
first = newNode;
else
//当原last节点存在时,原last的next指针指向当前新的节点
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
ArrayList和LinkedList区别:
①ArrayList基于动态数组,LinkedList基于链表。
②对于增加元素和删除元素LinkedList效率比较高,因为ArrayList要移动元素。
③对于遍历元素和随机访问ArrarList效率比较高,因为LinkedList要移动指针。
Vector实现类
底层是数据,是线程安全的(synchronized)重量级锁





















 2158
2158











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








