多线程
1、概念

调度器:cpu
2、线程创建
三种创建方式 Callable在工作的时候用的多,现在只做了解
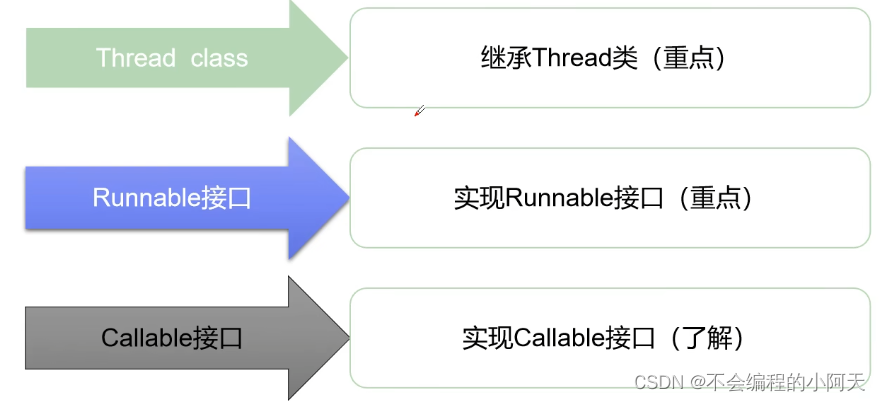
2.1、第一种创建方法 Thread
- 自定义线程类继承Thread类
- 重写run()方法,编写线程执行体
- 创建线程对象,调用start()方法启动线程
注意:线程不一定立即执行,CPU安排调度
//创建线程方式一:继承Thread类,重写run()方法,调用start开启线程
//总结:注意,线程开启不一定立即执行,由CPU调度执行
public class Testhead1 extends Thread{
public void run(){
//run方法线程体
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("我在看代码---"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//main线程 主线程
Thread thread = new Testhead1();
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("我在学习多线程---"+i);
}
}
}
运行结果为
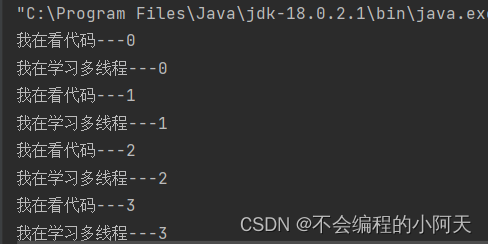
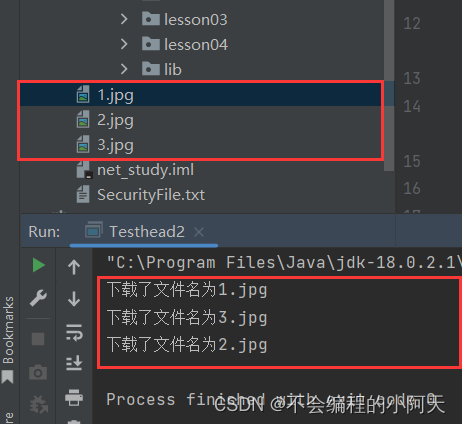
2.2、网络图片下载
//练习Thread,实现多线程同步下载图片
public class Testhead2 extends Thread{
private String url;
private String name;
public Testhead2(String url,String name) {
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
//下载图片线程执行体
public void run(){
WebDownloader webDownloader = new WebDownloader();
webDownloader.downloader(url,name);
System.out.println("下载了文件名为"+name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Testhead2继承了Thread可直接调用该类的方法
new Testhead2("https://tse2-mm.cn.bing.net/th/id/OIP-C.Q3JZ--bFUwc1fclDMTiLoQHaE8?w=263&h=180&c=7&r=0&o=5&dpr=1.3&pid=1.7","1.jpg").start();
new Testhead2("https://tse1-mm.cn.bing.net/th/id/OIP-C.9DpIDMm2OXTn2VjrS6XvLwHaDj?w=270&h=180&c=7&r=0&o=5&dpr=1.3&pid=1.7","2.jpg").start();
new Testhead2("https://tse2-mm.cn.bing.net/th/id/OIP-C.Ahu8mcvKb7IyF0bHPpiWZAHaE8?w=279&h=186&c=7&r=0&o=5&dpr=1.3&pid=1.7","3.jpg").start();
}
}
//下载器
class WebDownloader{
//下载方法
public void downloader(String url,String name){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
运行结果为
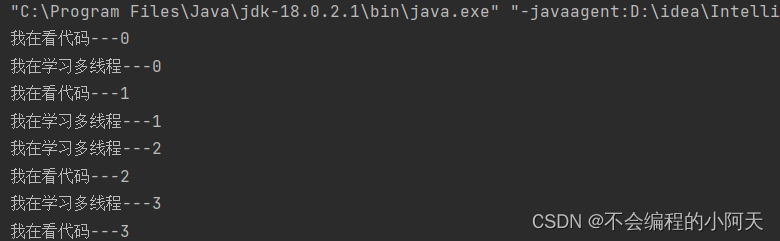
2.2、第二种创建方法 Runnable
public class Testhead3 implements Runnable{
public void run(){
//run方法线程体
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("我在看代码---"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Runnable接口的实现对象
Testhead3 testhead3 = new Testhead3();
//创建线程对象,通过线程对象来开启我们的线程,代理
// Thread thread = new Thread(testhead3);
// thread.start();
new Thread(testhead3).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("我在学习多线程---"+i);
}
}
}
运行结果为
小结


案例一 抢票
//买火车票的例子
public class TestThread4 implements Runnable{
//票数
private int ticketNums = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if (ticketNums <= 0){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "——>拿到了第" + ticketNums-- + "张票");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread4 testThead4 = new TestThread4();
new Thread(testThead4,"小明").start();
new Thread(testThead4,"老师").start();
new Thread(testThead4,"黄牛").start();
}
}
运行结果为:有可能两个人抢到一张票(线程不安全)
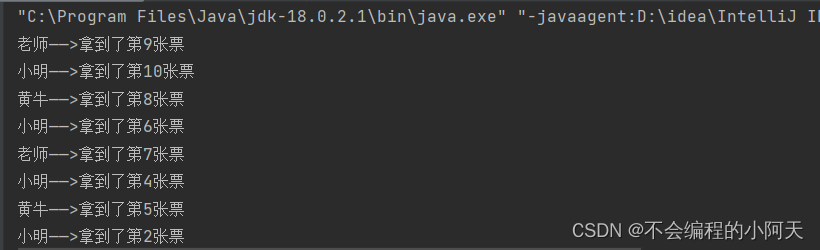
案例二 龟兔赛跑
//模拟龟兔赛跑
public class Race implements Runnable{
//胜利者
private static String winner;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
//判断比赛是否结束
boolean flag = gameOver(i);
if (flag == true){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->跑了" + i + "步");
if (Thread.currentThread().getName() == "兔子" && i%10==0){
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
//判断是否完成比赛
private boolean gameOver(int steps){
//判断是否有胜利者
if (winner != null){
return true; //已经存在胜利者了
}else {
//判断步数是否到100
if (steps >= 100){
winner = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("Winner is " + winner);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Race race = new Race();
new Thread(race, "兔子").start();
new Thread(race, "乌龟").start();
}
}
运行结果为
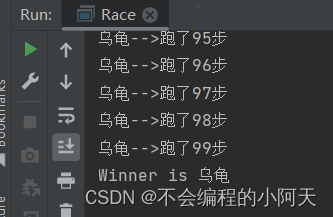
2.3、第三种创建方法Callable接口(了解即可)

//线程创建方式三:实现Callable接口
public class TestCallable implements Callable<Boolean> {
private String url;
private String name;
public TestCallable(String url, String name) {
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
//下载图片线程执行体
//需要返回值
public Boolean call(){
WebDownloader webDownloader = new WebDownloader();
webDownloader.downloader(url,name);
System.out.println("下载了文件名为"+name);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
TestCallable t1 = new TestCallable("https://tse2-mm.cn.bing.net/th/id/OIP-C.Q3JZ--bFUwc1fclDMTiLoQHaE8?w=263&h=180&c=7&r=0&o=5&dpr=1.3&pid=1.7", "1.jpg");
TestCallable t2 = new TestCallable("https://tse1-mm.cn.bing.net/th/id/OIP-C.9DpIDMm2OXTn2VjrS6XvLwHaDj?w=270&h=180&c=7&r=0&o=5&dpr=1.3&pid=1.7", "2.jpg");
TestCallable t3 = new TestCallable("https://tse2-mm.cn.bing.net/th/id/OIP-C.Ahu8mcvKb7IyF0bHPpiWZAHaE8?w=279&h=186&c=7&r=0&o=5&dpr=1.3&pid=1.7", "3.jpg");
//创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//提交执行
Future<Boolean> r1 = ser.submit(t1);
Future<Boolean> r2 = ser.submit(t2);
Future<Boolean> r3 = ser.submit(t3);
//获取结果
boolean rs1 = r1.get();
boolean rs2 = r2.get();
boolean rs3 = r3.get();
//关闭服务
ser.shutdownNow();
}
}
//下载器
class WebDownloader{
//下载方法
public void downloader(String url,String name){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
运行结果为
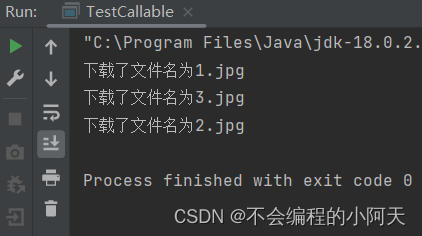
静态代理
//静态代理模式总结:
//真实对象和代理对象都要实现同一个接口
//代理对象要是真实角色
//好处
//代理对象可以做很多真实对象实现不了的事情
//真实对象专注做自己的事情
public class StaticProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
You you = new You();
// WeddingCompany weddingCompany = new WeddingCompany(you);
// weddingCompany.HappyMarry();
new WeddingCompany(new You()).HappyMarry();
}
}
interface Marry{
void HappyMarry();
}
//真实角色,你去结婚
class You implements Marry{
@Override
public void HappyMarry() {
System.out.println("xxx要结婚了,超开心");
}
}
//代理角色,帮助你结婚
class WeddingCompany implements Marry{
//代理谁——》真实角色
private Marry target;
public WeddingCompany(Marry target){
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public void HappyMarry() {
before();
this.target.HappyMarry();
after();
}
private void before(){
System.out.println("结婚之前,布置现场");
}
private void after(){
System.out.println("结婚之后,收尾款");
}
}
运行结果为

Lamda表达式(用于简化代码,属于函数式编程)
函数式接口的定义:
- 如果只包含唯一一个抽象方法,那么它就是一个函数时接口。
- 对于函数式接口,我们可以通过lamda表达式来创建该接口的对象。
//总结:
//lamda表达式只能有一行代码的情况下才能简化成为一行
//前提是接口为函数式接口
//多个函数也可以去掉参数类型,要去掉都去掉,必须加上括号
public class TestLamda2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ILove love = null;
//lamda 表达式简化
love = (int a) -> {
System.out.println("I Love You -->" + a);
};
//
// //简化1.参数类型
love = (a) -> {
System.out.println("I Love You -->" + a);
};
//简化2.简化括号,有多个参数需要加括号
love = a -> {
System.out.println("I Love You -->" + a);
};
//简化3.去掉花括号 前提:代码只有一行
love = a ->
System.out.println("I Love You -->" + a);
love.love(1);
love.love(2);
}
}
interface ILove{
void love(int a);
}
class Love implements ILove{
@Override
public void love(int a) {
System.out.println("I Love You -->" + a);
}
}
运行结果为
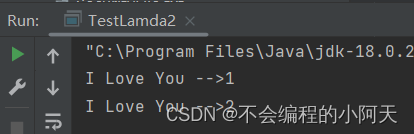
3、线程的操作
3.1、线程状态(5个状态)
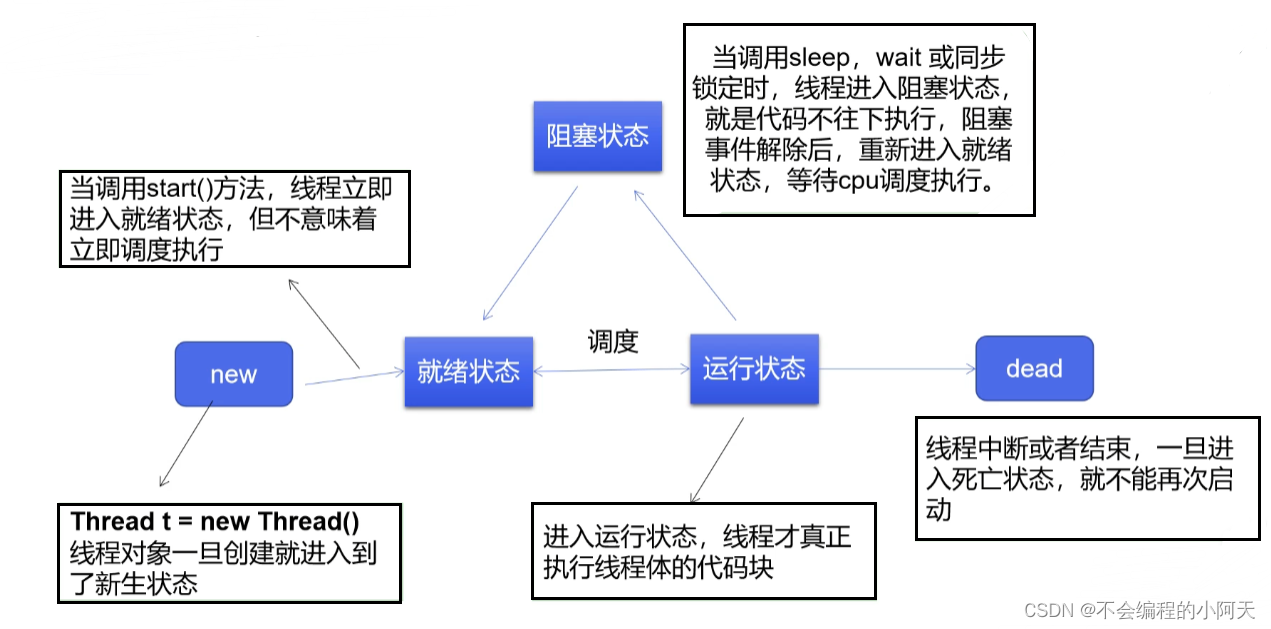
线程方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| setPriority(int newPriority) | 更改线程的优先级 |
| static void sleep(long millis) | 在指定的毫秒数内让当前正在执行的线程休眠 |
| void join() | 等待该线程终止 |
| static void yield() | 暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程 |
| void interrupt() | 中断线程,不建议使用 |
| boolean isAlive() | 测试线程是否处于活动状态 |
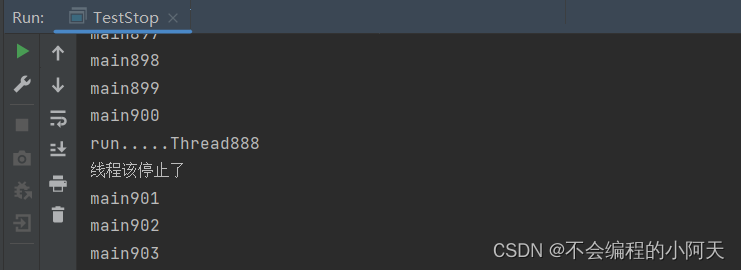
3.2、线程停止
- 不推荐使用JDK提供的stop()、destroy()方法。【已废弃】
- 推荐线程自己停下来
- 建议使用一个标志位进行终止变量,当flag = false,则终止线程运行。
public class TestStop implements Runnable{
//1.设置一个标志位
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (flag){
System.out.println("run.....Thread" + i++);
}
}
//2.设置一个公开的方法停止线程,转换标志位
public void stop(){
this.flag = false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestStop testStop = new TestStop();
new Thread(testStop).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("main"+i);
if (i==900){
//调用stop方法切换标志位,让线程停止
testStop.stop();
System.out.println("线程该停止了");
}
}
}
}
运行结果为
3.3、线程休眠
- sleep(时间)指定当前线程阻塞的毫秒数;
- sleep存在异常InterruptedException;
- sleep时间达到后线程进入就绪状态;
- sleep可以模拟网络延时,倒计时等;
- 每个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁;
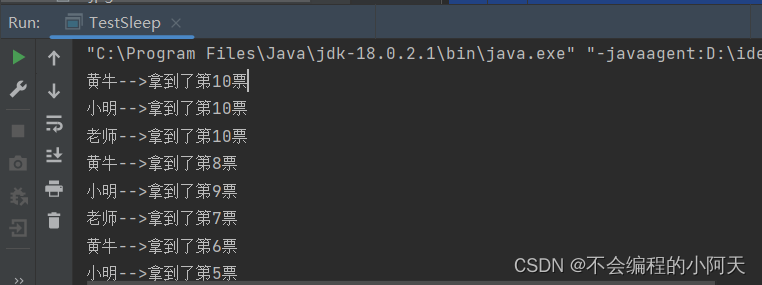
3.3.1、模拟网络延时,放大问题
public class TestSleep implements Runnable{
//票数
private int ticketNums = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if (ticketNums <= 1){
break;
}
//模拟延时 放大问题
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->拿到了第" + ticketNums-- + "票");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestSleep ticket = new TestSleep();
new Thread(ticket,"小明").start();
new Thread(ticket,"老师").start();
new Thread(ticket,"黄牛").start();
}
}
输出结果是
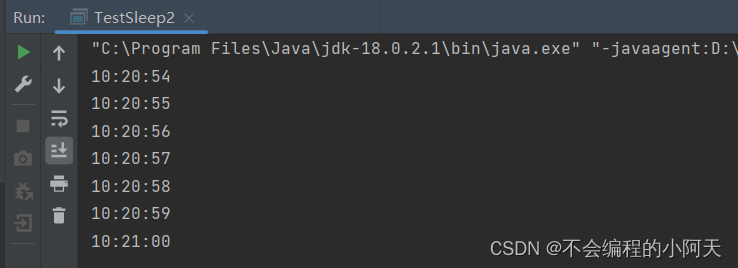
3.3.2、模拟倒计时
public class TestSleep2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true){
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(date));
}
}
//模拟倒计时
public static void tenDown(){
int nums = 10;
while (true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(nums--);
if (nums <= 0){
break;
}
}
}
}
运行结果为
3.4、线程礼让
-
礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞
-
将线程运行状态转换为就绪状态
-
让CPU重新调度,礼让不一定成功!看CPU心情
public class TestYield { public static void main(String[] args) { MyYield myYield = new MyYield(); new Thread(myYield,"a").start(); new Thread(myYield,"b").start(); } } class MyYield implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->开始执行"); //线程礼让 Thread.yield(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->结束执行"); } }运行结果为
3.5、线程的强制执行(Join方法)
- join合并线程,待此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞
- 可以想象成插队
public class TestJoin implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("VIP线程来了" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//启动我们的线程
TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin();
Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);
thread.start();
//启动主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
System.out.println("main方法正在执行" + i);
if (i==50){
thread.join();
}
}
}
}
运行结果为
3.6、观察线程的状态
public class TestState{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(".......");
}
});
//观察状态
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //NEW
//观察启动
thread.start(); //启动线程
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //RUN
//只要线程不终止就一直输出状态
while (thread.getState() != Thread.State.TERMINATED){
Thread.sleep(5000);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
}
}
}
//已经结束的线程不能再次启动
运行结果是

3.7、线程的优先级

注意:
- 线程调度器:用来控制CPU
- 线程优先级高不一定先执行,但是权重高,大概率先执行。
public class TestPriority {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//主线程优先级默认为5 不可改动
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority();
Thread t1 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t2 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t3 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t4 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t5 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t6 = new Thread(myPriority);
t1.start();
t2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); //设置优先级最慢
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //设置优先级最快
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(4); //设置优先级为4
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(-1); //设置优先级为负数
t5.start();
t6.setPriority(11); //设置优先级超出最大数值
t6.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
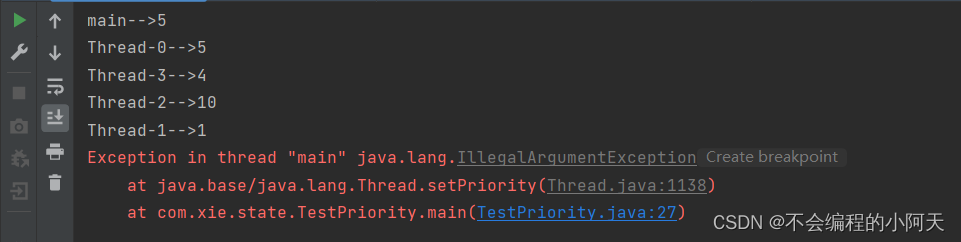
运行结果为
3.8、守护(daemon)线程

public class TestDeamon {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
You you = new You();
God god = new God();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true); //开启守护线程,默认为关闭
Thread thread1 = new Thread(you);
thread1.start();
thread.start();
}
}
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 365; i++) {
System.out.println("你开心的活着");
}
System.out.println("======goodbye world!!======");
}
}
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("上帝守护着你");
}
}
}
运行结果为
4、线程的同步
- 并发:多个线程同时操作同一个资源
- 形成条件:队列加锁

4.1、三大不安全案例
(1)不安全的买票
//不安全的买票
//线程不安全,有负数
public class UnsafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ButTicket butTicket = new ButTicket();
new Thread(butTicket,"小明").start();
new Thread(butTicket,"路人").start();
new Thread(butTicket,"黄牛").start();
}
}
class ButTicket implements Runnable{
//票
private int ticketNums = 10;
boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag){
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
private void buy() throws InterruptedException {
//判断是否有票
if(ticketNums <= 0){
flag = false;
}
//模拟延时
Thread.sleep(1000);
//买票
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到了第" + ticketNums-- + "张票");
}
}
运行结果为
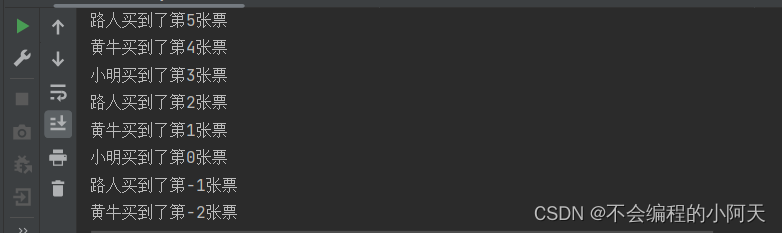
(2)不安全的取钱
//不安全的取钱
//两个人去银行取钱,同一个账户
public class UnSafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//账户
Account account = new Account(100,"结婚基金");
Drawing you = new Drawing(account,70,"你");
Drawing girlFriend = new Drawing(account,100,"她");
you.start();
girlFriend.start();
}
}
//账户
class Account{
int money; //余额
String name; //人名
public Account(int money,String name){
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
}
//银行:模拟取款
class Drawing extends Thread{
Account account; //账户
int drawingMoney; //现在手里有多少钱
int nowMoney;
public Drawing(Account account,int drawingMoney,String name){
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
}
//取钱
public void run(){
//判断有没有钱
if(account.money <= 0){
System.out.println(account.name+"余额为"+account.money);
System.out.println("余额已不足");
return;
}
//卡内余额 = 余额 - 你取的钱
account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;
//你手里的钱
nowMoney = nowMoney+drawingMoney;
System.out.println(account.name+"余额为"+account.money);
//Thread.currentThread().getName() == this.getName()
System.out.println(this.getName()+"手里的钱"+nowMoney);
}
}
运行结果为
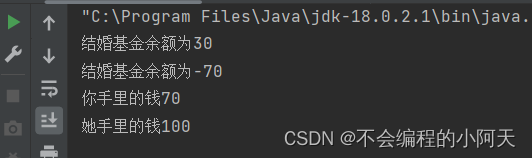
(3)线程不安全的集合
//线程不安全的集合 两个线程同一时间操作了同一个位置,会覆盖
//所以元素会变少
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ArrayList<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
strings.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(strings.size());
}
}
运行结果为
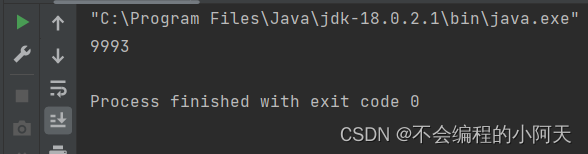
4.2、同步方法及同步块


代码根据4.1的三大不安全案例做改动
(1)安全的买票
public class UnsafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ButTicket butTicket = new ButTicket();
new Thread(butTicket,"小明").start();
new Thread(butTicket,"路人").start();
new Thread(butTicket,"黄牛").start();
}
}
class ButTicket implements Runnable{
//票
private int ticketNums = 10;
boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag){
try {
buy();
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
private synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException {
//判断是否有票
if(ticketNums <= 0){
flag = false;
return;
}
//买票
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到了第" + ticketNums-- + "票");
}
}
运行结果为

(2)安全的取钱
public class UnSafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//账户
Account account = new Account(100,"结婚基金");
Drawing you = new Drawing(account,70,"你");
Drawing girlFriend = new Drawing(account,100,"她");
you.start();
girlFriend.start();
}
}
//账户
class Account{
int money; //余额
String name; //人名
public Account(int money,String name){
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
}
//银行:模拟取款
class Drawing extends Thread{
Account account; //账户
int drawingMoney; //现在手里有多少钱
int nowMoney;
public Drawing(Account account,int drawingMoney,String name){
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
}
//取钱
public void run(){
synchronized (account){
//判断有没有钱
if(account.money <= drawingMoney){
System.out.println(account.name+"余额为"+account.money);
System.out.println("余额已不足");
System.out.println(this.getName()+"手里的钱"+nowMoney);
return;
}
//卡内余额 = 余额 - 你取的钱
account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;
//你手里的钱
nowMoney = nowMoney+drawingMoney;
System.out.println(account.name+"余额为"+account.money);
//Thread.currentThread().getName() == this.getName()
System.out.println(this.getName()+"手里的钱"+nowMoney);
}}
}
运行结果为
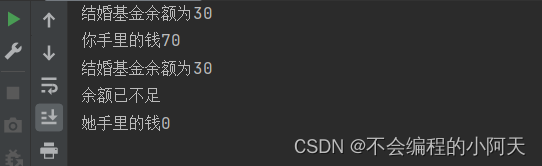
(3)线程安全的集合
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ArrayList<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (strings) {
strings.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}).start();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(strings.size());
}
}
运行结果为
扩充:JUC安全类型的集合(CopyOnWriteArrayList)
public class TestJUC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
运行结果为
4.3、死锁
多个线程各自占有一些资源,并且互相等待其他线程占有的资源才能运行,而导致两个或者多个线程都在等待对方释放资源,都停止执行的情形,某一个同步块同时拥有”两个以上对象的锁”时,就有可能发生“死锁”的问题。

public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Makeup makeup = new Makeup(0,"灰姑娘");
Makeup makeup1 = new Makeup(1,"白雪公主");
new Thread(makeup).start();
new Thread(makeup1).start();
}
}
//口红
class Lipstick{}
//镜子
class Mirrors{}
class Makeup extends Thread{
//需要的资源只有一份,用static确保只有一份
static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();
static Mirrors mirror = new Mirrors();
int choice; //选择
String girlName; //使用化妆品的人
Makeup(int choice,String girlName){
this.choice = choice;
this.girlName = girlName;
}
public void run(){
//化妆
try {
makeup();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//化妆,互相持有对方的锁,就是需要拿到对方的资源
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {
if (choice == 0){
synchronized (lipstick){
System.out.println(this.girlName+"获得了口红的锁");
Thread.sleep(1000);
synchronized (mirror){
System.out.println(this.girlName+"获得了镜子的锁");
}
}
}else {
synchronized (mirror){
System.out.println(this.girlName+"获得了镜子的锁");
Thread.sleep(2000);
synchronized (lipstick){
System.out.println(this.girlName+"获得了口红的锁");
}
}
}
}
}
运行结果为

4.4、Lock(显示的锁)

public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestLock2 testLock2 = new TestLock2();
new Thread(testLock2).start();
new Thread(testLock2).start();
new Thread(testLock2).start();
}
}
class TestLock2 implements Runnable{
int ticketNums = 10;
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
lock.lock(); //加锁
if (ticketNums > 0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(ticketNums--);
}else {
break;
}
}finally {
lock.unlock(); //解锁
}
}
}
}
运行结果为
synchronized与Lock的对比:
- Lock是显示锁(手动开启和关闭锁,别忘记关闭锁)synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放
- Lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁
- 使用Lock锁,JVM将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好。并且有更好的扩展性(提供更多的子类)
- 优先使用顺序:
- Lock>同步代码块(已经进入了方法体,分配了相应资源)>同步方法(在方法体之外)
5、线程的协作

5.1管程法
//测试:生产者消费者模型--:>利用缓冲区解决:管程法
//生产者,消费者,产品,缓冲区
public class TestPC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynContainer synContainer = new SynContainer();
new Productor(synContainer).start();
new Consumer(synContainer).start();
}
}
//生产者
class Productor extends Thread{
SynContainer container;
public Productor(SynContainer container){
this.container = container;
}
//生产
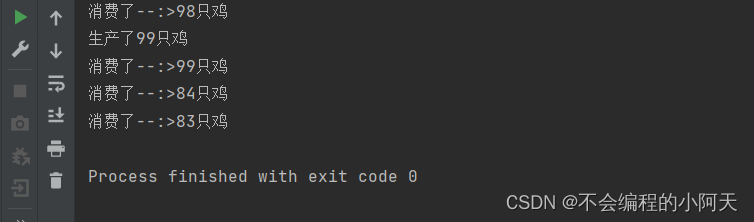
public void run(){
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
container.push(new Chicken(i));
System.out.println("生产了"+i+"只鸡");
}
}
}
//消费者
class Consumer extends Thread{
SynContainer container;
public Consumer (SynContainer container){
this.container = container;
}
//消费
public void run(){
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("消费了--:>"+container.pop().id +"只鸡");
}
}
}
//产品
class Chicken{
int id; //产品编号
public Chicken(int id){
this.id = id;
}
}
//缓冲区
class SynContainer{
//容量计数器
int count = 0;
//需要一个容器
Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10];
public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken){
//如果容器满了,就需要等待消费者进行消费
if (count == chickens.length){
//通知消费者进行消费,等待生产
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//如果没有满,需要丢入产品
chickens[count] = chicken;
count++;
//可以通知消费者进行消费了
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized Chicken pop(){
//判断是否能消费
if(count <= 0){
//通知生产者进行生产,等待消费
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//如果已经满了,需要购买产品
count--;
Chicken chicken = chickens[count];
//可以通知生产者进行生产了
this.notifyAll();
return chicken;
}
}
运行结果为
5.2信号灯法
//测试生产者消费问题2:信号灯法,标志位解决
public class TestPC2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv = new TV();
new Player(tv).start();
new Watcher(tv).start();
}
}
//生产者-->演员
class Player extends Thread{
TV tv;
public Player(TV tv){
this.tv = tv;
}
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if (i%2==0){
this.tv.play("哈哈哈哈");
}else {
this.tv.play("广告时间");
}
}
}
}
//消费者-->观众
class Watcher extends Thread{
TV tv;
public Watcher(TV tv){
this.tv = tv;
}
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i <20 ; i++) {
this.tv.watch();
}
}
}
//产品-->节目
class TV{
//演员表演,观众等待 T
//观众观看,演员等待 F
String voice; //节目
boolean flag = true;
//表演
public synchronized void play(String voice){
if (!flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("演员表演了:"+voice);
//通知观众观看
this.notifyAll(); //通知唤醒
this.voice = voice;
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
//观看
public synchronized void watch(){
if (flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("观看了:"+voice);
//通知演员表演
this.notifyAll();// 通知唤醒
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
}
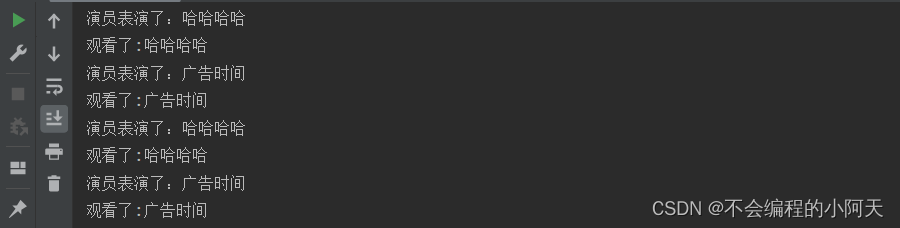
运行结果为
6、线程池


//测试线程池
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建服务,创建线程池
//newFixedThreadPool 参数为:线程池大小
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
//关闭连接
service.shutdown();
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
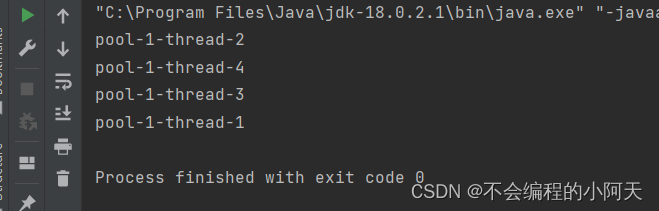
运行结果为





















 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








