文章目录
一、文件存储
1、案例演示
文本框中输入内容,点击写入后,文件存储到data目录中,点击读取,读取到输入框下的文本框中

内部存储路径

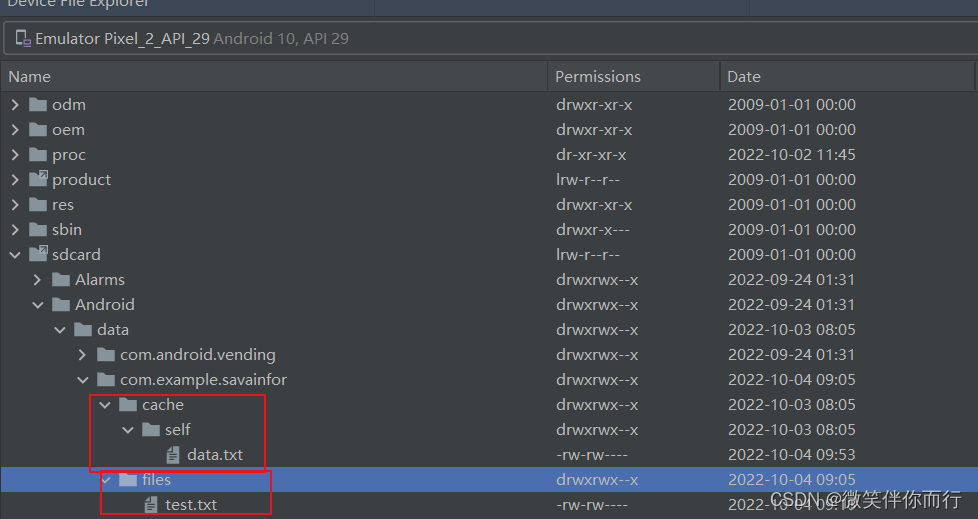
外部存储路径
2、参考代码
2.1、activity_main.xml总体部署
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edittext1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></EditText>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text1"
android:textSize="25dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></TextView>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="字节流写入"></Button>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="字节流读取"></Button>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="字符流写入"></Button>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="字符流读取"></Button>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="字节流外部存"></Button>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="字节流外部取"></Button>
</LinearLayout>
2.2、Mainactiy.java总体部署
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private EditText editText1;
private TextView textView;
private Button button1;
private Button button2;
private Button button3;
private Button button4;
private Button button5;
private Button button6;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initview();
}
//判断没有文件创建新文件
public static File getFile(String filePath){
//通过 文件路径出啊年文件对象
File file=new File(filePath);
//判断父文件是否存在,如果不存在就创建一个新文件
if(!file.getParentFile().exists()){
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
if(!file.exists()){
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e("创建文件失败",e.getMessage());
}
}
return file;
}
//获取id设置监听
public void initview(){
editText1=findViewById(R.id.edittext1);
textView=findViewById(R.id.text1);
button1=findViewById(R.id.button1);
button2=findViewById(R.id.button2);
button3=findViewById(R.id.button3);
button4=findViewById(R.id.button4);
button5=findViewById(R.id.button5);
button6=findViewById(R.id.button6);
button1.setOnClickListener(this);
button2.setOnClickListener(this);
button3.setOnClickListener(this);
button4.setOnClickListener(this);
button5.setOnClickListener(this);
button6.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//外部存储根目录/self/data.txt
String filePath=getExternalCacheDir().getPath()+File.separator+"self"+File.separator+"data.txt";
//test.txt
String path = getExternalFilesDir(null).getAbsolutePath() + "/test.txt";
String edit=editText1.getText().toString().trim();
//点击id判断
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.button1:
break;
case R.id.button2:
button2(MainActivity.this,"1",null);
break;
case R.id.button3:
button3(filePath,edit);
break;
case R.id.button4:
button4(filePath);
break;
case R.id.button5:
File file = getExternalFilesDir(null);
try {
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(path, true);
String str = editText1.getText().toString();
fos.write(str.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
case R.id.button6:
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = fis.read(b);
String str2 = new String(b, 0, len);
textView.setText(str2);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
}
}
//字节流写入文件
public void button1(Context context, String fileName, String content){
FileOutputStream out=null;
try {
//获取数据流对象
//MODE_PRIVATE:默认的操作模式,表示当指定同样文件名的时候,当该文件名有内容时,再次调用会覆盖原内容。
//MODE_APPEND:表示该文件如果已存在就往文件里面追加内容。
out=context.openFileOutput(fileName+".txt",MODE_PRIVATE);
//将数据通过流对象写出到文件
out.write(content.getBytes());
//输出到页面
Toast.makeText(this,"成功写入"+content,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(out!=null){
out.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//字节流读出文件
public void button2(Context context, String fileName, String content){
FileInputStream in=null;
try {
//获取数据流对象
in=context.openFileInput(fileName+".txt");
//字符数组
byte b[]=new byte[in.available()];
in.read(b);
//输出到页面
content=new String(b);
textView.setText(content.toString());
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"成功读出"+content,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(in!=null){
in.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//字符流写入文件
public void button3(String filePath,String content){
//调用getFile方法创建文件
File file=getFile(filePath);
FileWriter fileWriter=null;
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter=null;
//创建缓冲流对象,实现数据写入
try {
fileWriter=new FileWriter(file);
fileWriter.write(content);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"成功写入"+content,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(fileWriter!=null){
fileWriter.close();
}
if(bufferedWriter!=null){
bufferedWriter.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//字符流读出文件
public String button4(String filePath){
//调用getFile方法创建文件
File file=getFile(filePath);
String str=null;
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
FileReader fr=null;
BufferedReader br=null;
//创建缓冲流对象,实现数据写入
try {
fr=new FileReader(file);
br=new BufferedReader(fr);
while ((str=br.readLine())!=null){
sb.append(str);
}
textView.setText(sb);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(fr!=null){
fr.close();
}
if(br!=null){
br.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
二、内部存储
1、字节流写入文件
//MODE_PRIVATE:默认的操作模式,表示当指定同样文件名的时候,当该文件名有内容时,再次调用会覆盖原内容。
//MODE_APPEND:表示该文件如果已存在就往文件里面追加内容。
//字节流写入文件
//context上下文,fileNamewe文件名,content传输内容
public void button1(Context context, String fileName, String content){
FileOutputStream out=null;
try {
//获取数据流对象
out=context.openFileOutput(fileName+".txt",MODE_PRIVATE);
//将数据通过流对象写出到文件
out.write(content.getBytes());
//输出到页面
Toast.makeText(this,"成功写入"+content,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(out!=null){
out.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2、字节流读取文件
//字节流读出文件
public void button2(Context context, String fileName, String content){
FileInputStream in=null;
try {
//获取数据流对象
in=context.openFileInput(fileName+".txt");
//字符数组
byte b[]=new byte[in.available()];
in.read(b);
//输出到页面
content=new String(b);
textView.setText(content.toString());
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"成功读出"+content,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(in!=null){
in.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
三、外部存储
1、字符流写入文件
//字符流写入文件
public void button3(String filePath,String content){
//调用getFile方法创建文件
File file=getFile(filePath);
FileWriter fileWriter=null;
//创建缓冲流对象,实现数据写入
try {
fileWriter=new FileWriter(file);
fileWriter.write(content);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"成功写入"+content,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(fileWriter!=null){
fileWriter.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2、字符流读出文件
//字符流读出文件
public String button4(String filePath){
//调用getFile方法创建文件
File file=getFile(filePath);
String str=null;
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
FileReader fr=null;
BufferedReader br=null;
//创建缓冲流对象,实现数据写入
try {
fr=new FileReader(file);
br=new BufferedReader(fr);
while ((str=br.readLine())!=null){
sb.append(str);
}
textView.setText(sb);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(fr!=null){
fr.close();
}
if(br!=null){
br.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
3、文件路径
在 Android SDK 29 之前,想要查看外部存储的真实目录只需要调用 Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory() 就可以了,但是在 Android SDK 29 之后,这个方法就被废弃了,如下所示,在 SDK 为29 的情况下,getExternalStorageDirectory() 这个方法显示的就是被废弃了
所以呢谷歌提供了 getExternalFilesDir() 和 getExternalCacheDir() 这两个方法来获取外部存储的私有目录,前一个存放需要长时间保存的数据,后一个就存一些临时数据,它们位于 SDCard/Android/data/包名/files(cache) 下面。
getExternalFilesDir() 和 getExternalCacheDir() 这两个方法来获取外部存储的私有目录是不需要任何权限的
//外部存储根目录/self/data.txt
String filePath=getExternalCacheDir().getPath()+File.separator+"self"+File.separator+"data.txt";
//test.txt
String path = getExternalFilesDir(null).getAbsolutePath() + "/test.txt";























 788
788











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










