目录

一、Spring简介
1.缓解了工程的复杂性。
2.2002,首次推出Spring的雏形。
给软件行业带来了春天。
3.Spring框架是由于软件开发的复杂性而创建的。
spring就是一个轻量级的控制反转(IOC)和面向切面编程(ACP)的框架
4.spring组成:
七大模块:
spring core
支持aop 、dao 、orm 、web、 context 、web MVC
5.现代化的java开发就是基于spring的开发。
6.spring boot :一个快速开发的脚手架。
基于springboot可以快速的开发单个微服务。
7.spring cloud:基于springboot实现的。
学习springboot前提是掌握spring和springMVC。
弊端:发展了太久违背了原来的理念,配置十分繁琐,配置太多!
二、IOC
1.IOC:是一种思想。
之前思想:
(1)UserDao接口。
(2)UserDaoImpl实现类。
(3)UserService业务接口。
(4)UserServiceImpl业务实现类。
在之前的业务中,我们会根据用户的需求来修改源代码。
代码量十分大,修改一次成本太大。
2.这种思想从本质上解决了问题,我们不再需要去管理对象的创建了。系统的耦合性大大降低,可以更加专注在业务的实现上。这是IOC原型。
3.IOC本质:DI是实现IOC的一种方法。获得依赖对象的方式反转了。
IOC是spring框架的核心内容。
Hello spring
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
用XML需引入这一段。
id =变量名
class = new 的对象
property 相当于给对象中的属性设置一个值。
IOC是一种编程思想,由主动编程变成被动的接收。
实例化容器。
对象由spring来创建、管理、装配。
“容器在手,天下我有”
4.IOC创建对象的方式
使用无参构造创建对象,默认。
假设我们要使用有参构造创建对象。
举例:
(1)无参构造
User类当中:
public class User {
private String name;
public User() {
}
public User(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("name="+name);
}
}
Beans:
<bean id ="user" class="com.ioc.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="宿展健"/>
</bean>
Test当中:
public class Mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//构造好容器
User user=(User) context.getBean("user");
user.show();
}}
有参构造
下标方式:
<bean id ="user" class="com.ioc.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="我爱学习"/>
</bean>
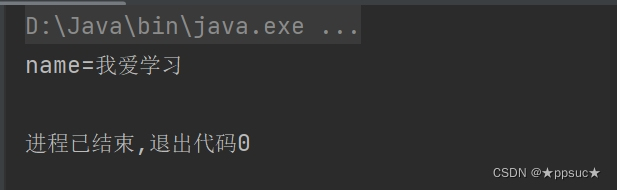
类型:(不建议使用,若有两个相同的类型,就无法识别)
<bean id ="user" class="com.ioc.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="java"/>
</bean>
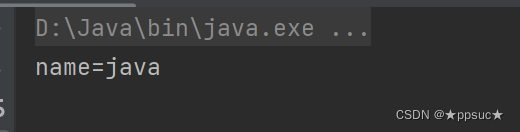
直接通过参数名
<bean id ="user" class="com.ioc.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="sz"/>
</bean>
总结:在配置文件加载的时候,容器中的管理的对象就已经初始化了。
5.spring配置
别名
<alias name="user" alias="user2"></alias>
如果添加了别名我们也可以用别名来取到这个对象。
Bean的配置
/id是bean的唯一标识符,也就是想当于我们学的对象名
class:bean 对象所对应的全限定名:包名+类型
name:也是别名,name 可以同时取多个别名:alias只能一一对应
<bean id="usert" class="com.ioc.pojo.UserT"/>
6.Import
这个import,一般用于团队开发使用,他可以将多个配置文件,导入合并为一个。
<import resource="beans.xml"/>
假设,现在项目中有多个人开发,这三个人负责不同的类开发,不同的类需要注册在不同的bean中,我们可以用import将所有人的beans.xml合并为一个。
ApplicationContext.xml
使用的时候用该配置即可。
7.DI依赖注入
(1)构造器注入
(2)Set方式注入(重点)
依赖注入:Set注入。
依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器。
注入:bean对象中的所有属性,由容器来注入。
//第一种普通值注入,value
Studentstudent=(Student)context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
<beanid="student"class="com.di.Student">
<propertyname="name"value="szj"/>
</bean>
环境搭建:
1.复杂类型
publicclassAddress{
privateStringaddress;
publicStringgetAddress(){
returnaddress;
}
publicvoidsetAddress(Stringaddress){
this.address=address;
}
}
2.真实对象
publicclassStudent{
privateStringname;
privateAddressaddress;
privateString[]books;
privateList<String>hobbys;
privateMap<String,String>card;
privateSet<String>games;
privatePropertiesinfo;
privateStringwife;
3.beans.xml
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<beanid="student"class="com.di.Student">
<propertyname="name"value="szj"/>
</bean>
</beans>
4.测试类:
publicclassmytest{
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){
ApplicationContextcontext=newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//第一种普通值注入,value
Studentstudent=(Student)context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}
拓展方式注入:
(1)普通值注入
<propertyname="name"value="szj"/>
(2)bean注入
<propertyname="address"ref="address"/>
(3)数组注入
<propertyname="books">
<array>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</array>
</property>
(4)list注入
<propertyname="books">
<list>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</list>
</property>
(5)map注入
<propertyname="books">
<map>
<entrykey=""value=""></entry>
</map>
</property>























 1362
1362











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










