day1
mysql
| bin | 可执行文件 操作mysql |
|---|---|
| docs | 文档 |
| include | .h头文件 |
| lin | 库文件 |
启动
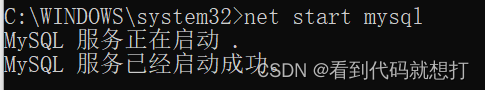
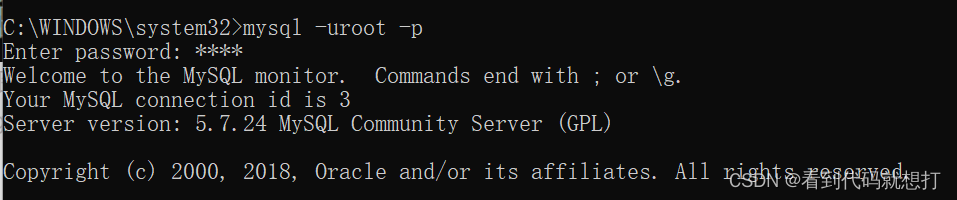
登录mysql
退出

登录参数
mysql -u用户名 -p密码 -h要连接的mysql服务器的ip地址(默认127.0.0.1) -P端口号(默认3306)
卸载
net stop mysql
mysqld -remove mysql
mysql数据模型
由二维表组成 主键…
数据库就是硬盘上的文件夹
mysql自带的数据库中 自带的有许多表文件(自定义的暂时没有)
frm结尾:表文件
myd结尾:数据文件
sql语言
sql语法
1.sql语句以分号结尾
2.不区分大小写 关键字建议大写
3.注释
单行注释:
– – 注意有个空格
多行注释:
/* 注释*/
sql分类

DDL—操作数据库
查询: show databases;
创建:create database 数据库名称;
创建(判断):create databases if not exists 数据库名称;
删除:drop databases 数据库名称;
使用:use 数据库名称;
查看当前使用:select databases ();
DDL—操作表
查询当前数据库下所有表名称:show tables;
查询表结构:desc 表名称;
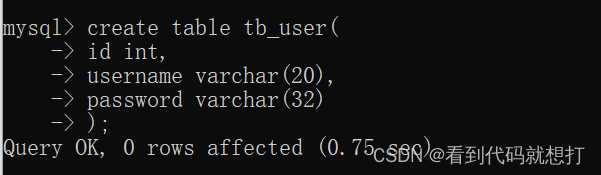
创建:create table 表名(
字段名1 数据类型,
字段名2 数据类型,
字段名n 数据类型
);
最后一行不加逗号
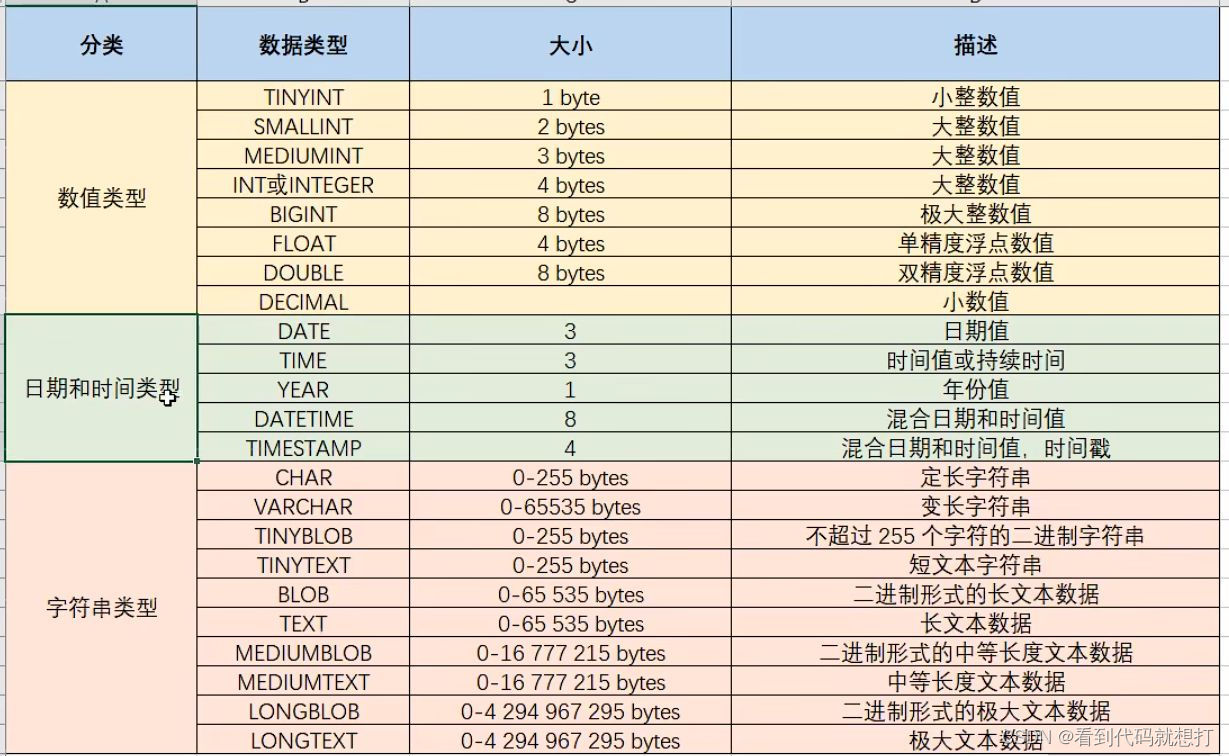
数据类型: 《mysql数据类型.xlsx》
数值 日期 字符串
age int
score double (总长度,小数点后保留的位数)
birthday date 只有年月日
name char(10)
name varchar(10)
删除表
drop table 表名;
修改表
修改表名:alter table 表名 rename to 新表名;
添加一列:alter table 表名 add 列名 数据类型;
修改数据类型:alter table 表名 modify 列名 新数据类型;
修改列名和数据类型:alter table 表名 change 列名 新列名 新数据类型;
删除列:alter table 表名 drop 列名;
DML—操作数据
1.添加数据
指定列添加数据:
insert into 表名(列名1,列名2,…)values(值1,值2,…);
全部列添加数据:
insert into 表名 (列名1,列名2,…)values(值1,值2,…);
查看所有数据:
select * from 表名
字符中可以输入中文(用于incorrect string value报错)
alter table student convert to CHARACTER set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin;
修改数据:
update 表名 set 列名1=值1,列名2=值2,…[where 条件];
如:update student set sex=‘女’ where name=‘张三’;
注意:如果update语句没有加where条件,表中所有数据全部修改。
删除数据:
delete from 表名 [where 条件];
例如:delete from student where name=‘977’;
DQL----数据查询
select 字段列表
from 表名列表
where 条件列表
group by 分组列表
having 分组后条件
order by 排序字段
limit 分页限定
DQL基础查询:
select 列名,列名 from 列表;
例:select name,age from student; --查询某几列
select distinct 列名 from 表名; 去除重复记录
例:select distinct address from student;
select 列名,列名1 as 别名,列名2 as 别名 from student;重命名
例:select name,math as 数学成绩,english as 英语成绩 from student;
DQL条件查询
条件查询语句: select 字段列表 from 表名 where 条件列表;
– 1.查询年龄大于20的学员
select * from student where age > 20;
– 2.查询年龄再20到30之间的学员
select * from student where age >= 20 and age <=30 ;
或者 select * from student where age between 20 and 30 ;
– 3.查询入学日期在19980901和19990901之间
select * from student where hire_date between ‘1998-09-01’ and ‘1999-09-01’;
– 4.查询年龄等于18岁的学员
select * from student where age = 18;
– 5. 查询年龄等于18岁 或者 年龄等于20岁 或者年龄等于22岁的学员信息
select * from student where age = 18 or age = 20 or age= 22;
或者:select * from student where age in (18,20,22);
– 6.查询英语成绩为null的学员信息
注意::null值的比较不能使用= !=。需要使用 is 或者is not 比较
select * from student where english is null;
模糊查询 like
通配符:
1._:代表单个任意字符
2.%代表任意个数字符
– 1.查询姓马的学员
select * from student where name like ‘马%’;
– 2.查询第二字是花的学员(保证第一个字有 后面无所谓)
select * from student where name like ‘_花%’;
– 3.查询名字里带有德字的学员信息
select * from student where name like ‘%德%’;
排序查询
select 字段列表 from 表名 order by 排序字段名1 [排序方式1],排序字段名2 [排序方式2]…;
排序方式:
ASC升序排序 默认
DESC:降序排序
– 1.查询学生信息,按照年龄升序排序
select * from student order by age asc;
– 2.查询学生信息,按照数学成绩降序排列
select * from student order by math desc;
– 3. 查询学生信息,按照数学成绩降序排列,如果数学成绩一样,再按照英语成绩升序排序
select * from student order by math desc,english asc;
DQL分组查询
聚合函数:将一列数据作为一个整体,进行纵向计算。
聚合函数分类:
| 函数名 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| count(列名) | 统计数量(一般用不为null的列) |
| max(列名) | 最大值 |
| min (列名) | 最小值 |
| sum(列名) | 求和 |
| avg(列名) | 平均值 |
语法:
count统计的列名不能为null
count取值:1.主键(非空 且唯一) 2.*
select 聚合函数(列名)from 表;
– 1.统计班级一共有多少个学生
select count(id) from student;
– 2.查询数学成绩的最高分
select max(math) from student;
– 3.查询数学成绩的总分
select sum(math) from student;
分组查询语法
select 字段列表 from 表名 [where 分组前条件限定] group by 分组字段名 [having 分组后条件过滤];
注意:分组后,查询的字段为聚合函数和分组字段,查询其他字段无意义见下面例1粗体
where和having的区别:
where是分组前进行限定 不满足where 不参与分组,having是分组后对结果进行过滤
where不能对聚合函数进行判断,having可以
– 1.查询男同学和女同学各自的数学平均分
select avg(math) from student group by sex ;-- 并不知道对应的性别
select sex,avg(math) from student group by sex ;-- 改进版
– 2.查询男同学和女同学各自的数学平均分,以及各自人数
select sex,avg(math),count() from student group by sex;
– 3.查询男同学和女同学各自的数学平均分数,以及各自人数,要求:分数低于70不参与分组
select sex,avg(math),count() from student where math > 70 group by sex;
– 3.查询男同学和女同学各自的数学平均分数,以及各自人数,要求:分数低于70不参与分组,分组之后人数大于2
select sex,avg(math),count() from student where math > 70 group by sex having count() > 2;
执行顺序:where >聚合函数> having
分页查询limit
select 字段列表 from 表名 limit 起始索引,查询条目数;
起始索引 从0开始
*计算公式:起始索引=(当前页码-1)每页显示的条数
– 1.从0开始查询,查询3条数据
select * from student limit 0,3;
– 2.每页显示3条数据,查询第1页数据
select * from student limit 0,3;
– 3.每页显示3条数据,查询第2页数据 (索引从3开始,也就是第4个)
select * from student limit 3,3;
– 4.每页显示3条数据,查询第3页数据 (索引从6开始,也就是第7个)
select * from student limit 6,3;
DQL小结
select 字段列表
from 表名列表
where 列表
group by 分组字段
having 分组后条件
order by 排序字段
limit 分页限定





















 403
403











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








