目录
一、TreeSet
概述:
TreeSet底层基于红黑树实现。对于数值型数据类型默认按照升序排序,Character、String默认按照字典顺序升序排序 ↓↓
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> sets1 = new TreeSet<>();
Collections.addAll(sets1, 5,2,8,1);
System.out.println(sets1); // setsl:[1, 2, 5, 8]
Set<String> sets2 = new TreeSet<>();
Collections.addAll(sets2, "c","b","a");
System.out.println(sets2); // sets2:[a, b, c]
}而对于自定义类型在不做任何处理的情况下就向TreeSet集合中添加数据将会报错,原因很简单:因为TreeSet不晓得自定义数据类型的排序规则 ↓↓
/*
Student:
private String id;
private String name;
private double score;
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Student> sets = new TreeSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("1", "张三", 80);
sets.add(s1); //报错!
}
解决方案一:
让自定义类实现Comparable<>接口并重写compareTo()方法来制定自定义类型的排序规则。
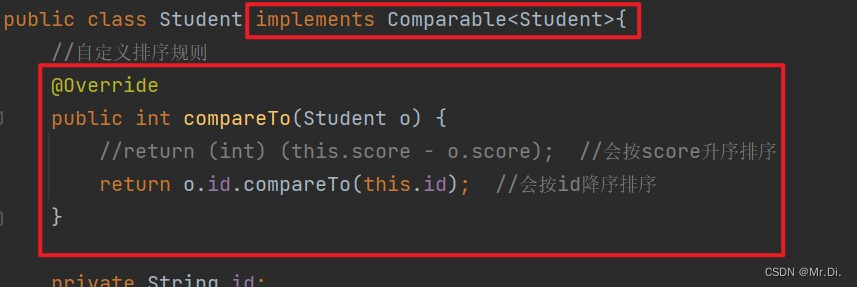

解决方案二:
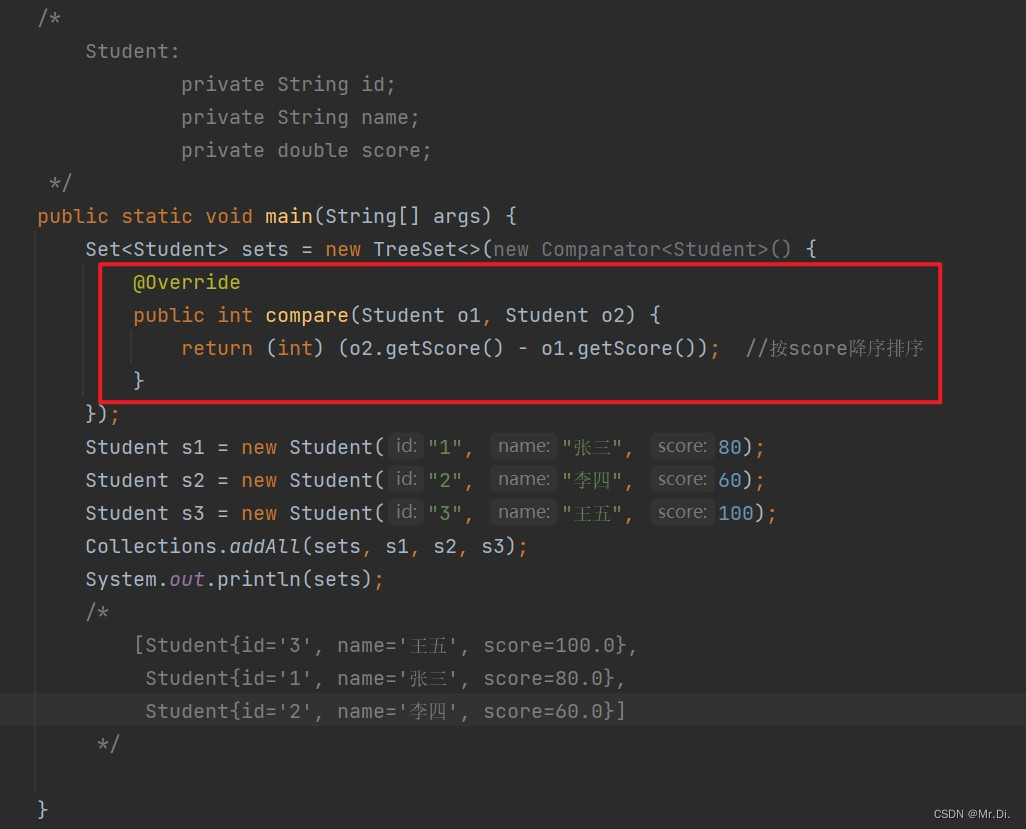
根据TreeSet提供的有参构造器,提供Compartor<>接口的对象,即在创建TreeSet对象时就指定排序规则。

二、TreeMap
概述
TreeMap底层也是基于红黑树实现。添加到集合中的元素默认将会按照键(key)升序排序(key的类型为数值型、Charactor、String的情况)。而如果键的类型为自定义类型的话,在不进行任何处理的情况下将会报错。原因和解决方案与TreeSet相同 👆↑
按值排序
注意TreeMap只能根据键(key)进行排序,如果要想进行按value进行排序的话只能借助其他集合。基本思路:先将Map集合添加到一个List集合(键值对类型元素的List)中,然后对List集合再进行按value排序。
/*
Student:
private String id;
private String name;
private double score;
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Student> maps = new TreeMap<>();
Student s1 = new Student("001", "张三", 90);
Student s2 = new Student("002", "李四", 100);
Student s3 = new Student("003", "王五", 80);
maps.put(s1.getId(), s1);
maps.put(s2.getId(), s2);
maps.put(s3.getId(), s3);
//将maps集合添加到List集合中,此时的lists集合的元素为键值对类型。
List<Map.Entry<String, Student>> lists = new ArrayList<>(maps.entrySet());
//对转换后的lists集合 进行按value排序
Collections.sort(lists, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Student>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Student> o1, Map.Entry<String, Student> o2) {
return (int) (o1.getValue().getScore() - o2.getValue().getScore()); //按score升序排序
}
});
for (Map.Entry<String, Student> list : lists) {
System.out.println(list.getKey() + ":" + list.getValue());
}
/*
结果:
003:Student{id='003', name='王五', score=80.0}
001:Student{id='001', name='张三', score=90.0}
002:Student{id='002', name='李四', score=100.0}
*/
}




















 159
159











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








