提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
目录
3.附加到package、class、method等上面,相当于给他们添加课额外的信息
一、注解以及注解的格式
1、注解简单是来说是给程序做出解释
2、以@注释名在代码存在,还可以添加参数
3.附加到package、class、method等上面,相当于给他们添加课额外的信息
二、元注解
是用于负责注解其他注解,Java定义了四个 meta——annotation类, 可以在java.lang.annotation包下找到(@Taget ,@Retention, @Docunented,@lnherited)
package bilinili;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
//元注解
@myannotation
public class Test02 {
public void test() {
}
}
/*定义一个注解,
* Target表示注解可以用在哪些地方*/
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
/*Retentions 表示我们注解在需要在什么地方保存该注释信息,用于描述注解的生命周期
* runtiem>class>sourse
* runtime 写的较多*/
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//Documented 表示是否将我们注解生成在Javadoc
@Documented
// Inherited 子类可以继承父类的注解
@Inherited
@interface myannotation{
}
三、自定义注解
package bilinili;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
public class Test03 {
//注解一定要赋值,也可以设置为空值、有默认值可以不定义
@myannocation(name = "马晓夏",school = "成都东软学院")
public void test(){
}
@我的注解("000")//只有value才能省略不写参数名
public void test1(){
}
}
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface myannocation{
String name(); //注解的参数 + String name();
int age() default -1;
int id() default 0;
String school();
}
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface 我的注解{
String value();
}
二、反射
Java反射就是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;并且能改变它的属性。而这也是Java被视为动态(或准动态,为啥要说是准动态,因为一般而言的动态语言定义是程序运行时,允许改变程序结构或变量类型,这种语言称为动态语言。从这个观点看,Perl,Python,Ruby是动态语言,C++,Java,C#不是动态语言。)语言的一个关键性质。
package bilibili;
public class Test01 extends Object {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//通过反射获取类的class对象
Class c1 = Class.forName("bilibili.USER");
System.out.println(c1);
//一个类在内存只有一个class对象
Class c2 = Class.forName("bilibili.USER");
Class c3 = Class.forName("bilibili.USER");
Class c4 = Class.forName("bilibili.USER");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
System.out.println(c4.hashCode());
}
}
//实体类
class USER{
private String name;
private int id;
private int age;
public USER() {
}
public USER(String name, int id, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "USER{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
1.得到class的几个方法
package bilibili;
//测试class类的创建方式有哪些
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1.可以new对象
Person person =new Students();
System.out.println("这个人是"+person.name);
//2.通过对象获得
Class c1 = person.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//3.可以通过forname()获得,会抛出异常
Class c2 = Class.forName("bilibili.Students");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
//4.通过类名.class获得
Class c3 =Students.class;
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
//5.基本内置类型的包装类都有type属性
Class c4 =Integer.TYPE;
System.out.println(c4);
//获得父类类型
Class c5 = c1.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(c5);
}
}
class Person{
public String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class Students extends Person{
public Students(){
this.name ="学生";
}
}
class Teacher extends Person{
public Teacher(){
this.name ="老师";
}
}
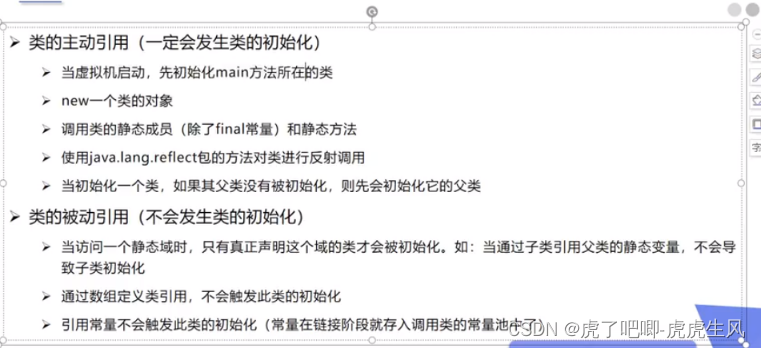
2.类的初始化
package bilibili;
//测试类什么时候初始化
public class Test06 {
static {
System.out.println("Main类被加载");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1.主动引用
Son son = new Son();
//2.反射也会产生主动引用
Class.forName("bilibili.Son");
//3.子类调用父类的方法不会引起初始化
System.out.println(Son.b);
//4.数组也不会被加载初始化,只是给空间起来名
Son[] array = new Son[3];
}
}
class Father{
static int b =2;
static {
System.out.println("父类被加载");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
static {
System.out.println("子类被加载");
m = 300;
}
static int m = 100;
static final int M = 1;
}
3. 类的加载器
package bilibili;
public class Test07 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//获取系统的类加载器
ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println(systemClassLoader);
//获取系统类加载器的父类加载器---扩展类加载器
ClassLoader parent = systemClassLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(parent);
//获取扩展类加载器的父类加载器-->跟加载器
ClassLoader parent1 =parent.getParent();
System.out.println(parent1);
//测试当前类是哪个加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = Class.forName("bilibili.Test07").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader);
//如何获得系统类的加载器可以加载的路径
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.class.path"));
}
}
4.获取类的运行时结构
package bilibili;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class class1 = Class.forName("bilibili.USER");
//获得类的名字
System.out.println(class1.getName());
System.out.println(class1.getSimpleName()); //getSimpleName获得类的简单名称
//获得类的属性
System.out.println("===========================");
Field[] field = class1.getFields();//只能找到public属性
field=class1.getDeclaredFields(); //找到全部的属性
for (Field field1 : field){
System.out.println(field);
}
//获得指定属性的值
System.out.println("=====================");
Field name = class1.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name);
//获得类的方法
System.out.println("=====================");
Method[] methods =class1.getMethods();
for (Method method :methods){
System.out.println("正常的"+method);
}
//获得本类的所有方法
methods = class1.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method:methods){
System.out.println("getDeclaredMethods"+method);
}
//获得指定方法
Method getName = class1.getMethod("getName",null);
Method setName =class1.getMethod("setName", String.class);
System.out.println(getName);
System.out.println(setName);
//获得指定构造器
System.out.println("==============================");
Constructor[] constructors = class1.getConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
constructors = class1.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println("*"+constructor);
}
System.out.println("========================");
//获得指定构造器
Constructor declaredConstructor = class1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class,int
.class);
System.out.println("指定"+declaredConstructor);
}
}
五、动态对象通过反射执行对象
package bilibili;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//动态的创建对象,通过反射
public class Test09 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
//获得class对象
Class c1 = Class.forName("bilibili.USER");
//调用了user的无参构造器
USER user = (USER) c1.newInstance();
System.out.println(user);
//通过构造器创建对象
Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class,int.class);
USER user2 = (USER) constructor.newInstance("小马",001,21);
System.out.println(user2);
System.out.println("=======================");
//通过反射调用普通方法
USER user3 = (USER) c1.newInstance();
Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
//invoke:激活,
setName.invoke(user3,"小马");
System.out.println(user3.getName());
//通过反射操作属性
System.out.println("==================");
USER user4 = (USER)c1.newInstance();
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
//不能直接操作私有属性,需要关闭程序安全监测,属性或方法的setAccessible(true);
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(user4,"小马2");
System.out.println(user4.getName());
}
}
六、性能对比
package bilibili;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test10 {
//性能检测用三种不同的方法更快
//普通方法调用
public static void test01(){
USER user = new USER();
long starttime =System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
user.getName();
}
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("普通方法执行时间"+(endtime-starttime)+"ms");
}
//反射调用
public static void test02() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
USER user = new USER();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName", null);
long starttime =System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
getName.invoke(user,null);
}
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("反射方法执行时间"+(endtime-starttime)+"ms");
}
//关闭安全检测
public static void test03() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
USER user = new USER();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName", null);
long starttime =System.currentTimeMillis();
getName.setAccessible(true);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
getName.invoke(user,null);
}
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("关闭检测方法执行时间"+(endtime-starttime)+"ms");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException {
test01();
test02();
test03();
}
}
七、小结
package bilibili;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
//反射操作注解练习
public class Test12 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class c2 = Class.forName("bilibili.student2");
//通过反射获得注解
Annotation[] annotations = c2.getAnnotations();
System.out.println(annotations);
//获得注解value的值
tablemxx tablemxx =(tablemxx) c2.getAnnotation(tablemxx.class);
String value =tablemxx.value();
System.out.println(value);
}
}
@tablemxx("db_students")
class student2{
@Fieldmxx(columnName = "db_int",type = "int",length = 10)
private int id;
@Fieldmxx(columnName = "db_age",type = "int",length = 10)
private int age;
@Fieldmxx(columnName = "db_name",type = "varchar",length = 10)
private String name;
public student2() {
}
public student2(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "student2{" +
"id=" + id +
", age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface tablemxx{
String value();
}
//属性的注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Fieldmxx{
String columnName();
String type();
int length();
}





















 1177
1177











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








