完成效果
请求报文
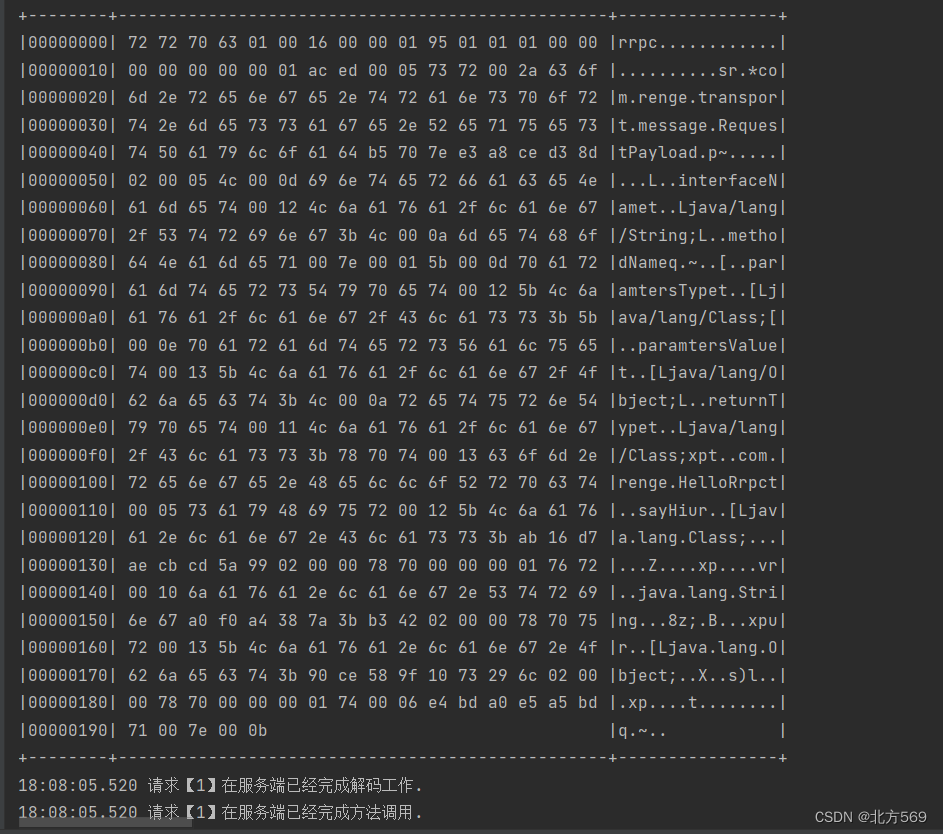
响应报文

报文格式:请看我这一篇文章
http://t.csdn.cn/4zVa9
本次主要实现服务提供方与服务调用方之间的封装报文与序列化,压缩预计今晚实现,具体代码在gitee: rengerpc: rrpc远程方法调用框架开发
一、netty网络传输
1.流程图
此前我们已经实现了服务调用方与提供方的基础通信与zookeeper创建调用节点,channel缓存等也已经实现,本次直接使用多个handler进行封装报文与序列化,为真正的网络传输做铺垫

2.代理设计模式
rrpc 是用来解决两个应用之间的通信,而网络则是两台机器之间的“桥梁”,只有架好了桥梁,我们才能把请求数据从一端传输另外一端。
对于服务端和客户端,他们做的事情都很确定:
服务端:暴露接口,等待客户端的远程访问,执行方法,返回结果。
客户端:引入接口,实现接口,在实现中编写网络请求代码和结果处理代码。
对于客户端而言,其中涉及的过程如 封装请求、选择通道、等待响应等功能,我们不可能为每一个方法调用都编写相同的逻辑。这是在给方法调用做增强,因此我们需要使用代理模式和装饰器模式。
在服务调用方调用方法时使用代理设计模式,完成基础通信工作
代码路径:rrpc_framwork.com.renge.ReferenceConfig
/**
* 代理设计模式,生成一个api接口的代理对象
*
* @return
*/
public T get() {
//此处一定使用动态代理完成了一些工作
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Class<T>[] classes = new Class[]{interfaceRef};
InvocationHandler handler = new RrpcConsumerInvocationHandler(registry,interfaceRef);
//使用动态代理生成代理对象
Object helloproxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, classes, handler);
return (T) helloproxy;
}3.netty的pipeline
在netty中请求的处理都是使用的IO多路复用,同时他提供了非常友好的请求处理方式就是pipeline(流水线)。他提供了基本的入站和出站的能力,并且抽象了两个接口ChannelInboundHandler(入栈处理器)和ChannelOutboundHandler(出栈处理器),当然他们共同继承ChannelHandler接口,同时为我们实现了大量的通用的入站和出站处理器,
当我们在消费端调用writeAndFlush方法时,网络通信就开始了,大致的流程如下:
1、对于消费方,开始做出站的工作,中间会经历多个出站处理器,主要的核心逻辑是将请求对象封装成报文。
2、消息经过消费方的出站处理程序后就变成了二进制字节流报文,就会进入服务提供方,开始进入提供方的入站逻辑,核心就是解析请求报文。
3、得到请求的之后,提供方根据请求携带的负载选定合适的对象和方法进行方法调用,得到结果。
4、调用方开始封装响应,并调用writeAndFlush将响应写出,进入提供方的出站逻辑,主要就是封装响应报文。
5、调用方接受响应,进入入站逻辑,解析响应,得到结果。
因为我们封装的私有报文,自己编写handler可以对报文进行很多自定义的操作,因此我们用来解析和封装请求以及响应的处理器是由我们自己编写。
一、服务提供方 发送报文 writeAndFlush(object) 响应 pipeline就生效了,报文开始出站 ---> 第一个处理器 in/out log ---> 第二个处理器 编码器(out)(转化 rrpcrequest -> msg(请求报文),序列化,压缩) object包含 1、请求id (long)//请求id需要一些算法所以需要8个字节的long 2、压缩类型 (1byte) 3、序列化的方式 (1byte) 4、消息类型(普通请求,心跳检测请求)(1byte) //调用方法的描述 不定长的内容 5、负载 payload(接口的名字,方法的名字,参数列表,返回值类型)) 二、服务调用方 通过netty接受响应报文 pipeline就生效了,报文开始出站 ---> 第一个处理器 in/out log ---> 第二个处理器 解码器(in)(解压缩,反序列化,msg-> rrpcrequest) ---> 想办法处理 (in) rrpcrequest 执行方法调用,得到结果 三、 执行方法调用,得到结果
请求报文格式(独有请求类型 request Type1.普通 2.心跳)
* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
* +----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+
* | magic |ver |head len| full length | qt | ser|comp| RequestId |
* +-----+-----+-------+----+----+----+----+-----------+----- ---+--------+----+----+----+----+----+----+---+---+
* | |
* | body |
* | |
* +--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---+public enum RequestType {
REQUEST((byte)1,"普通请求"),HEART_BEAT((byte)2,"心跳检测请求");
private byte id;
private String type;
RequestType(byte id, String type) {
this.id = id;
this.type = type;
}
public byte getId() {
return id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
}
响应报文格式(独有响应码code:1.成功 2.失败)
* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
* +----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+----+
* | magic |ver |head len| full length |code| ser|comp| RequestId |
* +-----+-----+-------+----+----+----+----+-----------+----- ---+--------+----+----+----+----+----+----+---+---+
* | |
* | body |
* | |
* +--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---+public enum ResponseCode {
SUCCESS((byte) 1,"成功"),FAIL((byte) 2,"失败");
private byte code;
private String desc;
ResponseCode(byte code, String desc) {
this.code = code;
this.desc = desc;
}
}
下面就是处理器的核心代码
二、封装报文与序列化
1、服务双方基础通信代码
代码目录
服务提供方
public class ProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//服务提供方,需要注册服务,启动服务
//1.封装要发布的服务
//2.定义注册中心
// 定义具体的服务
ServiceConfig<HelloRrpc> service = new ServiceConfig<>();
service.setInterface(HelloRrpc.class); //设置实例
service.setRef(new HelloRrpcImpl());
//3.通过启动引导程序,启动服务提供方
// (1) 配置 -- 应用的名称 -- 注册中心 -- 序列化协议 --压缩方式
// (2) 发布服务
//创建注册中心
RrpcBootstrap.getInstance()//获取实例对象
.application("first-rrpc-provider")//起名
//***配置注册中心***
.registry(new RegistryConfig("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"))
.protocol(new ProtocalConfig("jdk")) //序列化
//***发布服务***
.publish(service)
.start();
}
}服务调用方
@Slf4j
public class ConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//服务调用方 想进一切办法获取代理对象
// reference一定用生成代理的模板方法,get()
ReferenceConfig<HelloRrpc> reference = new ReferenceConfig<>();
reference.setInterface(HelloRrpc.class);
// 代理做了些什么,
// 1、连接注册中心
// 2、拉取服务列表
// 3、选择一个服务并建立连接
// 4、发送请求,携带一些信息(接口名,参数列表,方法的名字),获得结果
RrpcBootstrap.getInstance()//获取实例对象
.application("first-rrpc-consumer")
.registry(new RegistryConfig("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"))
.reference(reference);//referce代理
HelloRrpc helloRrpc = reference.get();
String sayHi = helloRrpc.sayHi("你好rrpc");
log.info("sayHi-->{}",sayHi);
}
}
2、报文传输流核心代码(都在framwork.rrpc_core模块下)
1.代码目录
2.请求核心代码
1.provider,通过start启动netty服务,调用handler启动网络传输,调用解码器RrpcMessageDecoder()进行解析consumer传来的报文
代码路径:com.renge.RrpcBootstarp
/**
* 启动netty服务
*/
public void start() {
//1.创建enentloop Netty的Reactor线程池,初始化了一个NioEventLoop数组,用来处理I/O操作,如接受新的连接和读/写数据
//老板只负责处理请求,之后会将请求分发至worker
//默认比例1:5
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(2);
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup(10);
try {
//2.需要服务器引导程序
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//3.进行对服务器的配置
serverBootstrap = serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//通过工厂方法设计模式实例化一个channel
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//入栈请求 处理入栈请求
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//配置childHandler来通知一个关于消息处理的InfoServerHandler实例
//我们需要添加入站和出战的的handler 引入内部类
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler())
.addLast(new RrpcRequestDecoder())
//根据请求进行方法调用
.addLast(new MethodCallHandler())
//给响应编码
.addLast(new RrpcResponseEncoder());
}
});
//4,绑定端口
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
//阻塞接收相关信息
// 阻塞操作,closeFuture()开启了一个channel的监听器(这期间channel在进行各项工作),直到链路断开
//closeFuture().sync()会阻塞当前线程,直到通道关闭操作完成。这可以用于确保在关闭通道之前,程序不会提前退出。
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//优雅关闭
try {
boss.shutdownGracefully().sync();
worker.shutdownGracefully().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}RrpcMessageDecode:Netty提供了LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,自动屏蔽TCP底层的拆包和粘 包问题,只需要传入正确的参数,即可轻松解决“读半包“问题。
@Slf4j
public class RrpcMessageDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder {
public RrpcMessageDecoder() {
super( // 找到当前报文的总长度,截取报文,截取出来的报文我们可以去进行解析
// 最大帧的长度,超过这个maxFrameLength值会直接丢弃
MessageFormatConstant.MAX_FRAME_LENGTH,
// 长度的字段的偏移量,
MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC.length + MessageFormatConstant.VERSION_LENGTH + MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_FIELD_LENGTH,
// 长度的字段的长度
MessageFormatConstant.FULL_FIELD_LENGTH,
// todo 负载的适配长度
-(MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC.length + MessageFormatConstant.VERSION_LENGTH
+ MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_FIELD_LENGTH + MessageFormatConstant.FULL_FIELD_LENGTH),
0);
}
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
Object decode = super.decode(ctx, in);
if (decode instanceof ByteBuf byteBuf){
return decodeFrame(byteBuf);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 解析报文
* @param byteBuf
* @return
*/
private Object decodeFrame(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
//1.解析魔数
byte[] magic = new byte[MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC.length];
byteBuf.readBytes(magic);
//检测魔数是否匹配
for (int i = 0; i <magic.length; i++) {
if (magic[i] != MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC[i]){
throw new RuntimeException("----The request obtained is not legitimate");
}
}
//2.解析版本号
byte version = byteBuf.readByte();
if (version!=MessageFormatConstant.VERSION){
throw new RuntimeException("----The obtained version number is not supported");
}
//3.头部长度
short headLength = byteBuf.readShort();
//4.总长度
int fullLength = byteBuf.readInt();
//5.请求类型
byte requestType = byteBuf.readByte();
//6.序列化的类型
byte serializeType = byteBuf.readByte();
//7.压缩类型
byte compressType = byteBuf.readByte();
//8.请求id
long requestId = byteBuf.readLong();
//封装为rrpcRequest
RrpcRequest rrpcRequest=new RrpcRequest();
rrpcRequest.setRequestType(requestType);
rrpcRequest.setSerializeType(serializeType);
rrpcRequest.setCompressType(compressType);
rrpcRequest.setRequestId(requestId);
//心跳请求没有payload
if (requestType == RequestType.HEART_BEAT.getId()){
return rrpcRequest;
}
//body
int payloadLength = fullLength-headLength;
byte[] payload = new byte[payloadLength];
byteBuf.readBytes(payload);
//有了字节数组就可以进行压缩和反序列化
//todo 解压缩
//反序列化
//这样写不需要关流
try (ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(payload);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis)) {
RequestPayload requestPayload = (RequestPayload) ois.readObject();
rrpcRequest.setRequestPayload(requestPayload);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error("请求{}反序列化时发生了异常",requestId,e);
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()){
log.debug("请求【{}】在服务端已经完成解码工作.",rrpcRequest.getRequestId());
}
//解析完成之后返回
return rrpcRequest;
}
}
2.consumer,通过 ReferenceConfig<T>.get()方法调用代理对象RrpcConsumerInvocationHandler,实现负载报文的封装
* 该类封装了客户端通信的基础逻辑,每一个代理对象的远程调用过程都封装在了invoke方法中
* 1.发现可用服务 2.建立连接 3.发送请求 4.得到结果
@Slf4j
public class RrpcConsumerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//一个注册中心 一个接口
private final Registry registry;
private final Class<?> interfaceRef;
public RrpcConsumerInvocationHandler(Registry registry, Class<?> interfaceRef) {
this.registry = registry;
this.interfaceRef = interfaceRef;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//有方法和参数 去 获取对象
//我们调用sayhi 事实上会走进这个代码段
// log.info("method->{}", method.getName());
// log.info("args->{}", args);
//1.发现服务 从注册中心 寻找一个可用的服务
//传入服务的名字,接口的全限定名就是服务名称 返回一个ip+port
// InetSocketAddress address = registry.lookup(interfaceRef.getName());
InetSocketAddress address = registry.lookup(interfaceRef.getName());
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("服务调用方,发现了服务[{}]的可用主机[{}]", interfaceRef.getName(), address);
}
//.使用netty连接服务器 发送调用的 服务的名字+方法名+参数列表 --->得到结果
//每次调用都会新建一个netty的连接,长连接不可取 浪费资源
//解决方案 缓存channel 尝试从缓存中获取channek 如果为获取 则创建新的连接 并进行缓存
//2.将缓存保存在RrpcBootStrap中,从缓存中获取一个channel
Channel channel = getAvaliableChannel(address);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("获取了和[{}]建立的连接通道,准备发送数据", address);
}
/**
* 封装报文
*/
//封装负载
RequestPayload requestPayload = RequestPayload.builder()
.interfaceName(interfaceRef.getName())
.methodName(method.getName())
.paramtersType(method.getParameterTypes())
.paramtersValue(args)
.returnType(method.getReturnType())
.build();
//TODO 需要对报文请求参数进行处理
RrpcRequest rrpcRequest = RrpcRequest.builder()
.requestId(1L)
.requestType(RequestType.REQUEST.getId())
.serializeType((byte) 1)
.compressType((byte) 1)
.requestPayload(requestPayload)
.build();
/**
* ---------------------异步策略----------------------
* 添加监听器 读取返回结果
*/
//4.写出报文
// 需要将CompletableFuture暴露并挂起
CompletableFuture<Object> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
RrpcBootstrap.PENDING_REQUEST.put(1L, completableFuture);
//writeAndFlush 写出一个请求 请求的实例加入pipeline执行出战的一系列操作 将请求转化成二进制报文
channel.writeAndFlush(rrpcRequest).addListener((ChannelFutureListener) promise -> {
//当前的promise将来的结果是writeAndFlush的返回结果
//一旦数据写出,promise结束,我们要的是服务端传给我们的返回值
/* if (promise.isDone()){
completableFuture.complete(promise.getNow());
}*/
//这里只需要处理异常 将completableFuture挂起并暴露,并且在获取服务器响应时调用
if (!promise.isSuccess()) {
completableFuture.completeExceptionally(promise.cause());
}
});
//如果completableFuture没有被处理,这里会阻塞,等待complete方法的执行
//5.获取像运营结果
return completableFuture.get(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 根据地址获取可用通道
*
* @param address
* @return
* @throws InterruptedException
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws TimeoutException
*/
private Channel getAvaliableChannel(InetSocketAddress address) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
//尝试从缓存中获取
Channel channel = RrpcBootstrap.CHANNEL_CACHE.get(address);
if (channel == null) {
//await方法 会阻塞会等待连接成功再返回,netty还提供了异步处理的逻辑
//sync方法 也是阻塞当前线程 获取返回值 连接的过程是异步的 发送数据的过程是异步的
// channel = NettyBootStrapInitializer.getBootstrap()
// .connect(address).await().channel();
//阻塞会影响数据执行速度 添加异步策略(对未来的承诺)
//通过completable异步获取channel
CompletableFuture<Channel> channelFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
NettyBootStrapInitializer.getBootstrap().connect(address).addListener(
(ChannelFutureListener) promise -> {
if (promise.isDone()) {
//异步执行
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("已经和【{}】成功建立了连接", address);
}
channelFuture.complete(promise.channel());
} else if (!promise.isSuccess()) {
channelFuture.completeExceptionally(promise.cause());
}
});
channel = channelFuture.get(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//缓存channel
RrpcBootstrap.CHANNEL_CACHE.put(address, channel);
}
if (channel == null) {
log.error("获取或建立与{}通道时发生异常", address);
throw new NetworkExcecption("获取通道时发生异常");
}
return channel;
}
}3.创建netty客户端辅助对象NettyBootStrapInitializer,调用 RrpcMessageEncoder()对报文进行编码
@Slf4j
public class NettyBootStrapInitializer {
//客户端辅助对象
private static Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
//静态代码块避免多个进程同时访问带来的问题 静态代码块在类第一次被调用或实例化时就会被执行,只会执行一次,用于初始化一些值
static {
//自定义线程池 EventLoopGroup:I/O线程池,负责处理Channel对应的I/O事件;
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
bootstrap = bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//实例化一个channel 通道,代表一个连接,每个Client请对会对应到具体的一个Channel;
.handler(new ConsumerChannelInitializer());
}
private NettyBootStrapInitializer() {
}
public static Bootstrap getBootstrap() {
return bootstrap;
}
}
RrpcMessageEncode
* 报文:
* 21个固定字节
* 4B magic(魔数) ----> rrpc.getBytes
* 1B version ----> 1
* 2B header length 首部的长度
* 4B full length 报文总长度 (定长解决毡包粘包问题
* 1B mt 消息类型 ==》request type
* 1B serialize 序列化的长度
* 1B comp 压缩的类型
* 8B RequestID
* <p>
* body
*/
@Slf4j
public class RrpcMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<RrpcRequest> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RrpcRequest rrpcRequest, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
//封装报文
//4个字节的魔数
byteBuf.writeBytes(MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC);
//一个字节版本号
byteBuf.writeByte(MessageFormatConstant.VERSION);
//两个字节头部的长度
byteBuf.writeShort(MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_LENGTH);
//总长度 需要body的长度 writeIndex(写指针) 把写指针移到4个位置之后 (留着写总长度)
byteBuf.writerIndex(byteBuf.writerIndex() + MessageFormatConstant.FULL_FIELD_LENGTH);
//3个类别
byteBuf.writeByte(rrpcRequest.getRequestType());
byteBuf.writeByte(rrpcRequest.getSerializeType());
byteBuf.writeByte(rrpcRequest.getCompressType());
//8字节的请求id
byteBuf.writeLong(rrpcRequest.getRequestId());
//判断是否是心跳请求 如果是心跳请求就不处理body
//写入请求体body
byte[] body = getBodyBytes(rrpcRequest.getRequestPayload());
if (body != null){
byteBuf.writeBytes(body);
}
int bodyLength = body ==null ? 0 : body.length;
//重新处理报文的总长度
//1.先保存写指针位置
int writerIndex = byteBuf.writerIndex();
//2.将写指针的位置移至总长度的位置
byteBuf.writerIndex(MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC.length
+ MessageFormatConstant.VERSION_LENGTH + MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_FIELD_LENGTH);
byteBuf.writeInt(MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_LENGTH + bodyLength);
//将写指针归为
byteBuf.writerIndex(writerIndex);
}
private byte[] getBodyBytes(RequestPayload requestPayload) {
//针对不同的消息类型不同的处理 心跳请求 没有pauload
if (requestPayload == null){
return null;
}
try {
//对象 --- 》 字节数组 序列化和压缩
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
outputStream.writeObject(requestPayload);
//TODO 压缩
return bos.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("序列化时出现异常");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}4.请求与响应间的处理器(用于数据封装与传递)ConsumerChannelInitializer,调用RrpcRequestEncoder()与RrpcResponseDecoder()
public class ConsumerChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline()
//netty自带的日志处理器
.addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG))
//消息编码器
.addLast(new RrpcRequestEncoder())
//入栈的解码器
.addLast(new RrpcResponseDecoder())
//处理结果
.addLast(new MySimpleChannelInboundHandler());
}
}
5.请求方法调用处理器 MethodCallHandler(用于请求与响应之间数据的传递与封装)
@Slf4j
public class MySimpleChannelInboundHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RrpcResponse> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RrpcResponse rrpcResponse) throws Exception {
//服务提供方给与的结果
Object returnValue = rrpcResponse.getBody();
//从全局挂起的请求中寻找与之匹配的completableFuture
CompletableFuture<Object> completableFuture = RrpcBootstrap.PENDING_REQUEST.get(1L);
completableFuture.complete(returnValue);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()){
log.debug("以寻找到编号为[{}]的completableFuture,处理响应结果",rrpcResponse.getRequestId());
}
}
}
3.响应核心代码
1.RrpcResponseEncoder
@Slf4j
public class RrpcResponseEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<RrpcResponse> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RrpcResponse rrpcResponse, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
//封装报文
//4个字节的魔数
byteBuf.writeBytes(MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC);
//一个字节版本号
byteBuf.writeByte(MessageFormatConstant.VERSION);
//两个字节头部的长度
byteBuf.writeShort(MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_LENGTH);
//总长度 需要body的长度 writeIndex(写指针) 把写指针移到4个位置之后 (留着写总长度)
byteBuf.writerIndex(byteBuf.writerIndex() + MessageFormatConstant.FULL_FIELD_LENGTH);
//3个类别
byteBuf.writeByte(rrpcResponse.getCode());
byteBuf.writeByte(rrpcResponse.getSerializeType());
byteBuf.writeByte(rrpcResponse.getCompressType());
//8字节的请求id
byteBuf.writeLong(rrpcResponse.getRequestId());
//判断是否是心跳请求 就不处理响应体
//发送"ping" "pong"
//写入请求体body
byte[] body = getBodyBytes(rrpcResponse.getBody());
if (body != null){
byteBuf.writeBytes(body);
}
int bodyLength = body ==null ? 0 : body.length;
//重新处理报文的总长度
//1.先保存写指针位置
int writerIndex = byteBuf.writerIndex();
//2.将写指针的位置移至总长度的位置
byteBuf.writerIndex(MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC.length
+ MessageFormatConstant.VERSION_LENGTH + MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_FIELD_LENGTH);
byteBuf.writeInt(MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_LENGTH + bodyLength);
//将写指针归为
byteBuf.writerIndex(writerIndex);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()){
log.debug("响应【{}】在调用端已经完成编码工作.",rrpcResponse.getRequestId());
}
}
private byte[] getBodyBytes(Object body) {
//针对不同的消息类型不同的处理 心跳请求 没有pauload
if (body == null){
return null;
}
try {
//对象 --- 》 字节数组 序列化和压缩
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
outputStream.writeObject(body);
//TODO 压缩
return bos.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("序列化时出现异常");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
2.RrpcResponseDecoder
@Slf4j
public class RrpcResponseDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder {
public RrpcResponseDecoder() {
super( // 找到当前报文的总长度,截取报文,截取出来的报文我们可以去进行解析
// 最大帧的长度,超过这个maxFrameLength值会直接丢弃
MessageFormatConstant.MAX_FRAME_LENGTH,
// 长度的字段的偏移量,
MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC.length + MessageFormatConstant.VERSION_LENGTH + MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_FIELD_LENGTH,
// 长度的字段的长度
MessageFormatConstant.FULL_FIELD_LENGTH,
// todo 负载的适配长度
-(MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC.length + MessageFormatConstant.VERSION_LENGTH
+ MessageFormatConstant.HEADER_FIELD_LENGTH + MessageFormatConstant.FULL_FIELD_LENGTH),
0);
}
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
Object decode = super.decode(ctx, in);
if (decode instanceof ByteBuf byteBuf){
return decodeFrame(byteBuf);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 解析报文
* @param byteBuf
* @return
*/
private Object decodeFrame(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
//1.解析魔数
byte[] magic = new byte[MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC.length];
byteBuf.readBytes(magic);
//检测魔数是否匹配
for (int i = 0; i <magic.length; i++) {
if (magic[i] != MessageFormatConstant.MAGIC[i]){
throw new RuntimeException("----The request obtained is not legitimate");
}
}
//2.解析版本号
byte version = byteBuf.readByte();
if (version!=MessageFormatConstant.VERSION){
throw new RuntimeException("----The obtained version number is not supported");
}
//3.头部长度
short headLength = byteBuf.readShort();
//4.总长度
int fullLength = byteBuf.readInt();
//5.请求类型
byte responseCode = byteBuf.readByte();
//6.序列化的类型
byte serializeType = byteBuf.readByte();
//7.压缩类型
byte compressType = byteBuf.readByte();
//8.请求id
long requestId = byteBuf.readLong();
//封装为rrpcRequest
RrpcResponse rrpcResponse=new RrpcResponse();
rrpcResponse.setCode(responseCode);
rrpcResponse.setSerializeType(serializeType);
rrpcResponse.setCompressType(compressType);
rrpcResponse.setRequestId(requestId);
//todo 心跳请求没有payload
/* if (requestType == RequestType.HEART_BEAT.getId()){
return rrpcRequest;
}
*/
//body
int bodyLength = fullLength-headLength;
byte[] payload = new byte[bodyLength];
byteBuf.readBytes(payload);
//有了字节数组就可以进行压缩和反序列化
//todo 解压缩
//反序列化
//这样写不需要关流
try (ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(payload);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis))
{
Object body = ois.readObject();
rrpcResponse.setBody(body);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error("请求{}反序列化时发生了异常",requestId,e);
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()){
log.debug("响应【{}】在调用端已经完成解码工作.",rrpcResponse.getRequestId());
}
//解析完成之后返回
return rrpcResponse;
}
}

























 745
745

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










