作者: 华丞臧.
专栏:【数据结构】
各位读者老爷如果觉得博主写的不错,请诸位多多支持(点赞+收藏+关注)。如果有错误的地方,欢迎在评论区指出。
推荐一款刷题网站 👉 LeetCode刷题网站
一、有效括号
题目描述
LeetCode.20 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,‘)’,‘{’,‘}’,‘[’,‘]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。

解题思路
我们知道在一个式子当中后出现的左括号要与先出现的右括号配对;那么对于左括号而言,就是先入后出符合栈的特性,所以我们用栈来存储左括号;当遇到右括号时,判断栈顶的括号和该右括号是否配对,如果配对成功则出栈栈顶元素,否则配对失败则return false,这样既保证了相同类型又保证了顺序闭合;当遍历完传入的字符串时,还需要检查栈中是否为空。
代码实现
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* data;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化栈
void StackInit(ST* ps);
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
//入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps);
//检查栈是否为空,如果为空返回非0结果,如果不为空返回0
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
//初始化栈
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->data);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->data, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->data = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->data[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
//出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->data[ps->top - 1];
}
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
//检查栈是否为空,如果为空返回非0结果,如果不为空返回0
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
/*if (ps->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}*/
return ps->top == 0;
}
bool isValid(char* s)
{
ST pst;
StackInit(&pst);
char* cur = s;
while(*cur)
{
if(*cur == '(' || *cur == '{' || *cur == '[')
{
StackPush(&pst,*cur);
}
else
{
if(StackEmpty(&pst))
{
StackDestroy(&pst);
return false;
}
char tmp = StackTop(&pst);
StackPop(&pst);
if((*cur == '}' && tmp != '{')
|| (*cur == ']' && tmp != '[')
|| (*cur == ')' && tmp != '('))
{
StackDestroy(&pst);
return false;
}
}
cur++;
}
bool flag = StackEmpty(&pst);
StackDestroy(&pst);
return flag;
}
二、用队列实现栈
题目描述
LeetCode.225 用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 压入栈顶。int pop()移除并返回栈顶元素。int top()返回栈顶元素。boolean empty()如果栈是空的,返回true;否则,返回false。

解题思路
队列是先入先出,而栈是先入后出。
用两个队列实现栈,进行入栈操作时把数据放入不为空的队列(两个队列都为空则随意);出栈时,把不为空的队列中元素倒入另一个为空的队列,只留一个元素,然后再返回这个元素的值并且删除该元素。只有两个队列都为空时,栈才为空;销毁时,注意要先销毁队列再销毁用队列实现的栈。
出队列:
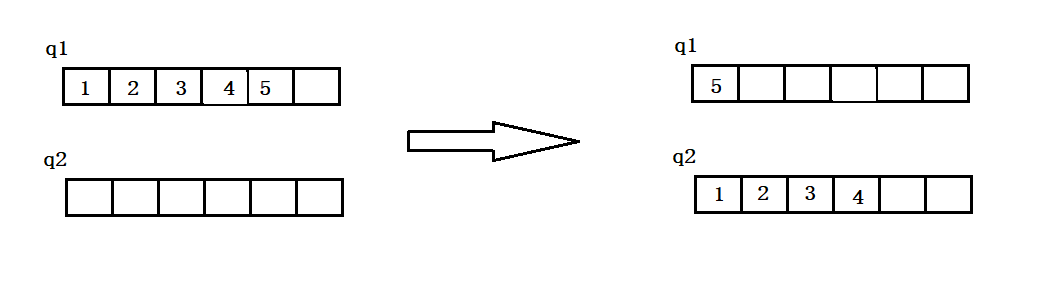
代码实现
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QListNode
{
struct QListNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QLNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QLNode* head;
QLNode* tail;
int size;
}QE;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(QE* q);
//队尾入队列
void QueuePush(QE* q,QDataType x);
//队头出队列
void QueuePop(QE* q);
//获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(QE* q);
//获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(QE* q);
//获取队列有效元素个数
int QueueSize(QE* q);
//检查队列是否为空,如果为空返回非0数,如果不为空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(QE* q);
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(QE* q);
//申请一个结点
QLNode* BuyQListNode(QDataType x);
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(QE* q)
{
assert(q);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
q->size = 0;
}
//申请一个结点
QLNode* BuyQListNode(QDataType x)
{
QLNode* newnode = (QLNode*)malloc(sizeof(QLNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//队尾入队列
void QueuePush(QE* q, QDataType x)
{
assert(q);
//申请一个结点
QLNode* newnode = BuyQListNode(x);
//分有数据和无数据
if (q->head == NULL && q->tail == NULL)
{
q->head = newnode;
q->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
q->tail->next = newnode;
q->tail = newnode;
}
q->size++;
}
//队头出队列
void QueuePop(QE* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
if (q->head->next == NULL)
{
free(q->head);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QLNode* tmp = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = tmp;
}
--q->size;
}
//获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(QE* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->head->data;
}
//获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(QE* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
//获取队列有效元素个数
int QueueSize(QE* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->size;
}
//检查队列是否为空,如果为空返回非0数,如果不为空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(QE* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->head == NULL && q->tail == NULL;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(QE* q)
{
assert(q);
while (q->head)
{
QLNode* tmp = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = tmp;
}
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
q->size = 0;
}
typedef struct {
QE q1;
QE q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if(obj == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
QueueInit(&obj->q1);
QueueInit(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q2) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
QE* empty = &obj->q1;
QE* nonempty = &obj->q2;
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
{
empty = &obj->q2;
nonempty = &obj->q1;
}
int tmp = 0;
while(QueueSize(nonempty) > 1)
{
QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(nonempty));
QueuePop(nonempty);
}
tmp = QueueFront(nonempty);
QueuePop(nonempty);
return tmp;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{
assert(obj);
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
{
return obj->q1.tail->data;
}
else if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q2) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return obj->q2.tail->data;
}
return 0;
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
三、用栈实现队列
题目描述
LeetCode.232 用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x)将元素x推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false

解题思路
用两个栈实现队列,那么我们把两个栈分为 入队列的栈 push 和 出队列的栈 pop;进行入队列操作时,把数据压入push。进行出队列操作时,如果pop为空,则把push中的数据压入pop中再进行出栈操作;如果push不为空,则直接对pop进行出栈操作。
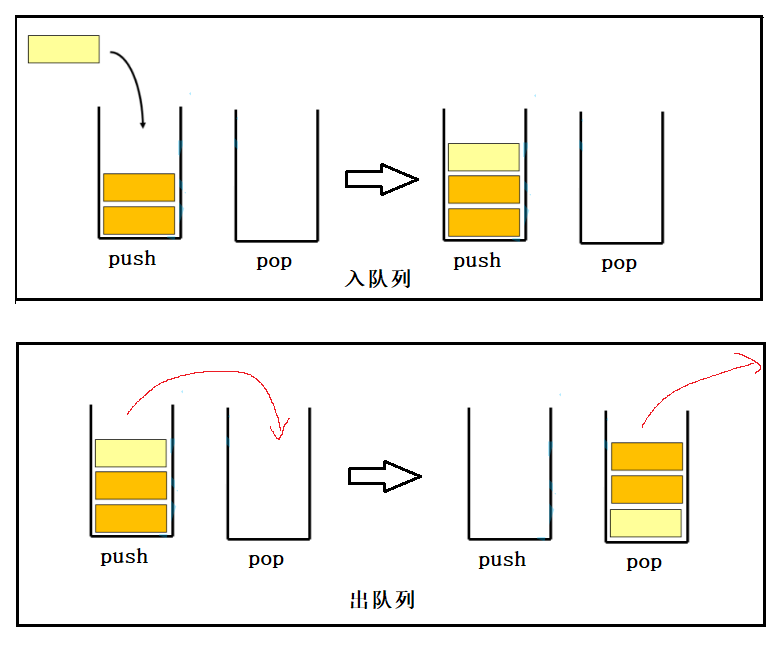
代码实现
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* data;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化栈
void StackInit(ST* ps);
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
//入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps);
//检查栈是否为空,如果为空返回非0结果,如果不为空返回0
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
//初始化栈
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->data);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->data, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->data = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->data[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
//出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
--ps->top;
}
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->data[ps->top - 1];
}
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
//检查栈是否为空,如果为空返回非0结果,如果不为空返回0
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
typedef struct {
ST push;
ST pop;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
StackInit(&obj->push);
StackInit(&obj->pop);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
StackPush(&obj->push,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
STDataType top = 0;
if(!StackEmpty(&obj->pop))
{
top = StackTop(&obj->pop);
StackPop(&obj->pop);
}
else
{
while(StackSize(&obj->push) > 0)
{
StackPush(&obj->pop,StackTop(&obj->push));
StackPop(&obj->push);
}
top = StackTop(&obj->pop);
StackPop(&obj->pop);
}
return top;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if(!StackEmpty(&obj->pop))
{
return StackTop(&obj->pop);
}
else
{
while(StackSize(&obj->push) > 0)
{
StackPush(&obj->pop,StackTop(&obj->push));
StackPop(&obj->push);
}
return StackTop(&obj->pop);
}
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return StackEmpty(&obj->push) && StackEmpty(&obj->pop);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
free(obj->push.data);
free(obj->pop.data);
free(obj);
}
四、设计循环队列
题目描述
LeetCode.622 设计循环队列
设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
你的实现应该支持如下操作:
MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为k。Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回-1。Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回-1。enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。
解题思路
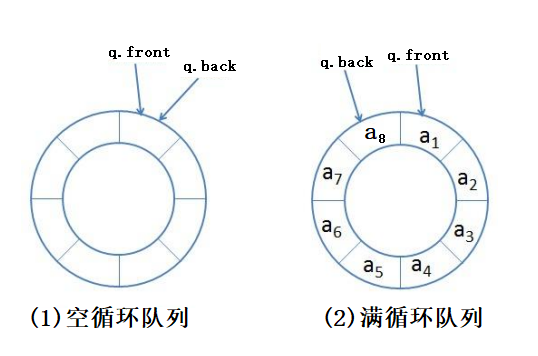
用数组实现循环队列,循环队列如上图所示,其长度是固定的,当循环队列存满时就不能存放新的数据了;给两个标记front和back,分别用来标记循环队列的第一个元素和最后一个元素;当 back 的下一个元素等于 front 时,循环队列存满就不能再存放数据了;当 bakc 等于 front 时,循环队列为空。删除队列元素只需要对 front 减一即可。
代码实现
typedef struct {
int* data;
int front;
int back;
int size;
int capacity;
} MyCircularQueue;
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
//return ((back - front + obj->capacity) % obj->capacity);
if(obj->size)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->size == obj->capacity ;
}
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*k);
if(tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
obj->data = tmp;
obj->front = obj->back = obj->size = 0;
obj->capacity = k;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->data[obj->back] = value;
obj->back++;
if(obj->back == obj->capacity)
{
obj->back = 0;
}
obj->size++;
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->front++;
if(obj->front == obj->capacity)
{
obj->front = 0;
}
obj->size--;
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->data[obj->front];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->data[(obj->back - 1 + obj->capacity) % obj->capacity];
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->data);
free(obj);
}























 992
992











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










