🍎 博客主页:🌙@披星戴月的贾维斯
🍎 欢迎关注:👍点赞🍃收藏🔥留言
🍇系列专栏:🌙 蓝桥杯
🌙我与杀戮之中绽放,亦如黎明的花朵🌙
🍉一起加油,去追寻、去成为更好的自己!
蓝桥杯倒计时 39天
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
🍎、递推
🍉、递推的简单定义
递推算法是一种用若干步可重复运算来描述复杂问题的方法。递推是序列计算中的一种常用算法。通常是通过计算前面的一些项来得出序列中的指定项的值。
🍉、递推问题分析的四个步骤
1、确定递推变量
2、建立递推关系
3、确定初始(边界)条件
4、对递推过程进行控制
🍉、递推改变一个位置的通用模板函数
void turn(char &c)
{
if(c == 'W') c = 'B'; //这个状态需要根据每一题题目具体分析
else c = 'W';
}
对递归结果和测试用例的看法:有时候我们的答案和样例会不一样,这是很正常的,我们只要输出一个正确的答案就ok了。
🍎、例题分析
🍇、(AcWing)砖块
本题链接: 砖块
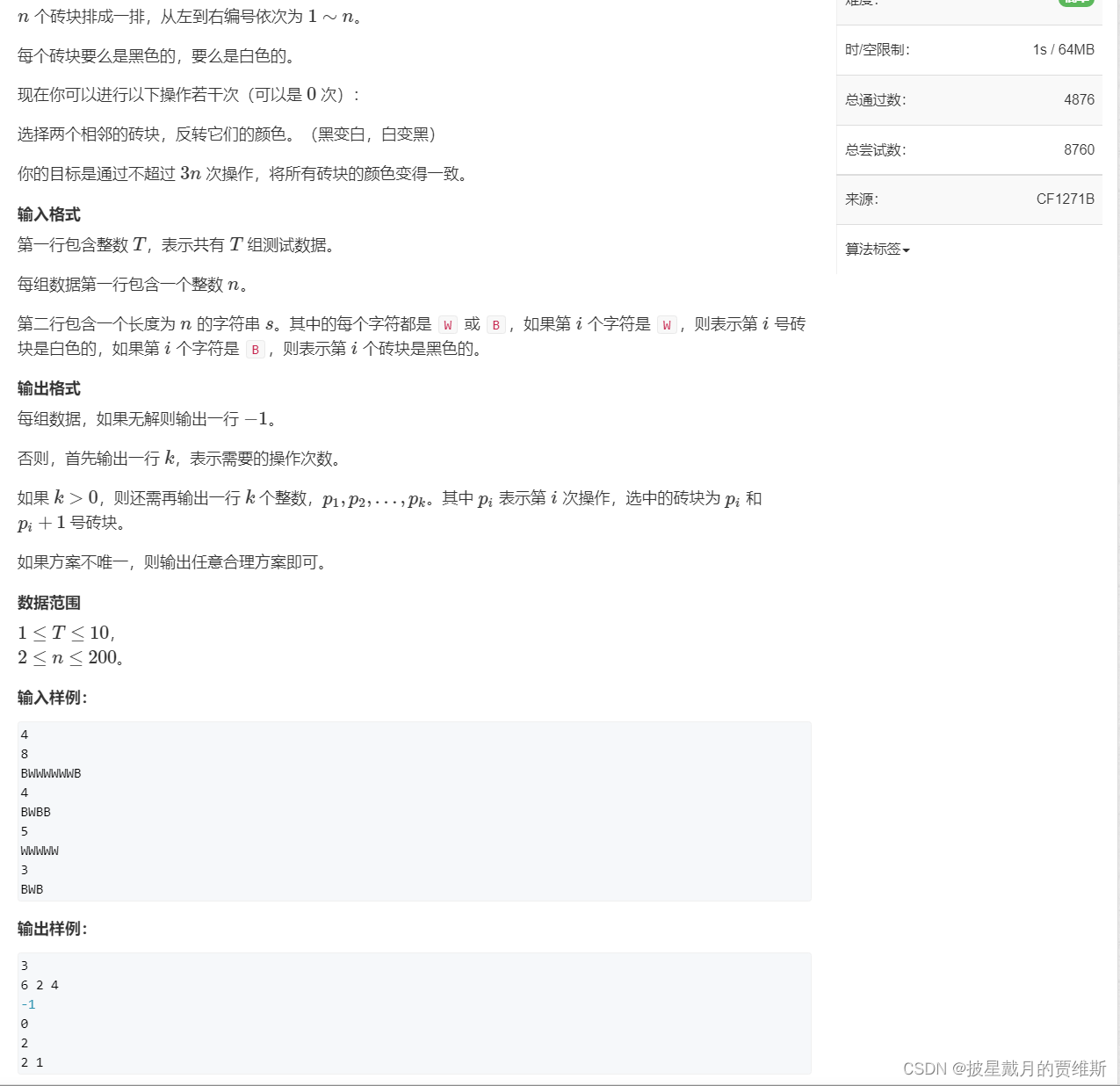
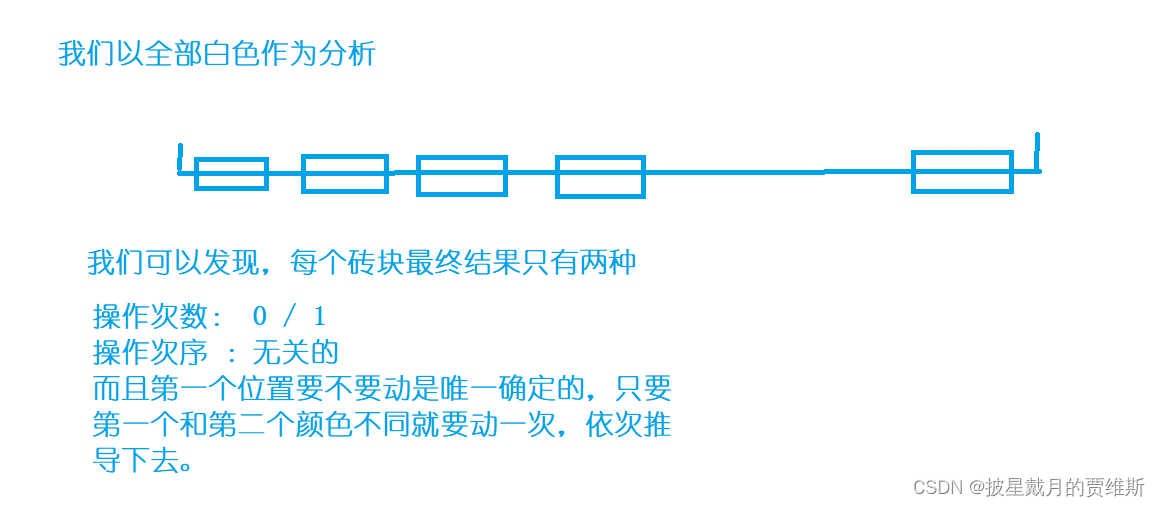
代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 203;
int t, n;
string str;
void update(char &c)
{
if(c == 'W') c = 'B';
else c = 'W';
}
bool cheak(char c)
{
vector<int> res; // 存所有的方案
string s = str; //设置s字符串拷贝原str
for(int i = 0; i + 1 < n; i++)
{
if(s[i] != c)
{
update(s[i]);
update(s[i + 1]);
res.push_back(i);//说明那个位置要被操作一下,要把这个方案记录到res里
}
}
if(s.back() != c) return false;
cout << res.size() << endl;
for(int x : res) cout << x + 1 << " ";
if(res.size()) cout << endl; // 如果方案数为0,直接输出一个回车
return true;
}
int main ()
{
cin >> t;
while(t --)
{
cin >> n >> str;
if(!cheak('W') && !cheak('B')) puts("-1");
}
return 0;
}
🍇、(AcWing)翻硬币
本题链接: 翻硬币

分析解题思路:
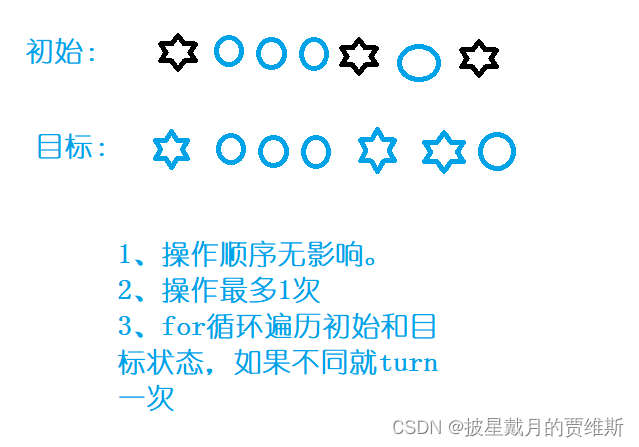
代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string a, b;
void turn(char &c)
{
if(c == 'o') c = '*';
else c = 'o';
}
int main ()
{
cin >> a >> b;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i + 1< a.size(); i++ )
{
if(a[i] != b[i])
{
turn(a[i]);
turn(a[i + 1]);
res++;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
🍇、(AcWing)费解的开关
本题链接: 费解的开关

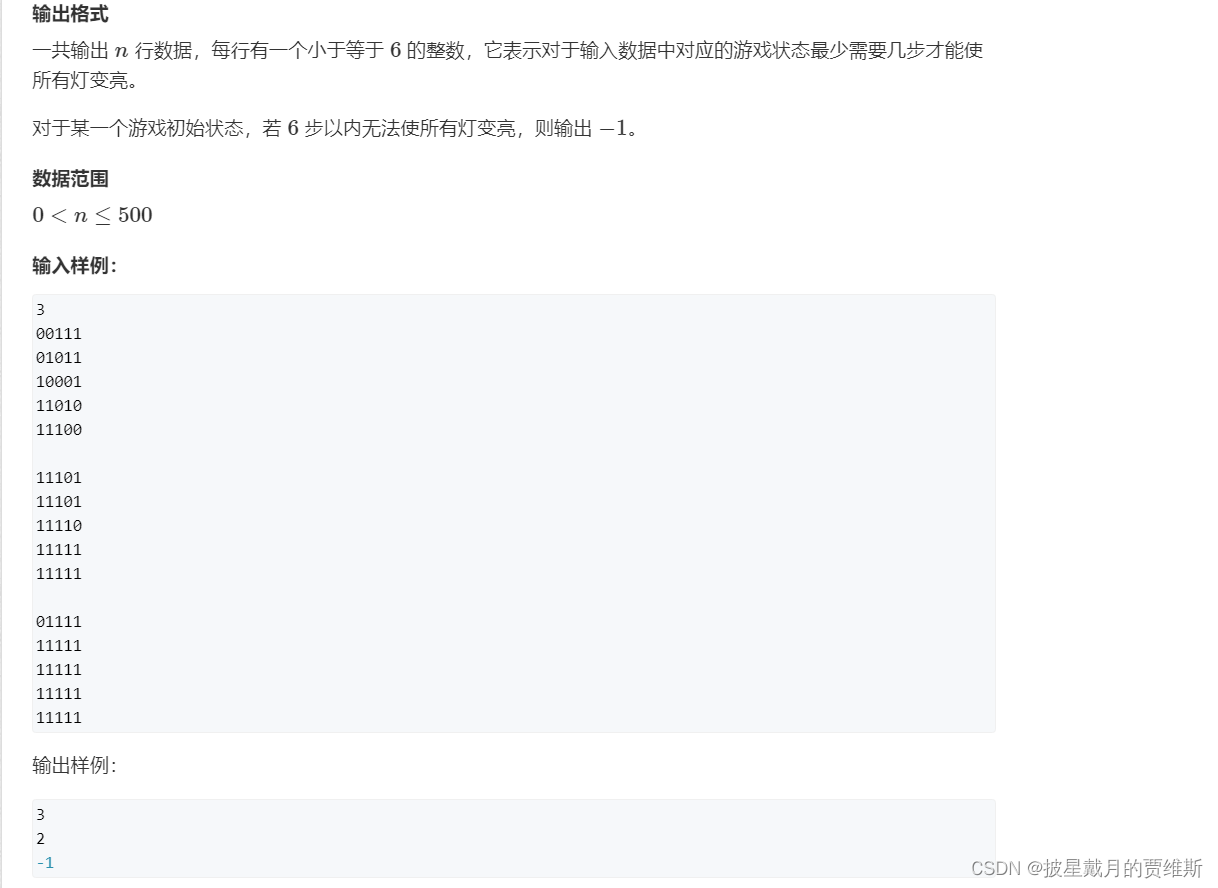
解题分析:
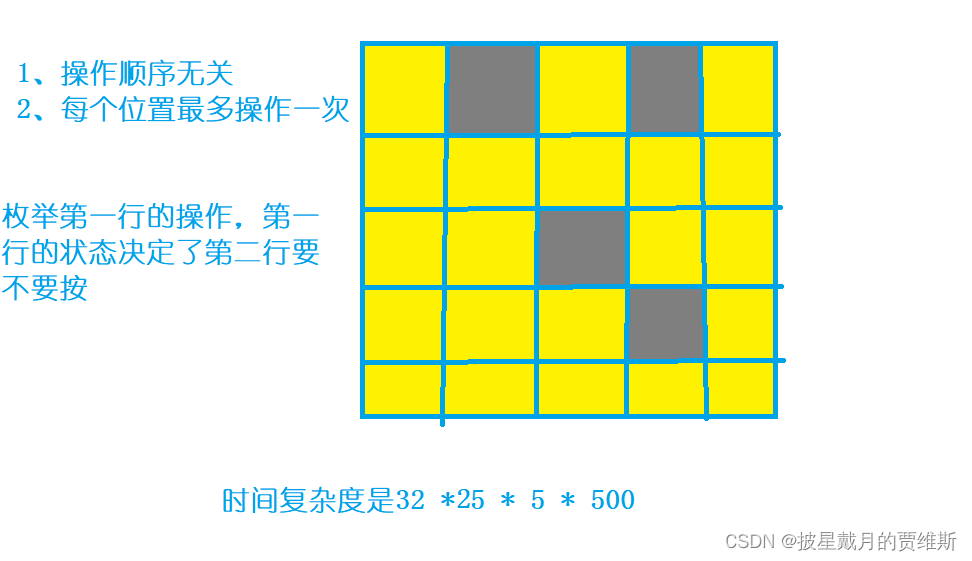 代码示例:
代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 1000000;
const int N = 6;
char g[N][N], backcup[N][N];
int dx[5] = { 0, -1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[5] = { 0, 0, 1, 0, -1};
void turn(int x, int y)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int a = dx[i] + x, b = dy[i] + y;
if(a >= 0 && a < 5 && b >= 0 && b < 5)
{
g[a][b] ^= 1;
}
}
}
int work()
{
int ans = INF;
for(int k = 0 ; k < 32; k++) //k从0枚举到32,是枚举每个位置对应的状态,是不是turn过
{
int res = 0; // 当前方案操作数的最小值
char backcup[N][N];
memcpy(backcup, g, sizeof g);
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)//针对第一层的操作
if(k >> j & 1) //位运算
{
res ++;
turn(0, j);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if(g[i][j] == '0')
{
res++;
turn(i + 1, j);
}
bool is_successful = true;
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
if(g[4][j] == '0')
{
is_successful = false;
break;
}
if(is_successful) ans = min(ans, res);
memcpy(g, backcup, sizeof g);
}
if(ans > 6) ans = -1;
return ans;
}
int main ()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) cin >> g[i];
cout << work() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
🍎、总结
本文简要介绍了递推算法的简要概念和几道递推算法的经典例题,希望大家读后能有所收获!

























 1431
1431











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










