现有两种方式实现Spring事务管理操作,一种是编程式事务管理和声明式事务管理,由于编程式事务管理的操作较为繁琐,故一般选择声明式事务管理。而声明式事务管理又有基于注解方式和基于XML配置文件方式。
注解声明式管理
首先,需要再配置文件中配置事务管理器,引入名称空间tx和开启事务注解:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--开启扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring.sql"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 开启Aspect生成代理对象-->
<!-- <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="86110101" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
</bean>
<!-- JdbcTemplate 对象 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!--注入 dataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--创建事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--开启事务注解-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
</beans> 然后在 service 类上面(或者 service 类里面方法上面)添加事务注解:
(1)@Transactional,这个注解添加到类上面,也可以添加方法上面
(2)如果把这个注解添加类上面,这个类里面所有的方法都添加事务
(3)如果把这个注解添加方法上面,为这个方法添加事务
一个简单的案例:
@Component
public class Usermy {
private String user;
private String password;
private int balance;
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public void setUser(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
}@Component
public class Usermyimpl{
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void add(Usermy um) {
//1 创建 sql 语句
String sql = "insert into user_table values(?,?,?)";
//2 调用方法实现
Object[] args = { um.getUser(),um.getPassword(),um.getBalance()};
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,args);
System.out.println(update);
}
public void addbalance(){
String sql="update user_table set balance=balance+? where user=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,500,"AA");
}
public void delebalance(){
String sql="update user_table set balance=balance-? where user=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,500,"BB");
}
}@Component
@Transactional
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private Usermyimpl usermyimpl;
public void addUS(Usermy um){
usermyimpl.add(um);
}
public void Bal(){ usermyimpl.addbalance();
int i=10/0;//这是手动模拟异常,正常测试可以将这行注释掉
usermyimpl.delebalance();}
}就有测试代码:
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
UserService us = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
us.Bal(); 在添加注解@Transactional可以在注解中配置注解相关参数.
参数propagation:事务传播行为
事务传播行为由传播属性决定,而传播属性分为七类: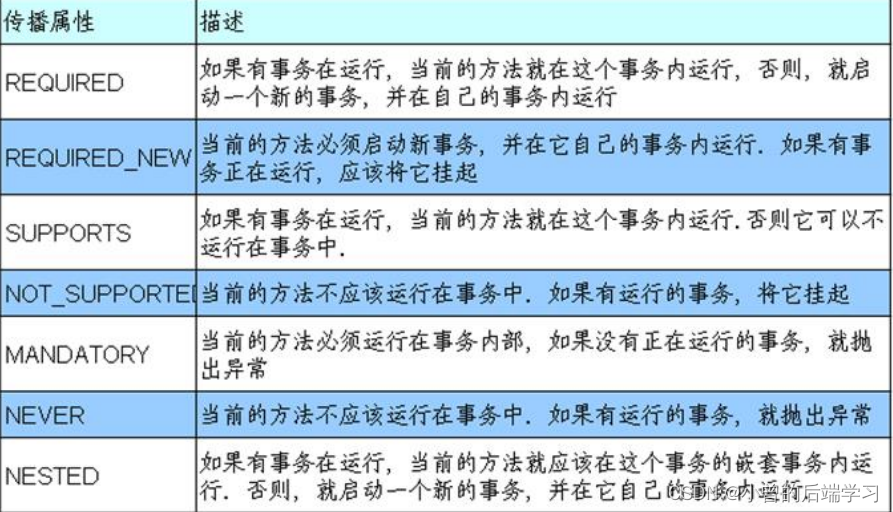
参数ioslation:事务隔离级别
我曾专门写了一篇来介绍事务的隔离级别,我就在这再重复一遍。
(1)事务有特性成为隔离性,多事务操作之间不会产生影响。不考虑隔离性产生很多问题
(2)有三个读问题:脏读、不可重复读、虚(幻)读
(3)脏读:一个未提交事务读取到另一个未提交事务的数据
(4)不可重复读:一个未提交事务读取到另一提交事务修改数据
(5)幻读:一个未提交事务读取到另一提交事务添加数据
不可重复读和幻读的区别在于一个对于一行数据,一个是对应一个范围内的数据。
我们可以通过设立事务隔离级别解决读问题: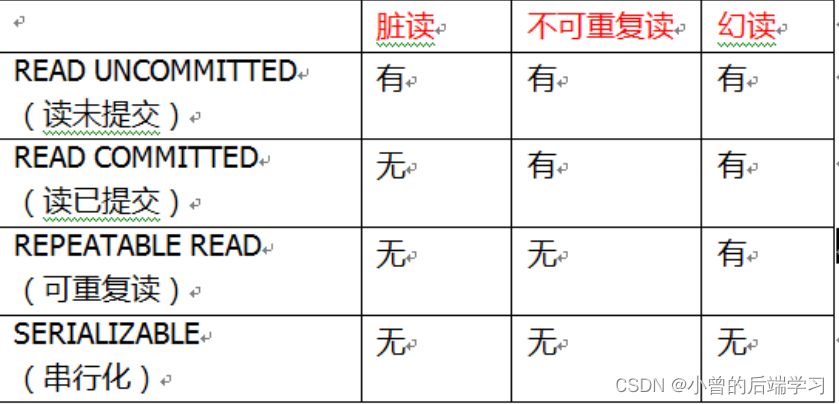
参数timeout:超时时间
(1)事务需要在一定时间内进行提交,如果不提交进行回滚。
(2)默认值是 -1 ,设置时间以秒单位进行计算。
参数readOnly:是否只读
(1)读:查询操作,写:添加修改删除操作。
(2)readOnly 默认值 false,表示可以查询,可以添加修改删除操作。
(3)设置 readOnly 值是 true,设置成 true 之后,只能查询。
参数rollbackFor:回滚
(1)设置出现哪些异常进行事务回滚。
参数noRollbackFor:不回滚
(1)设置出现哪些异常不进行事务回滚 。
XML式事务管理
在 spring 配置文件中进行配置:
第一步 配置事务管理器
第二步 配置通知
第三步 配置切入点和切面
接下来就是配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--开启扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring.sql"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 开启Aspect生成代理对象-->
<!-- <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="86110101" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
</bean>
<!-- JdbcTemplate 对象 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!--注入 dataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--创建事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--2 配置通知-->
<tx:advice id="txadvice">
<!--配置事务参数-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--指定哪种规则的方法上面添加事务-->
<tx:method name="Bal" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<!--<tx:method name="account*"/>-->
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--3 配置切入点和切面-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(*
com.spring.sql.UserService.*(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>就有测试代码:
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
UserService us = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
us.Bal();




















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








