总序:代码块中,第一部分为Main函数中代码,下半部分为相应的函数。
1.编写程序判断一个给定的关系R是否是等价关系
要求:
输入: 输入的关系中的每个元素均为自然数;
输出: R是否是等价关系
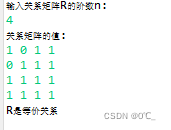
System.out.println("输入关系矩阵R的阶数n:");
int n;
n = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("关系矩阵的值:");
int [][] R = new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j ++) {
R[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
if(dengjia(R)) {
System.out.println("R是等价关系");
}else System.out.println("R不是等价关系");
public static boolean dengjia(int[][] r) {
int zifan = 1;
int duicheng = 1;
int chuandi = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < r.length; i ++) {
if(r[i][i] != 1) {
return false;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i< r.length; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < r.length; j ++) {
if(r[i][j] != r[j][i]) {
return false;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < r.length; i ++) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < r.length; j ++) {
for(int k = j + 1; k < r.length; k ++) {
if(r[i][j] == 1 && r[j][k] == 1 && r[i][k] != 1) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}运行结果展示:
2.编写函数,输出一个斐波那契数列
要求:
输入:一个自然数a;
输出:小于等于a的一个斐波那契数列
System.out.println("请输入a的值:");
int a = sc.nextInt();
LinkedList<Integer> li = new LinkedList<>();
li = feibo(a);
for(int i = 0; i < li.size(); i ++) {
System.out.print(li.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
public static LinkedList<Integer> feibo(int a) {
LinkedList<Integer>fbnq = new LinkedList<>();
fbnq.add(0);
fbnq.add(1);
while(fbnq.get(fbnq.size() - 1) + fbnq.get(fbnq.size() - 2) < a) {
fbnq.add(fbnq.get(fbnq.size() - 1) + fbnq.get(fbnq.size() - 2));
}
return fbnq;
}运行结果展示:

3.给定两个集合A和B,
的笛卡尔积。
输入: 集合A中的元素时字符,集合B中的元
素时自然数
要求:
输出:A和B的笛卡尔积
LinkedList<Integer> B = new LinkedList<>();
String A;
System.out.println("请输入A的值:");
A = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入B的值:(输入#结束)");
while(!sc.hasNext("#")) {
B.add(sc.nextInt());
}
LinkedList<LinkedList> dkj = new LinkedList<>();
dkj = dikaer(A.toCharArray(), B);
for (LinkedList<Integer> list : dkj) {
System.out.print("(" + (char)(list.get(0) + 'A') + ", " + list.get(1) + ")" + " ");
}
System.out.println();
public static LinkedList<LinkedList> dikaer(char A[], LinkedList<Integer> B) {
//A * B
LinkedList<LinkedList> dkj = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < B.size(); j ++) {
LinkedList<Integer> li = new LinkedList<>();
li.add(A[i] - 'A');
li.add(B.get(j));
dkj.add(new LinkedList<>(li));
}
}
return dkj;
}运行结果展示:

4.编写函数,实现集合的并、交、差和补运算
输入: 集合A和B,集合A和B中的元素均为自然数
输出: 集合A和B的并、交、差和补集合
LinkedList<Integer> B = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> A = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.println("请输入A的值:(输入#结束)");
while (true) {
if (sc.hasNextInt()) {
A.add(sc.nextInt());
} else if (sc.hasNext("#")) {
sc.next();
break; // 结束A的输入
}
}
System.out.println("请输入B的值:(输入#结束)");
while (true) {
if (sc.hasNextInt()) {
B.add(sc.nextInt());
} else if (sc.hasNext("#")) {
sc.next();
break; // 结束A的输入
}
}
LinkedList<LinkedList> re = new LinkedList<>();
re = yunsuan(A, B);
int cnt = 0;
for(LinkedList<Integer> list : re) {
if(cnt == 0) System.out.print("并集: ");
if(cnt == 1) System.out.print("A 交 B: ");
if(cnt == 2) System.out.print("A - B: ");
if(cnt == 3) System.out.print("A - B 并 B - A: ");
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i ++) {
System.out.print("(" + list.get(i) + ")" + " ");
}
System.out.println();
cnt ++;
}
System.out.println();
public static LinkedList<LinkedList> yunsuan(LinkedList<Integer> A, LinkedList<Integer> B){
// result[0]存放 A并B的结果,result[1]存放 A交B的结果,result[2]存放 A-B的结果,result[3]存放A - B并 B - A
//并运算
LinkedList<LinkedList> result = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> set = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for(int i = 0; i < A.size(); i ++) {// 存放A
set.add(A.get(i));
}
for(int i = 0; i < B.size(); i ++) {// 存放B
set.add(B.get(i));
}
result.add(new LinkedList<>(set));
//交运算-> A交B
HashMap<Integer, Integer>map = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<Integer, Integer>map2 = new HashMap<>();
LinkedList<Integer> li = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < A.size(); i ++) {
if(!map.containsKey(A.get(i))) {//把A中的元素放入map中
map.put(A.get(i), 1);
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < B.size(); i ++) {
if(!map2.containsKey(B.get(i))) {
map2.put(B.get(i), 1);
}
if(map.containsKey(B.get(i))) {//遍历map中的元素,若map中含有,则将其删除。
map.remove(B.get(i));
li.add(B.get(i));
}
}//之后map中剩余的元素就是A - B的结果。
result.add(new LinkedList<>(li));
//差运算-> A - B = A - A交B;
li.clear();
for(Integer key: map.keySet()) {
li.add(key);
}
result.add(new LinkedList<>(li));
//补集合 A - B 并 B - A
li.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < result.get(result.size() - 2).size(); i ++) {
int re = (int) result.get(result.size() - 2).get(i);
if(!map2.containsKey(re)) {
li.add(re);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < result.get(result.size() - 1).size(); i ++) {
int re = (int) result.get(result.size() - 1).get(i);
li.add(re);
}
result.add(new LinkedList<>(li));
return result;
}运行结果展示:

5.给定一个任意的自然数集合,将该集合按模5同余
关系分成5个等价类。
int[] A = new int[30];
Random r = new Random();
for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i ++) {
A[i] = r.nextInt(200) + 1;
}
LinkedList<LinkedList> re = new LinkedList<>();
re = five(A);
int cnt = 0;
for(LinkedList<Integer> list : re) {
System.out.print(cnt + "{");
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i ++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + ", ");
}
System.out.println("}");
cnt ++;
}
System.out.println();
public static LinkedList<LinkedList> five(int[] A){
LinkedList<LinkedList> result = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> zero = new LinkedList<>();//模5余0,以此类推
LinkedList<Integer> one = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> two = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> three = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> four = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i ++) {
if(A[i] % 5 == 0) {
zero.add(A[i]);
}
if(A[i] % 5 == 1) {
one.add(A[i]);
}
if(A[i] % 5 == 2) {
two.add(A[i]);
}
if(A[i] % 5 == 3) {
three.add(A[i]);
}
if(A[i] % 5 == 4) {
four.add(A[i]);
}
}
result.add(new LinkedList<>(zero));
result.add(new LinkedList<>(one));
result.add(new LinkedList<>(two));
result.add(new LinkedList<>(three));
result.add(new LinkedList<>(four));
return result;
}运行结果展示:






















 2052
2052











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








