binder相关学习都是参考老罗和邓凡平的相关文章学习总结的,
自己在学习的过程中,发现画图总结比较容易记忆,这里分享出来!!
当然如果你看过老罗或者邓凡平的博客,再来看看该篇博客也许效果会更好!!
关于Binder的java层机制讲解,大概会分为三篇博客讲解
Android Binder机制原理java层系列一(有图有代码很详细)
Android Binder机制原理java层系列二(有图有代码很详细)
Android Binder机制原理java层系列三(有图有代码很详细)
因为下面说到了aidl,这里给出aidl的类结构
(这里大家可以不用细看,直接看下面的画图即可,图中说到了aidl可以再回头看看)
interface IDonService {
void addService(in ServiceBean serviceBean);
ServiceBean getService();
int myPid();
}看下编译后的类结构
public interface IDonService extends android.os.IInterface {
/**
* Local-side IPC implementation stub class.
*/
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.rain.meter.main.lib.IDonService {
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.rain.meter.main.lib.IDonService";
/**
* Construct the stub at attach it to the interface.
*/
public Stub() {
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.rain.meter.main.lib.IDonService interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.rain.meter.main.lib.IDonService asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.rain.meter.main.lib.IDonService))) {
return ((com.rain.meter.main.lib.IDonService) iin);
}
return new com.rain.meter.main.lib.IDonService.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_addService: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
com.rain.meter.main.lib.bean.ServiceBean _arg0;
if ((0 != data.readInt())) {
_arg0 = com.rain.meter.main.lib.bean.ServiceBean.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
} else {
_arg0 = null;
}
this.addService(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getService: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
com.rain.meter.main.lib.bean.ServiceBean _result = this.getService();
reply.writeNoException();
if ((_result != null)) {
reply.writeInt(1);
_result.writeToParcel(reply, android.os.Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
} else {
reply.writeInt(0);
}
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_myPid: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _result = this.myPid();
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
private static class Proxy implements com.rain.meter.main.lib.IDonService {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() {
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override
public void addService(com.rain.meter.main.lib.bean.ServiceBean serviceBean) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if ((serviceBean != null)) {
_data.writeInt(1);
serviceBean.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
} else {
_data.writeInt(0);
}
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_addService, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public com.rain.meter.main.lib.bean.ServiceBean getService() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
com.rain.meter.main.lib.bean.ServiceBean _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getService, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
if ((0 != _reply.readInt())) {
_result = com.rain.meter.main.lib.bean.ServiceBean.CREATOR.createFromParcel(_reply);
} else {
_result = null;
}
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
@Override
public int myPid() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_myPid, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
static final int TRANSACTION_addService = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
static final int TRANSACTION_getService = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1);
static final int TRANSACTION_myPid = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 2);
}
public void addService(com.rain.meter.main.lib.bean.ServiceBean serviceBean) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public com.rain.meter.main.lib.bean.ServiceBean getService() throws android.os.RemoteException;
public int myPid() throws android.os.RemoteException;
}实现IDonservice.Stub
public class DonService extends Service {
private ServiceBean mServiceBean;
private IBinder mIBinder = new IDonService.Stub() {
@Override
public void addService(ServiceBean serviceBean) throws RemoteException {
mServiceBean = serviceBean;
}
@Override
public ServiceBean getService() throws RemoteException {
return mServiceBean;
}
@Override
public int myPid() {
return Process.myPid();
}
};
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Thread.currentThread().getName());
return mIBinder;
}
}具体看下在哪里使用
public class Donmain {
private IDonService iDonService;
private volatile static Donmain instance;
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//连接后拿到 Binder,转换成 AIDL,在不同进程会返回个代理
iDonService = IDonService.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
iDonService = null;
}
};
private Donmain(){}
public static Donmain getInstance(){
if (instance == null){
synchronized (Donmain.class){
if (instance == null){
instance = new Donmain();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
public void getService(Context context){
Intent intent1 = new Intent(context.getApplicationContext(), DonService.class);
context.bindService(intent1, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
if (iDonService != null){
try {
int pid = iDonService.myPid();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}Binder机制在java层,主要通过ServiceManager,Service和Client
1.ServiceManager主要把各种系统服务add到系统中管理
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, this, true);2.Service就是我们提供远程接口服务一端,即实现了Binder接口的类
列举几个:
1.我们经常写的aidl
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.rain.meter.main.lib.IDonService
2.ServiceManager的真正管理者,ServiceManagerNative
/**
* Native implementation of the service manager. Most clients will only
* care about getDefault() and possibly asInterface().
* @hide
*/
public abstract class ServiceManagerNative extends Binder implements IServiceManager看到没,他们都继承了Binder接口,即有了跨进程通信的能力,
但是这里注意下,他们都是abstract,那么具体实现方法肯定在实现类中完成
1.aidl的实现类很简单,就是我们经常写的这种格式,
即IBinder mIBinder = new IDonService.Stub
public class DonService extends Service {
private ServiceBean mServiceBean;
private IBinder mIBinder = new IDonService.Stub() {
@Override
public void addService(ServiceBean serviceBean) throws RemoteException {
mServiceBean = serviceBean;
}
@Override
public ServiceBean getService() throws RemoteException {
return mServiceBean;
}
@Override
public int myPid() {
return Process.myPid();
}
};
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Thread.currentThread().getName());
return mIBinder;
}
}
2.ServiceManagerNative的实现,看这个类的注释就会发现,
类很特别,它是在IServiceManager.cpp文件中实现的,看下部分代码
namespace android {
sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager()
{
if (gDefaultServiceManager != NULL) return gDefaultServiceManager;
{
AutoMutex _l(gDefaultServiceManagerLock);
while (gDefaultServiceManager == NULL) {
gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(
ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL));
if (gDefaultServiceManager == NULL)
sleep(1);
}
}
return gDefaultServiceManager;
}
好了以上就是提供服务的Service端内容,他们肯定都是继承或者实现了IBinder(Binder实现了IBinder),即有了跨进程通信的能力后,才能提供服务
3.Client端,就是获取服务的一端,这个很容易理解
1.对于aidl即我们获取aidl服务的地方
context.bindService(intent1, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
然后在mConnection的onServiceConnected中:IDonService.Stub.asInterface(service);
然后使用远程服务iDonService的各种方法
2.ServiceManager即我们get或者add服务的地方
getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, this, true);ServiceManager,Service和Client之间到底是如何通信的
Client端要使用Service提供的远程服务,首先必须从ServiceManager那里获取Service的服务,
IDonService.Stub.asInterface(service);
getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);1.但是呢,这里获取到的不是真正的Service,而是它的代理Proxy,
2.这个代理并没有继承或者实现Binder相关类或者接口,它本身不具备跨进程通信能力,
3.但是代理里面有个mRemote,这才是一个实现了IBinder的类,即BinderProxy(下面会详细说到BinderProxy都是啥)
4.当我们获取Service或者使用Service提供的方法时,就和Binder底层驱动交互了
5.底层Binder驱动又和ServiceManager交互
6.ServiceManager通过驱动又和Service交互
这里大家一定要知道,对于整个通信过程
Client要通过BinderProxy-->它的Native层映射就是BpBinder
Service要通过Binder-->它的Native层映射就是JavaBBinder
上个图感受下!
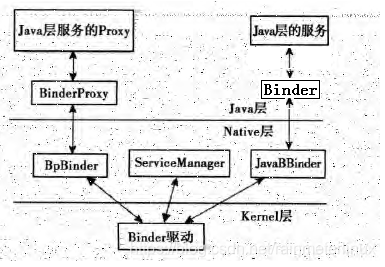
注意,图片有点大,要点击原图查看
下面先说点基础知识
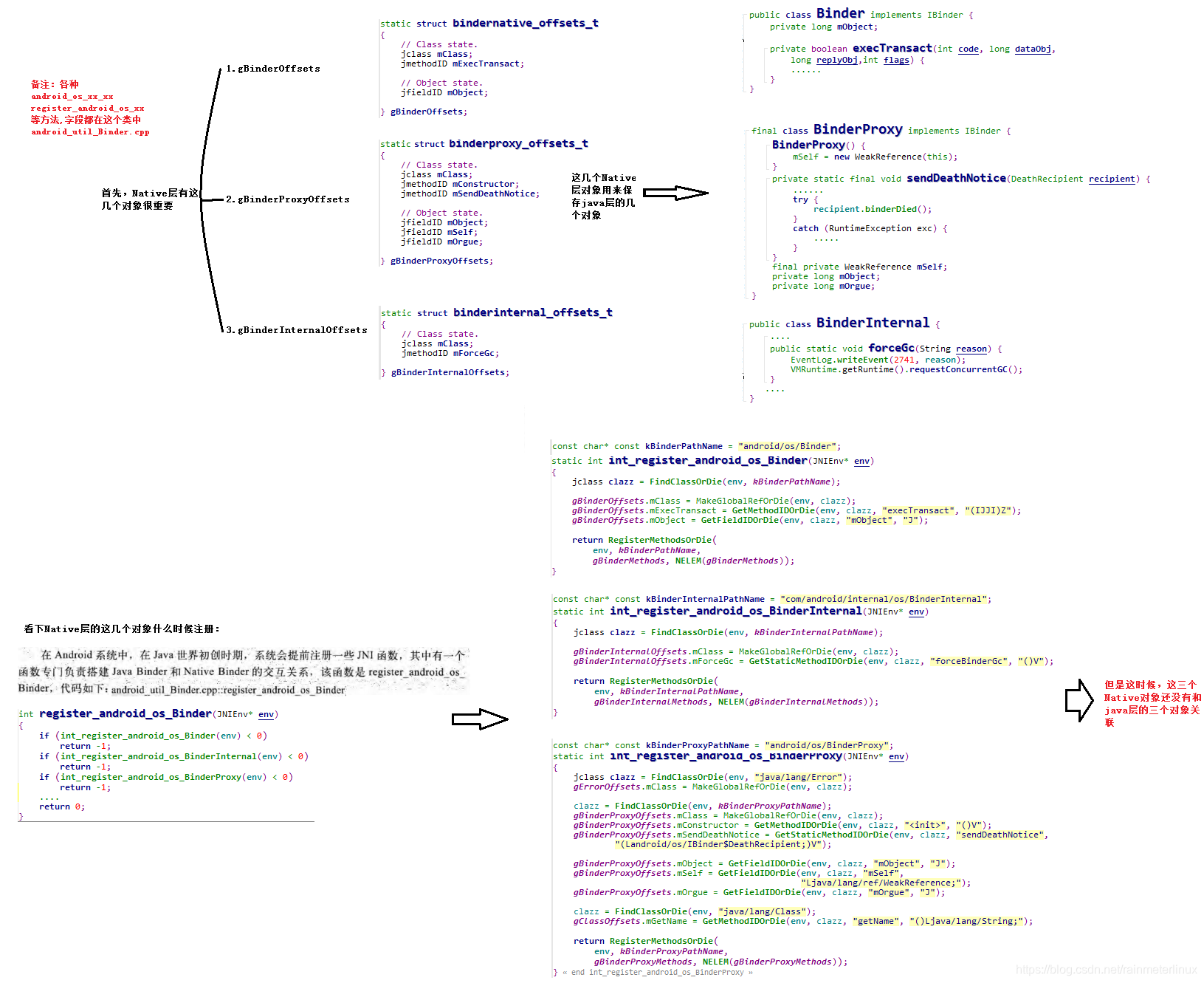
上图中gBinderOffsets和gBinderProxyOffsets顾名思义了
gBinderInternalOffsets以及它对应的java层BinderInternal类,它们都是Binder层用的类,我们一般开发程序不会使用,它的内部有个GcWatcher,该类用来处理和Binder架构有关的垃圾回收
下一篇我会详细讲解getService和addService,从里面引出上面各个对象之间的关系,相信你看完该篇博客会对Binder(java层)有个详细了解
























 1195
1195

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








