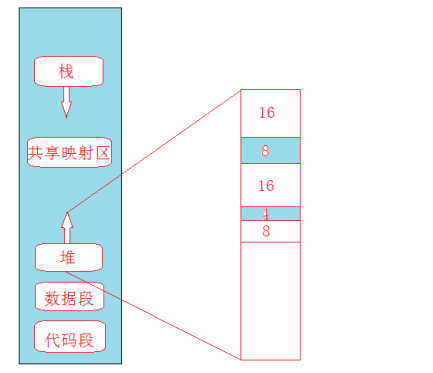
系统已经提供了动态分配内存的接口,malloc(),new(),为什么需要空间配置器?
空间配置器的存在是为了解决1)容器申请内存时产生的内存碎片问题2)频繁分配小块内存,效率太低
关于内存碎片,举一个例子:
假设系统依次分配了16Byte、8Byte、16Byte、4Byte,还剩余8Byte未分配,后来操作系统回收了上面的两个16byte,总的剩余空间有40byte,这时,操作系统想再分配24Byte,但是却不能分配出一个连续24Byte的空间,这就是内存碎片问题,事实上,这种内存碎片问题叫做外碎片,还有一种内存碎片问题叫做内碎片,后面会说到。
STL空间配置器的框架设计
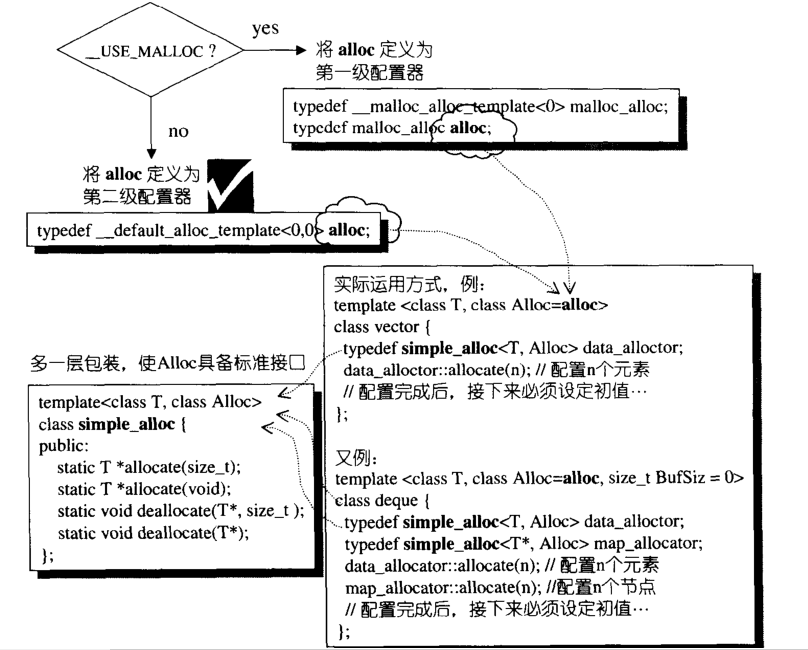
1)有一级空间配置器和二级空间配置器
2)通过__USE_MALLOC宏配置判断是否使用二级空间配置器
关于内存池:
在二级空间配置器中的核心就是内存池,它管理着自由链表
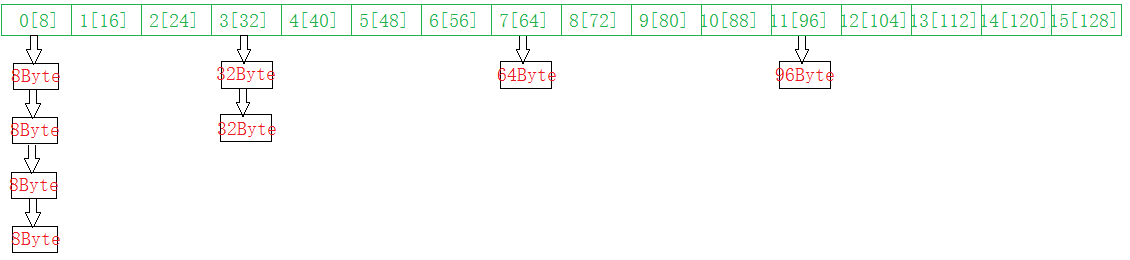
1)当一个容器需要分配内存时,如果需要的内存大小大于128个字节,就去一级空间配置器,小于就去二级空间配置器。
2)先去自由链表取,如果需要7个字节,就取8Byte的内存块,如果需要9字节就取16Byte的内存块,这也就是内碎片的问题。如果自由链表为空,就调用refill函数,从内存池中取出内存块挂到自由链表。
这两步都是allocate()函数干的事~~~
3)refill()函数会调用chunk_alloc()函数,函数返回20个所需内存块(如果不够,能分配多少分配多少),返回第一个内存块,剩余的挂到自由链表。
4)chunk_alloc()函数负责从内存池中取内存,如果内存池中的内存足够,bytes_left >= total_bytes ,则直接从内存池中取;内存池中的内存不足,但是够一个bytes_left >= size,则直接取能够取出来的;内存池中的内存不足,则从系统堆分配大块内存到内存池中。
源码:
<span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;">//</span><span style="color:#ff0000;font-family: 'Microsoft YaHei';">一级空间配置器,用来处理内存不足的情况</span><span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;">
template <int inst>
class __malloc_alloc_template {
private:
static void *oom_malloc(size_t);
static void *oom_realloc(void *, size_t);
public:
static void * allocate(size_t n)
{
void *result = malloc(n);
if (0 == result) result = oom_malloc(n);
return result;
}
static void deallocate(void *p, size_t /* n */)
{
free(p);
}
static void * reallocate(void *p, size_t /* old_sz */, size_t new_sz)
{
void * result = realloc(p, new_sz);
if (0 == result) result = oom_realloc(p, new_sz);
return result;
}
static void (* set_malloc_handler(void (*f)()))()
{
void (* old)() = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
__malloc_alloc_oom_handler = f;
return(old);
}
};
// malloc_alloc out-of-memory handling
#ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
template <int inst>
void (* __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = 0;
#endif
template <int inst>
void * __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::oom_malloc(size_t n)
{
void (* my_malloc_handler)();
void *result;
for (;;) {
my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
if (0 == my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }
(*my_malloc_handler)();
result = malloc(n);
if (result) return(result);
}
}
template <int inst>
void * __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::oom_realloc(void *p, size_t n)
{
void (* my_malloc_handler)();
void *result;
for (;;) {
my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
if (0 == my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }
(*my_malloc_handler)();
result = realloc(p, n);
if (result) return(result);
}
}
...
# ifdef __USE_MALLOC
typedef malloc_alloc alloc;
typedef malloc_alloc single_client_alloc;
# else
//二级空间配置器
template <bool threads, int inst>
class __default_alloc_template {
private:
...
enum {__ALIGN = 8}; //排列间隔
enum {__MAX_BYTES = 128}; //最大值
enum {__NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES/__ALIGN}; //自由链表大小
static size_t ROUND_UP(size_t bytes) { //将byte向上调整为8的倍数
return (((bytes) + __ALIGN-1) & ~(__ALIGN - 1));
}
__PRIVATE:
union obj { //自由链表的结点
union obj * free_list_link;
char client_data[1]; /* The client sees this. */
};
...
static size_t FREELIST_INDEX(size_t bytes) { //计算要使用自由链表中的哪一个下标的内存块,从1开始算
return (((bytes) + __ALIGN-1)/__ALIGN - 1);
}
static void *refill(size_t n);
...
static char *chunk_alloc(size_t size, int &nobjs);
static char *start_free; //内存池的起始位置
static char *end_free; //内存池的结束位置
static size_t heap_size; //从系统堆分配的总内存
...
public:
__default_alloc_template() {
// This assumes the first constructor is called before threads
// are started.
if (!__node_allocator_lock_initialized) {
InitializeCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock);
__node_allocator_lock_initialized = true;
}
}
...
public:
static void * allocate(size_t n)
{
obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list;
obj * __RESTRICT result;
if (n > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES) {
return(malloc_alloc::allocate(n));
}
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
result = *my_free_list;
if (result == 0) {
void *r = refill(ROUND_UP(n));
return r;
}
*my_free_list = result -> free_list_link;
return (result);
};
//释放空间,不是还给操作系统,而是插到自由链表
static void deallocate(void *p, size_t n)
{
obj *q = (obj *)p;
obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list;
if (n > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES) {
malloc_alloc::deallocate(p, n);
return;
}
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
...
q -> free_list_link = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = q;
}
static void * reallocate(void *p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz);
} ;
typedef __default_alloc_template<__NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS, 0> alloc;
typedef __default_alloc_template<false, 0> single_client_alloc;
char* __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::chunk_alloc(size_t size, int& nobjs)
{
char * result;
size_t total_bytes = size * nobjs;
size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free;
if (bytes_left >= total_bytes) {
result = start_free;
start_free += total_bytes;
return(result);
} else if (bytes_left >= size) {
nobjs = bytes_left/size;
total_bytes = size * nobjs;
result = start_free;
start_free += total_bytes;
return(result);
} else {
size_t bytes_to_get = 2 * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> 4);
// Try to make use of the left-over piece.
if (bytes_left > 0) {
obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list =
free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left);
((obj *)start_free) -> free_list_link = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = (obj *)start_free;
}
start_free = (char *)malloc(bytes_to_get);
if (0 == start_free) {
int i;
obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list, *p;
// Try to make do with what we have. That can't
// hurt. We do not try smaller requests, since that tends
// to result in disaster on multi-process machines.
for (i = size; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN) {
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i);
p = *my_free_list;
if (0 != p) {
*my_free_list = p -> free_list_link;
start_free = (char *)p;
end_free = start_free + i;
return(chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));
// Any leftover piece will eventually make it to the
// right free list.
}
}
end_free = 0; // In case of exception.
start_free = (char *)malloc_alloc::allocate(bytes_to_get);
// This should either throw an
// exception or remedy the situation. Thus we assume it
// succeeded.
}
heap_size += bytes_to_get;
end_free = start_free + bytes_to_get;
return(chunk_alloc(size, nobjs));
}
}
template <bool threads, int inst>
void* __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::refill(size_t n)
{
int nobjs = 20;
char * chunk = chunk_alloc(n, nobjs);
obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list;
obj * result;
obj * current_obj, * next_obj;
int i;
if (1 == nobjs) return(chunk);
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
result = (obj *)chunk;
*my_free_list = next_obj = (obj *)(chunk + n);
for (i = 1; ; i++) {
current_obj = next_obj;
next_obj = (obj *)((char *)next_obj + n);
if (nobjs - 1 == i) {
current_obj -> free_list_link = 0;
break;
} else {
current_obj -> free_list_link = next_obj;
}
}
return(result);
}
template <bool threads, int inst>
void*__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::reallocate(void *p, size_t old_sz,size_t new_sz)
{
void * result;
size_t copy_sz;
if (old_sz > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES && new_sz > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES) {
return(realloc(p, new_sz));
}
if (ROUND_UP(old_sz) == ROUND_UP(new_sz)) return(p);
result = allocate(new_sz);
copy_sz = new_sz > old_sz? old_sz : new_sz;
memcpy(result, p, copy_sz);
deallocate(p, old_sz);
return(result);
}
</span>























 181
181

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








