Write a function to reverse a linked list
Iterative Method
Iterate trough the linked list. In loop, change next to prev, prev to current and current to next.
Implementation of Iterative Method
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
/* Link list node */
struct
node
{
int
data;
struct
node* next;
};
/* Function to reverse the linked list */
static
void
reverse(
struct
node** head_ref)
{
struct
node* prev = NULL;
struct
node* current = *head_ref;
struct
node* next;
while
(current != NULL)
{
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
*head_ref = prev;
}
/* Function to push a node */
void
push(
struct
node** head_ref,
int
new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct
node* new_node =
(
struct
node*)
malloc
(
sizeof
(
struct
node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void
printList(
struct
node *head)
{
struct
node *temp = head;
while
(temp != NULL)
{
printf
(
"%d "
, temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
/* Drier program to test above function*/
int
main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct
node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 85);
printList(head);
reverse(&head);
printf
(
"\n Reversed Linked list \n"
);
printList(head);
getchar
();
}
|
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Recursive Method:
1) Divide the list in two parts - first node and rest of the linked list. 2) Call reverse for the rest of the linked list. 3) Link rest to first. 4) Fix head pointer
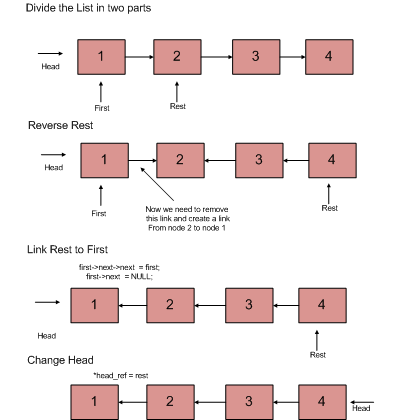
void
recursiveReverse(
struct
node** head_ref)
{
struct
node* first;
struct
node* rest;
/* empty list */
if
(*head_ref == NULL)
return
;
/* suppose first = {1, 2, 3}, rest = {2, 3} */
first = *head_ref;
rest = first->next;
/* List has only one node */
if
(rest == NULL)
return
;
/* reverse the rest list and put the first element at the end */
recursiveReverse(&rest);
first->next->next = first;
/* tricky step -- see the diagram */
first->next = NULL;
/* fix the head pointer */
*head_ref = rest;
}
|
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
References:
http://cslibrary.stanford.edu/105/LinkedListProblems.pdf





 本文介绍两种链表反转的方法:迭代法和递归法,并提供C语言实现代码。迭代法通过循环改变节点指针指向完成反转;递归法则将链表分为两部分进行反转链接。
本文介绍两种链表反转的方法:迭代法和递归法,并提供C语言实现代码。迭代法通过循环改变节点指针指向完成反转;递归法则将链表分为两部分进行反转链接。
















 621
621

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








