正规的方法, 创建一个deamon进程,需要很多步骤
1. fork()
2. 子进程setsid()
3. 主进程wait()
4. chdir()
5. umask()
非正规方法创建一个deamon进程的步骤:
1. 创建一个子进程fork(), 创建子进程的目的是为了后面的设置进程组ID.
2. 子进程执行setsid(), 执行setsid()有两个目的, 一是创建一个新的会话,二是设置进程组ID.
3. 主进程wait()
每个函数都有他的意义.稍后再研究一下:
创建一个deamon进程
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int n = fork();
pid_t pid;
fprintf(stdout, "PID:%d, PGID:%d, SID:%d\n", getpid(), getpgrp(), getsid(0));
int stat = 0;
if (n > 0) {
pid_t x = wait(&stat);
printf("child pid=%d\n", x);
if(WIFEXITED(stat) == 0) {
printf("child normal exited!\n");
}
} else if (n == 0) {
if(setsid() < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "setsid error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
while(1) {
printf("child.\n");
sleep(1);
}
}
return 0;
}输出:
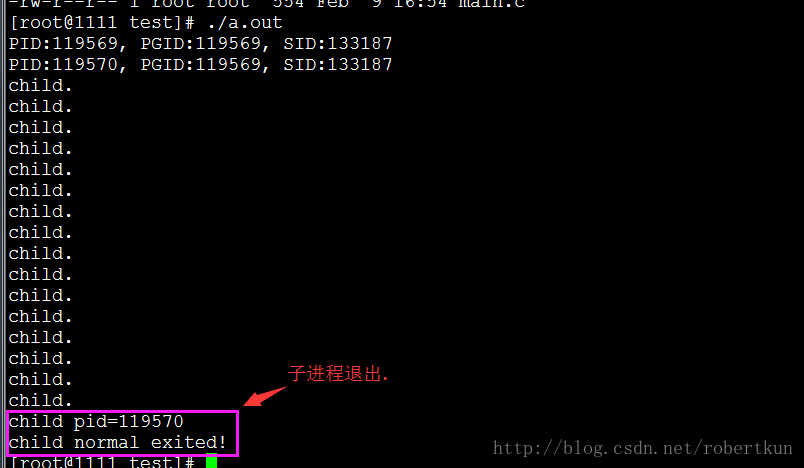
子进程退出后, 主进程仍然能正确启动子进程的demo:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
while(1) {
int n = fork();
pid_t pid;
fprintf(stdout, "PID:%d, PGID:%d, SID:%d\n", getpid(), getpgrp(), getsid(0));
int stat = 0;
if (n > 0) {
pid_t x = wait(&stat);
printf("child pid=%d\n", x);
if(WIFEXITED(stat) == 0) {
printf("child normal exited!\n");
}
} else if (n == 0) {
if(setsid() < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "setsid error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
while(1) {
printf("child.\n");
sleep(1);
}
}
sleep(5);
}
return 0;
}输出:
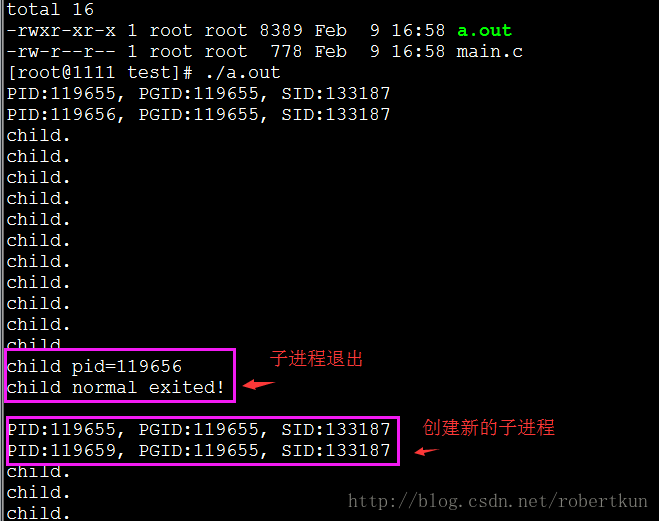
僵尸进程:
僵尸进程, 是指子进程先于父进程退出, 且退出时, 父进程没有收到子进程的退出信号.
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int n = fork();
pid_t pid;
fprintf(stdout, "PID:%d, PGID:%d, SID:%d\n", getpid(), getpgrp(), getsid(0));
if (n > 0) {
while(1) {
printf("parent.\n");
sleep(1);
}
} else if (n == 0) {
printf("child.\n");
}
return 0;
}输出:







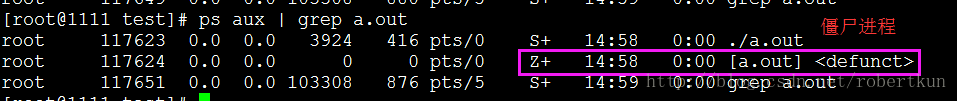














 725
725











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








