效果


实践
有时候AI生成的结果我们并不满意在进入下一步之前,我们需要对AI生成的结果进行人工审核,同意了才能进入下一个流程。
Human_Evaluation就是人工判断的一个简单示例。
internal classProgram
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
// Load .env file
DotEnv.Load();
// Get environment variables from .env file
var envVars = DotEnv.Read();
string ModelName = envVars["ModelName"];
string EndPoint = envVars["EndPoint"];
string ApiKey = envVars["ApiKey"];
Utils.ModelName = ModelName;
Utils.EndPoint = EndPoint;
Utils.ApiKey = ApiKey;
// 创建共享数据字典
var shared = new Dictionary<string, object>();
// 创建并运行流程
var humanEvalFlow = CreateFlow();
Console.WriteLine("\n欢迎使用人工判断示例!");
Console.WriteLine("------------------------");
await humanEvalFlow.RunAsync(shared);
Console.WriteLine("\n感谢使用人工判断示例!");
}
static AsyncFlow CreateFlow()
{
// 创建节点实例
var inputNode = new TaskInputNode();
var aiResponseNode = new AIResponseNode();
var humanApprovalNode = new HumanApprovalNode();
var endNode = new NoOpNode();
// 创建从输入节点开始的流程
var flow = new AsyncFlow(inputNode);
// 连接节点
_ = inputNode - "generate" - aiResponseNode;
_ = aiResponseNode - "approve" - humanApprovalNode;
_ = humanApprovalNode - "retry" - aiResponseNode; // 不接受时重新生成
_ = humanApprovalNode - "accept" - endNode; // 接受时结束流程
return flow;
}
}看一下整体的流程图:
graph TD
A[输入节点] -->|"generate"| B[AI回复节点]
B -->|"approve"| C[人工审核节点]
C -->|"approve"| D[结束节点]
C -->|"retry"| B
输入节点:
public classTaskInputNode : AsyncNode
{
protected override async Task<object> PrepAsync(Dictionary<string, object> shared)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n请输入需要AI处理的任务:");
string task = Console.ReadLine();
return task;
}
protected override async Task<object> ExecAsync(object prepResult)
{
string task = (string)prepResult;
Console.WriteLine($"\n已收到任务:{task}");
return task;
}
protected override async Task<object> PostAsync(Dictionary<string, object> shared, object prepResult, object execResult)
{
string task = (string)execResult;
shared["task"] = task;
return"generate";
}
}AI回复节点:
public classAIResponseNode : AsyncNode
{
privatestaticint attemptCount = 0;
protected override async Task<object> PrepAsync(Dictionary<string, object> shared)
{
return shared["task"];
}
protected override async Task<object> ExecAsync(object prepResult)
{
string task = (string)prepResult;
attemptCount++;
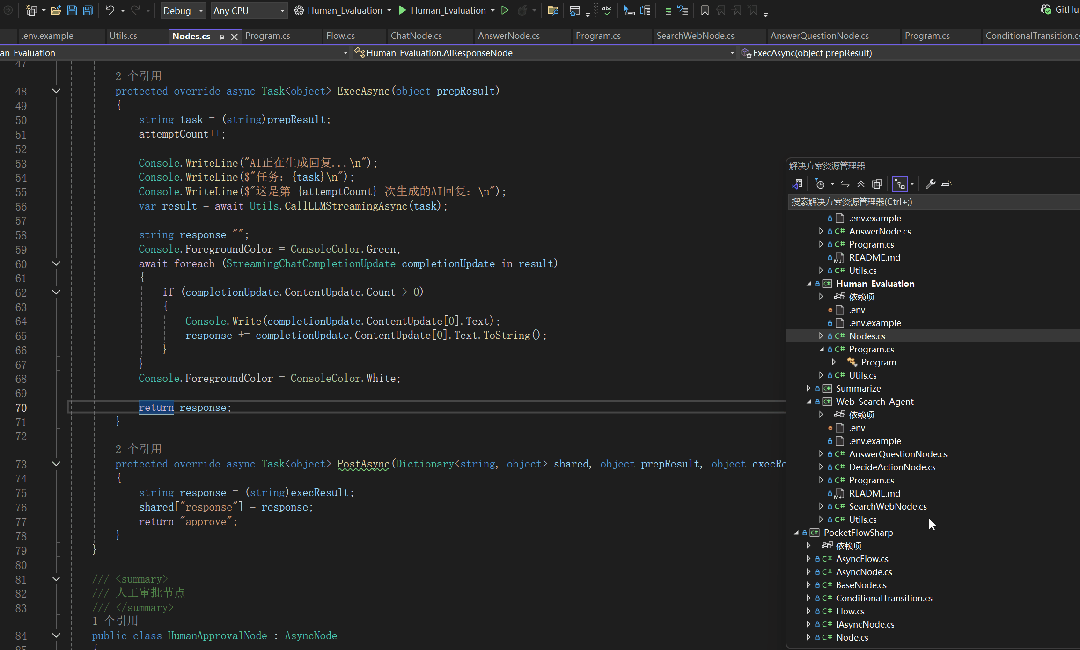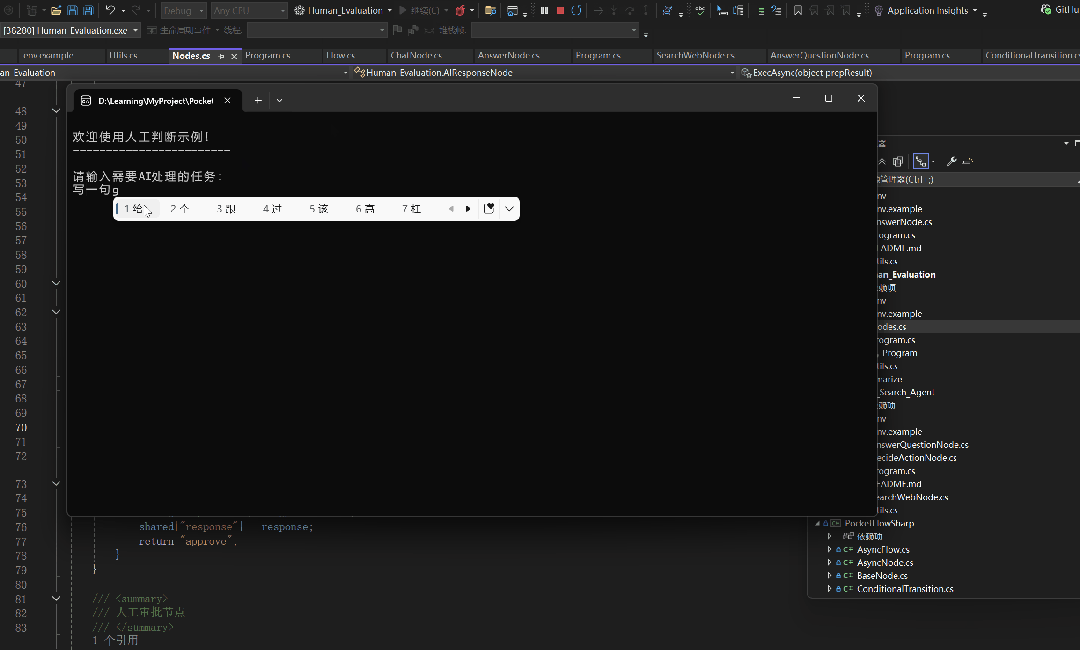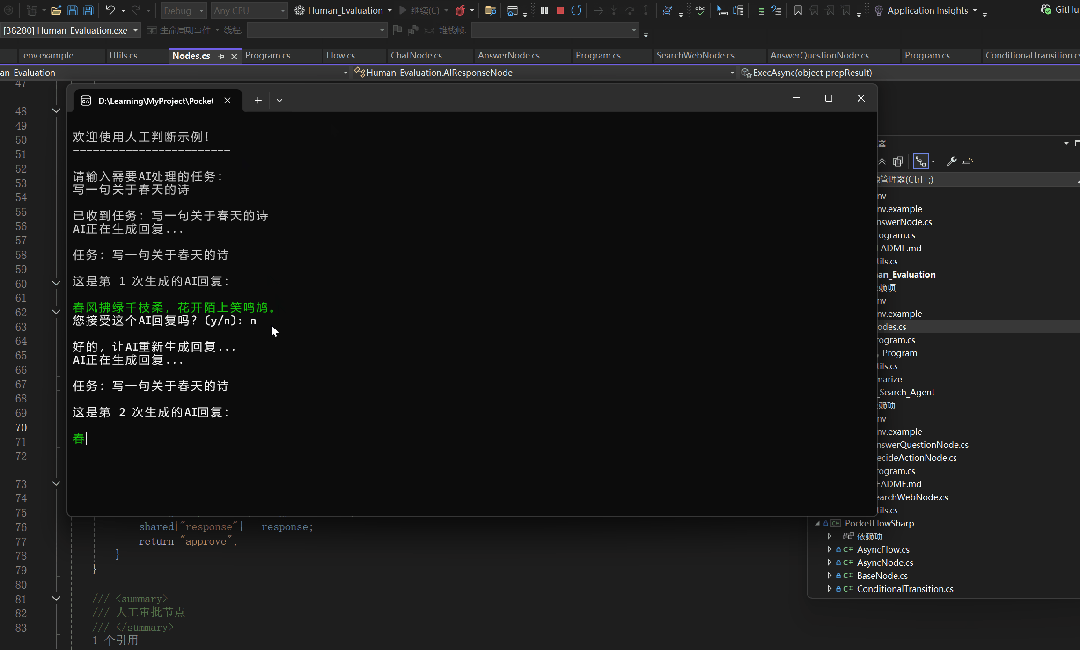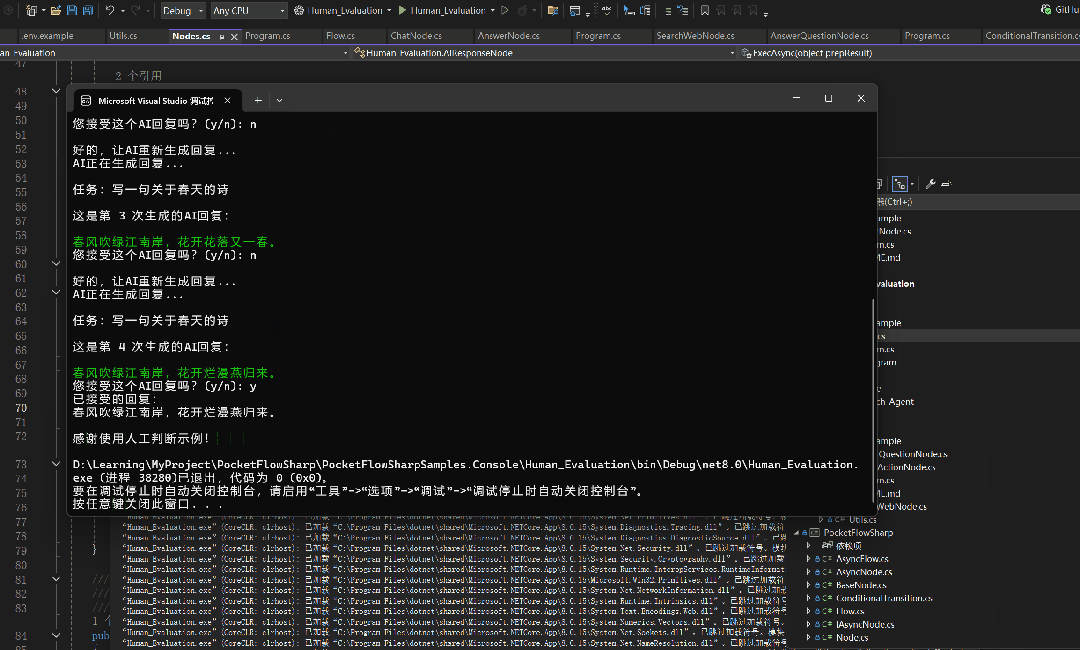
Console.WriteLine("AI正在生成回复...\n");
Console.WriteLine($"任务:{task}\n");
Console.WriteLine($"这是第 {attemptCount} 次生成的AI回复:\n");
var result = await Utils.CallLLMStreamingAsync(task);
string response="";
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
awaitforeach (StreamingChatCompletionUpdate completionUpdate in result)
{
if (completionUpdate.ContentUpdate.Count > 0)
{
Console.Write(completionUpdate.ContentUpdate[0].Text);
response += completionUpdate.ContentUpdate[0].Text.ToString();
}
}
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
return response;
}
protected override async Task<object> PostAsync(Dictionary<string, object> shared, object prepResult, object execResult)
{
string response = (string)execResult;
shared["response"] = response;
return"approve";
}
}人工审核节点:
public classHumanApprovalNode : AsyncNode
{
protected override async Task<object> PrepAsync(Dictionary<string, object> shared)
{
return shared["response"];
}
protected override async Task<object> ExecAsync(object prepResult)
{
Console.Write("\n您接受这个AI回复吗?(y/n): ");
string answer = Console.ReadLine()?.ToLower() ?? "n";
return answer;
}
protected override async Task<object> PostAsync(Dictionary<string, object> shared, object prepResult, object execResult)
{
string answer = (string)execResult;
if (answer == "y")
{
Console.WriteLine($"已接受的回复:\n{shared["response"]}");
return"accept";
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("\n好的,让AI重新生成回复...");
return"retry";
}
}
}结束节点:
public class NoOpNode : AsyncNode
{
protected override async Task<object> PrepAsync(Dictionary<string, object> shared) => null;
protected override async Task<object> ExecAsync(object prepResult) => null;
protected override async Task<object> PostAsync(Dictionary<string, object> shared, object prepResult, object execResult) => null;
}帮助类:
public staticclassUtils
{
publicstaticstring ModelName { get; set; }
publicstaticstring EndPoint { get; set; }
publicstaticstring ApiKey { get; set; }
public static async Task<string> CallLLMAsync(string prompt)
{
ApiKeyCredential apiKeyCredential = new ApiKeyCredential(ApiKey);
OpenAIClientOptions openAIClientOptions = new OpenAIClientOptions();
openAIClientOptions.Endpoint = new Uri(EndPoint);
ChatClient client = new(model: ModelName, apiKeyCredential, openAIClientOptions);
ChatCompletion completion = await client.CompleteChatAsync(prompt);
return completion.Content[0].Text;
}
publicstaticasync Task<AsyncCollectionResult<StreamingChatCompletionUpdate>> CallLLMStreamingAsync(string prompt)
{
ApiKeyCredential apiKeyCredential = new ApiKeyCredential(ApiKey);
OpenAIClientOptions openAIClientOptions = new OpenAIClientOptions();
openAIClientOptions.Endpoint = new Uri(EndPoint);
ChatClient client = new(model: ModelName, apiKeyCredential, openAIClientOptions);
var completion = client.CompleteChatStreamingAsync(prompt);
return completion;
}
}






















 5366
5366

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








