开篇提要:Websocket的本质就是对http请求进行升级,随后维持一个socket长连接,服务器通过该socket连接对客户端实时主动推送消息。
接下来我们看看springboot对websocket协议的具体实现:
1. 扫描Websocket的配置类,初始化ServerEndpointExporter对象并装载至bean容器
@Configuration
public class WebsocketConfig {
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}2. 在初始化ServerEndpointExporter对象过程中,扫描配置的各个Websocket的Endpoint,统一装载到annotatedEndpointClasses集合中(见ServerEndpointExporter类源码):
@Nullable
private List<Class<?>> annotatedEndpointClasses;其中,笔者示例中配置的Endpoint为以下所示:
@Slf4j
@Component
@ServerEndpoint("/ws")
public class WebsocketImpl {
public static final Set<Session> CLIENTS = new HashSet<>();
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session) {
log.info("已连接");
CLIENTS.add(session);
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText("test");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@OnClose
public void onClose(Session session) {
log.info("已移除");
CLIENTS.remove(session);
}
}3. 当客户端发来Websocket连接时,实际上是发送了一个http请求,并借此请求告知服务端准备使双方的通信方式升级为全双工的Websocket协议,我们来看看js发送的Websocket请求信息,如下所示:
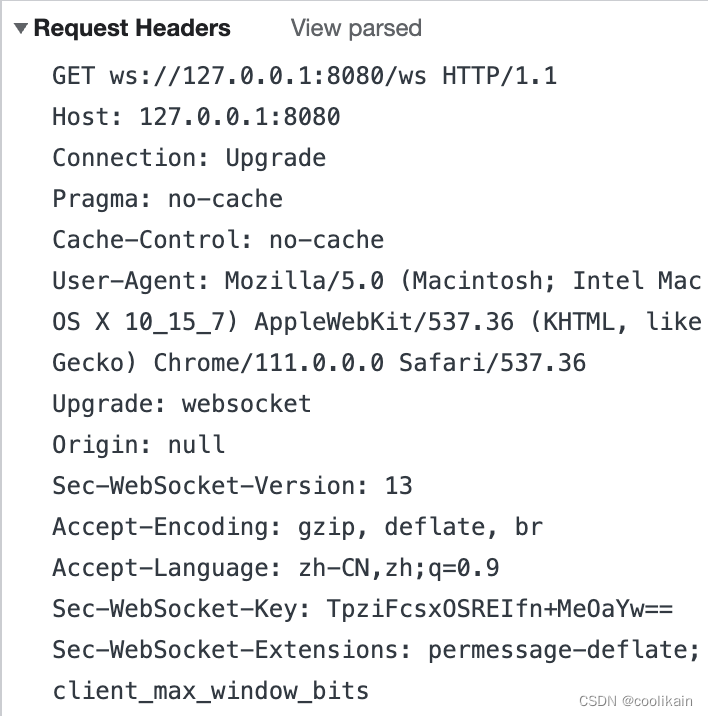
4. 服务端接收到此请求后,通过反射调用@OnOpen注解标记的方法完成Websocket连接请求,并在客户端与服务器之间维护一个Socket长连接,将客户端信息抽象成一个Session对象,以供开发人员便捷地调用相关API在代码中实现服务端对客户端的消息推送。
5. 最后,我们进入到session.getBasicRemote().sendText("test")方法的源码中观察其真正的消息推送方式,我们一直跟进到最后doWrite方法中,发现核心步骤就是基于NIO网络模型向socket中写ByteBuffer,以实现服务器主动发送数据:
protected void doWrite(boolean block, ByteBuffer from) throws IOException {
Future<Integer> integer = null;
try {
do {
integer = ((Nio2Channel)this.getSocket()).write(from);
long timeout = this.getWriteTimeout();
if (timeout > 0L) {
if ((Integer)integer.get(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) < 0) {
throw new EOFException(sm.getString("iob.failedwrite"));
}
} else if ((Integer)integer.get() < 0) {
throw new EOFException(sm.getString("iob.failedwrite"));
}
} while(from.hasRemaining());
} catch (ExecutionException var6) {
if (var6.getCause() instanceof IOException) {
throw (IOException)var6.getCause();
} else {
throw new IOException(var6);
}
} catch (InterruptedException var7) {
throw new IOException(var7);
} catch (TimeoutException var8) {
integer.cancel(true);
throw new SocketTimeoutException();
}
}总结:简单来时,就是HTTP升级 + Socket长连接的方式,这也解释了为什么叫做WebSocket的原因(Web + Socket),当然,这是我的个人猜想,哈哈哈。





















 1152
1152











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








