第一个bfs题目,总算看懂了
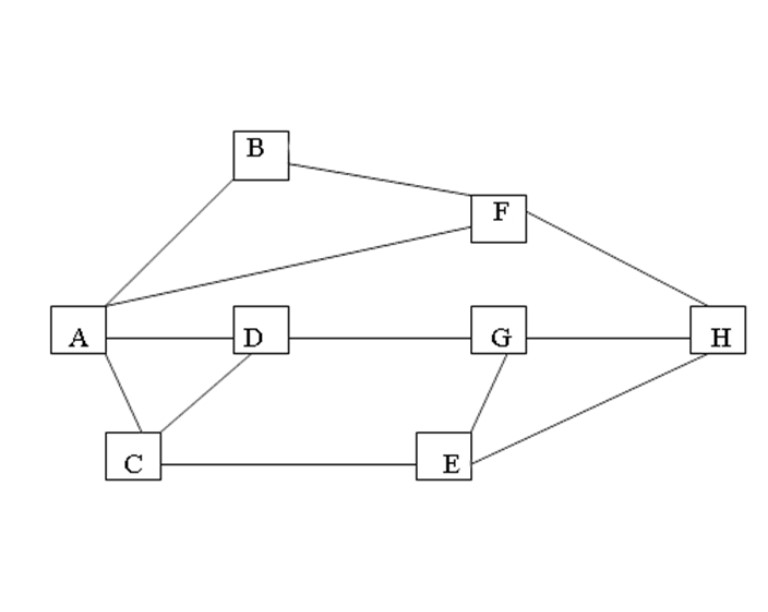
下图表示的是从城市A到城市H的交通图。从图中可以看出,从城市A到城市H要经过若干个城市。现要找出一条经过城市最少的一条路线。
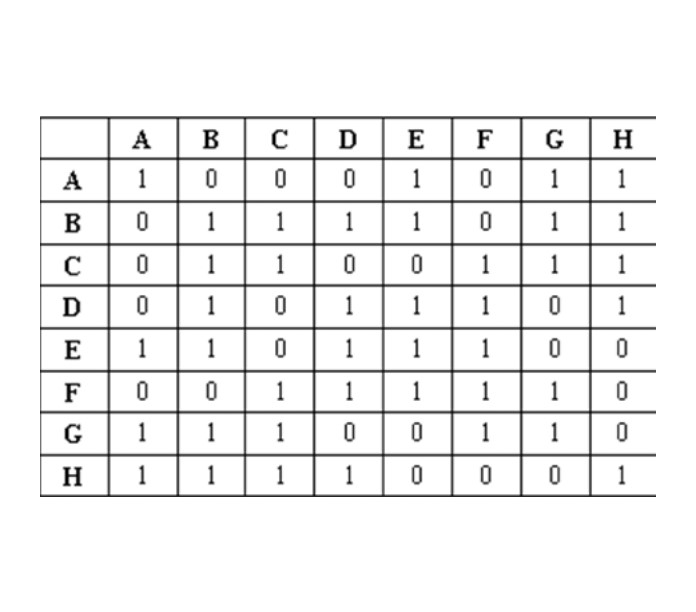
看到这图很容易想到用邻接距阵来表示,0表示能走,1表示不能走。如图。
首先想到的是用队列的思想。a数组是存储扩展结点的队列,a[i]记录经过的城市,b[i]记录前趋城市,这样就可以倒推出最短线路。具体过程如下:
(1) 将城市A入队,队首为0、队尾为1。
(2)将队首所指的城市所有可直通的城市入队(如果这个城市在队列中出现过就不入队,可用一布尔数组s[i]来判断),将入队城市的前趋城市保存在b[i]中。然后将队首加1,得到新的队首城市。重复以上步骤,直到搜到城市H时,搜索结束。利用b[i]可倒推出最少城市线路。
输入:
第一行一个整数n,表示几个城市
接下来2--n+1行
表示两个城市间之间的关系
输出:
倒序输出城市最短线路,中间用“--”隔开
样例数据输入
8
1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1
0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1
0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0
1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1
样例输出:
H--F--A
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int ju[101][101];//线路
int a[101],b[101];//a[]数组表示经历城市,b[]表示前一个城市的位置
bool s[101];//判断是否经历
int n;
void print(int);//输出
void bfs();//寻找
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j)
cin>>ju[i][j];
bfs();
return 0;
}
void bfs()
{
int head=0,tail=1;//队首为0、队尾为1
a[1]=1;//记录经过的城市
b[1]=0; //记录前一个城市
s[1]=1;//表示该城市已经到过
do
{
head++;//队首加一,出队
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)//搜索城市
{
if(!ju[a[head]][i]&&!s[i])//表示能走和没走过
{
tail++;//队尾加一,加入新的
a[tail]=i;
b[tail]=head;//记录这个城市的位置
s[i]=1;//表示经过了
if(tail==n)//第一次搜到H城市时路线最短
{
print(tail);
head=tail;
break;
}
}
}
}
while(head<tail);
}
void print(int t)//倒序输出
{
cout<<char(a[t]+64);
while(b[t])
{
t=b[t];
cout<<"--"<<char(a[t]+64);
}
}
























 225
225











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








