note: this passage serves for the analysis of Alec Jacobson’s thesis
1. what’s mass matrix
According to (2.50), mass matrix is given by:
2. matlab code analysis
function M = massmatrix(V,F, type)
% MASSMATRIX mass matrix for the mesh given by V and F
%
% M = massmatrix(V,F, type)
%
% Inputs:
% V #V x 3 matrix of vertex coordinates
% F #F x 3 matrix of indices of triangle corners
% type string containing type of mass matrix to compute
% 'full': full mass matrix for p.w. linear fem
% 'barycentric': diagonal lumped mass matrix obtained by summing 1/3
% 'voronoi': true voronoi area, except in cases where triangle is obtuse
% then uses 1/2, 1/4, 1/4
% Output:
% M #V by #V sparse mass matrix
%
% Copyright 2011, Alec Jacobson (jacobson@inf.ethz.ch)
%
% See also: massmatrix3
%
% should change code below, so we don't need this transpose
if(size(F,1) == 3)
warning('F seems to be 3 by #F, it should be #F by 3');
end
F = F';
% renaming indices of vertices of triangles for convenience
i1 = F(1,:); i2 = F(2,:); i3 = F(3,:);
%#F x 3 matrices of triangle edge vectors, named after opposite vertices
v1 = V(i3,:) - V(i2,:); v2 = V(i1,:) - V(i3,:); v3 = V(i2,:) - V(i1,:);
% computing the areas
if size(V,2) == 2
% 2d vertex data
dblA = v1(:,1).*v2(:,2)-v1(:,2).*v2(:,1);
elseif size(V,2) == 3
%n = cross(v1,v2,2); dblA = multinorm(n,2);
n = cross(v1,v2,2);
% dblA = norm(n,2);
% This does correct l2 norm of rows
dblA = (sqrt(sum((n').^2)))';
else
error('unsupported vertex dimension %d', size(V,2))
end
if strcmp(type,'full')
% arrays for matrix assembly using 'sparse'
% indices and values of the element mass matrix entries in the order
% (1,2), (2,1),(2,3), (3,2), (3,1), (1,3) (1,1), (2,2), (3,3);
i = [i1 i2 i2 i3 i3 i1 i1 i2 i3];
j = [i2 i1 i3 i2 i1 i3 i1 i2 i3];
offd_v = dblA/24.;
diag_v = dblA/12.;
v = [offd_v,offd_v, offd_v,offd_v, offd_v,offd_v, diag_v,diag_v,diag_v];
M = sparse(i,j,v,size(V,1), size(V,1));
%seamanj: 根据Quadrature rules, 对角线上为A_T/6,非对角线上为A_T/12①
%注意这里dblA为双倍的三角形面积
elseif strcmp(type,'barycentric')
% only diagonal elements
i = [i1 i2 i3];
j = [i1 i2 i3];
diag_v = dblA/6.;
v = [diag_v,diag_v,diag_v];
M = sparse(i,j,v,size(V,1), size(V,1));
%the entry M^d_i is the one third the sum of the areas of incident
%triangles on vertex i.②
elseif strcmp(type,'voronoi')
% just ported version of intrinsic code
% edges numbered same as opposite vertices
FT = F';
l = [ ...
sqrt(sum((V(FT(:,2),:)-V(FT(:,3),:)).^2,2)) ...
sqrt(sum((V(FT(:,3),:)-V(FT(:,1),:)).^2,2)) ...
sqrt(sum((V(FT(:,1),:)-V(FT(:,2),:)).^2,2)) ...
];
% 求三角形的边长
M = massmatrix_intrinsic(l,F',size(V,1),'voronoi');
%The voronoi mass matrix entry M^d_i for vertex i is the sum of its
%corresponding quadrilaterals from all incident triangles.
%具体请参照下一个文件③
else
error('bad mass matrix type')
end
% warn if any rows are all zero (probably unreferenced vertices)
if(any(sum(M,2) == 0))
warning('Some rows have all zeros... probably unreferenced vertices..');
end
end
①
注意这里它采用的是second set of quadrature rules for triangular elements
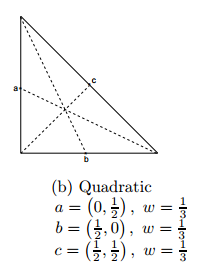
[http://math2.uncc.edu/~shaodeng/TEACHING/math5172/Lectures/Lect_15.PDF]
②
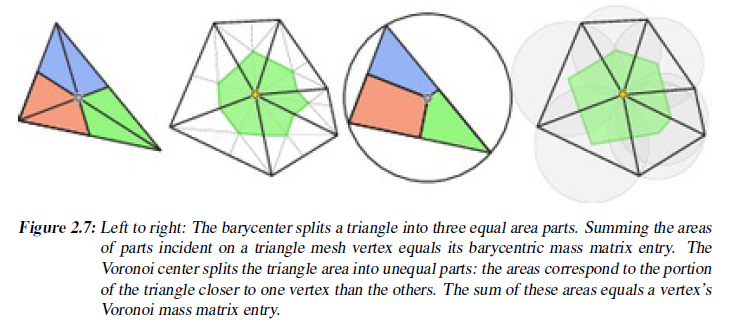

③
function [M] = massmatrix_intrinsic(l,F,nvert,masstype)
% MASSMATRIX_INTRINSIC compute the mass matrix from edge lengths only
%
% [M] = massmatrix_intrinsic(l,F)
%
% Inputs:
% l: #F by 3, array of edge lengths of edges opposite each face in F
% F: #F by 3, list of indices of triangle corners
% nvert: number of vertices, only needed to set size
% masstype: full, barycentric, or voronoi
% TODO: this is almost identical to massmatrix,
% only the area computation is different, need to refactor
%
% here's a handy line to view mass matrix entries on plot:
% text(UV(:,1), UV(:,2),zeros(size(UV,1),1),num2str(M(M>0)))
%
% Copyright 2011, Alec Jacobson (jacobson@inf.ethz.ch)
%
% See also: massmatrix
%
% should change code below, so we don't need this transpose
if(size(F,1) == 3)
warning('F seems to be 3 by #F, it should be #F by 3');
end
F = F';
% renaming indices of vertices of triangles for convenience
l1 = l(:,1); l2 = l(:,2); l3 = l(:,3);
% semiperimeters
s = (l1 + l2 + l3)*0.5;
% Heron's formula for area
dblA = 2*sqrt( s.*(s-l1).*(s-l2).*(s-l3));
% renaming indices of vertices of triangles for convenience
i1 = F(1,:); i2 = F(2,:); i3 = F(3,:);
if strcmp(masstype,'full')
% arrays for matrix assembly using 'sparse'
% indices and values of the element mass matrix entries in the order
% (1,2), (2,1),(2,3), (3,2), (3,1), (1,3) (1,1), (2,2), (3,3);
i = [i1 i2 i2 i3 i3 i1 i1 i2 i3];
j = [i2 i1 i3 i2 i1 i3 i1 i2 i3];
offd_v = dblA/24.;
diag_v = dblA/12.;
v = [offd_v,offd_v, offd_v,offd_v, offd_v,offd_v, diag_v,diag_v,diag_v];
elseif strcmp(masstype,'barycentric')
% only diagonal elements
i = [i1 i2 i3];
j = [i1 i2 i3];
diag_v = dblA/6.;
v = [diag_v,diag_v,diag_v];
elseif strcmp(masstype,'voronoi')
cosines = [ ...
(l(:,3).^2+l(:,2).^2-l(:,1).^2)./(2*l(:,2).*l(:,3)), ...
(l(:,1).^2+l(:,3).^2-l(:,2).^2)./(2*l(:,1).*l(:,3)), ...
(l(:,1).^2+l(:,2).^2-l(:,3).^2)./(2*l(:,1).*l(:,2))];
%seamanj:求cosine
barycentric = cosines.*l;
%seamanj:求质心,质心坐标为 a^2(b^2+c^2-a^2),b^2(c^2+a^2-b^2),c^2(a^2+b^2-c^2)参见④
normalized_barycentric = barycentric./[sum(barycentric')' sum(barycentric')' sum(barycentric')'];
%seamanj:Barycentric coordinates are homogeneous, so(t_1,t_2,t_3)=(ut_1,ut_2,ut_3) 引用④
areas = 0.25*sqrt( ...
(l(:,1) + l(:,2) - l(:,3)).* ...
(l(:,1) - l(:,2) + l(:,3)).* ...
(-l(:,1) + l(:,2) + l(:,3)).* ...
(l(:,1) + l(:,2) + l(:,3)));
partial_triangle_areas = normalized_barycentric.*[areas areas areas];
%seamanj:the areas of the triangles ΔA_1A_2P, ΔA_1A_3P, and ΔA_2A_3P are proportional to the barycentric coordinates t_3, t_2, and t_1 of P 引用④
quads = [ (partial_triangle_areas(:,2)+ partial_triangle_areas(:,3))*0.5 ...
(partial_triangle_areas(:,1)+ partial_triangle_areas(:,3))*0.5 ...
(partial_triangle_areas(:,1)+ partial_triangle_areas(:,2))*0.5];
%seamanj:这里条件cosines(:,1)<0当筛选器,注意左右两边都筛选
quads(cosines(:,1)<0,:) = [areas(cosines(:,1)<0,:)*0.5, ...
areas(cosines(:,1)<0,:)*0.25, areas(cosines(:,1)<0,:)*0.25];
quads(cosines(:,2)<0,:) = [areas(cosines(:,2)<0,:)*0.25, ...
areas(cosines(:,2)<0,:)*0.5, areas(cosines(:,2)<0,:)*0.25];
quads(cosines(:,3)<0,:) = [areas(cosines(:,3)<0,:)*0.25, ...
areas(cosines(:,3)<0,:)*0.25, areas(cosines(:,3)<0,:)*0.5];
i = [i1 i2 i3];
j = [i1 i2 i3];
v = reshape(quads,size(quads,1)*3,1);
else
error('bad mass matrix type')
end
M = sparse(i,j,v,nvert, nvert); %这里会做叠加的事
end
④
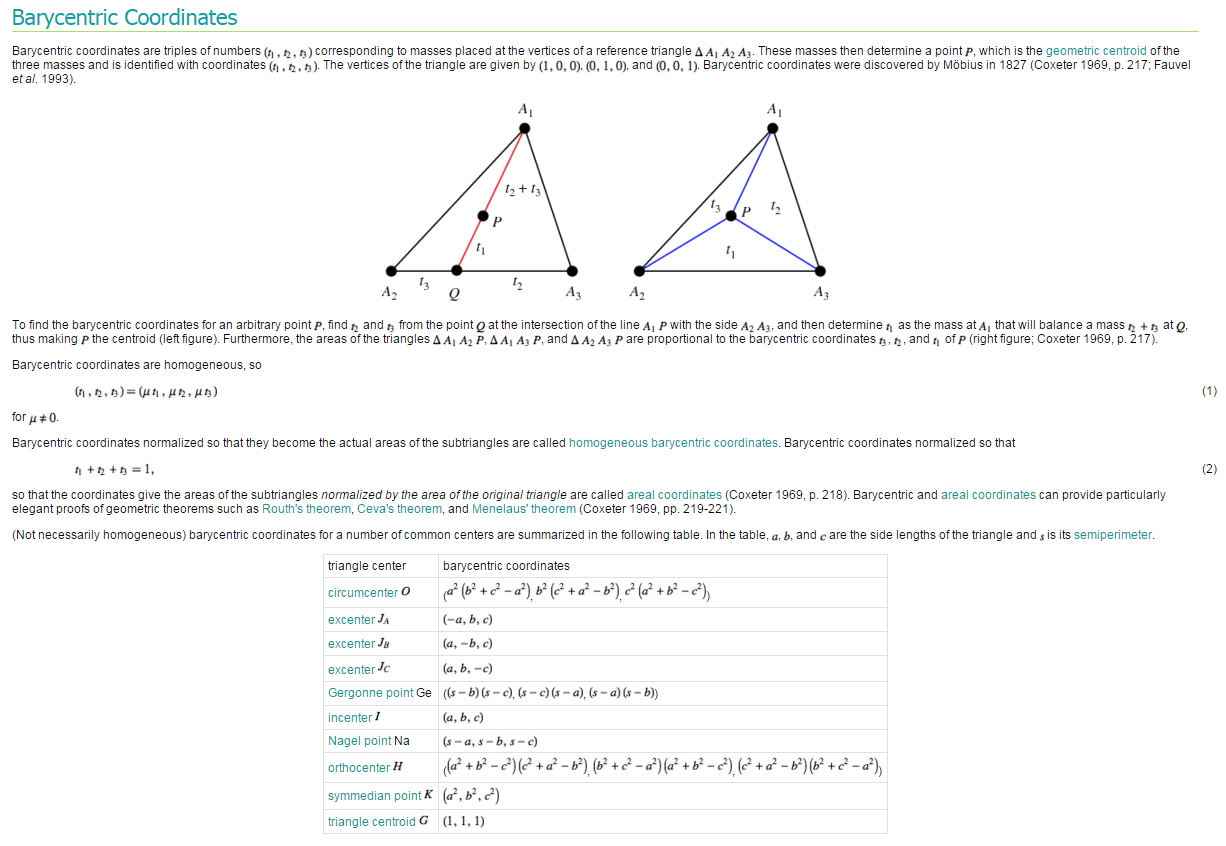
[http://mathworld.wolfram.com/BarycentricCoordinates.html]
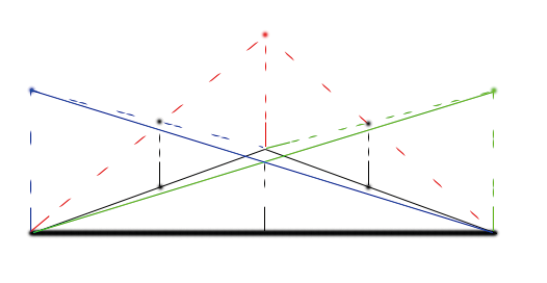
大部分的内容图片已经给出,这里我想说明下为什么质心坐标的公式为
barycentric = cosines.*l;
注意质心到三角形三个顶点的距离相等,所以这里质心也是外接圆的球心
即这里我们看到的
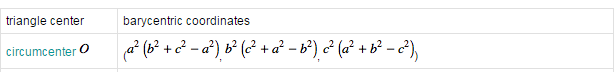
而matlab里面为cosines.*l, 这里我想推导下
将cosines写开来:
[(b2+c2−a2)/2bc,(c2+a2−b2)/2ac,(a2+b2−c2)/2ab]
将l写开来:
[a,b,c]
那么cosines.*l则为
[(b2+c2−a2)∗a/2bc,(c2+a2−b2)∗b/2ac,(a2+b2−c2)∗c/2ab]
再根据
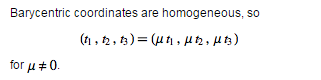
我们将cosines.*l里面的三个分量同时乘以
2abc
,则得到
[(b2+c2−a2)∗a2,(c2+a2−b2)∗b2,(a2+b2−c2)∗c2]



























 547
547

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








