Interface
Interface这个关键字(keyword),产生了一个抽象类,类里面的方法(method)全是抽象的,有方法名,方法参数,及返回值的类,而因为有Interface,一个类可以实现多个 interface,使Java可以达成类在继承上多态(multiple inheritance)的功能。因此在基础父类没有成员变量,也不需要实现方法时,会倾向使用 Interface,增加代码的可重用性。
如果有一个类,其中有几个方法是我们要写另一个方法时,所需要用到的。受限於继承关系,只能拿该类或其子类为参数,因此代码的可重用性便会受限。如果该类不是一个「类」而是一个 Interface,我们便可以写一个方法,接收实现某 Interface的所有类,大大地提高了代码的可重用性,如下:
public class InterfacePractice {
interface move {
int moveDistance = 0; // 默认为 final static
String getName(); // 该方法默认为 public,实现的类只能用 public 并实现该抽象方法
String howToMove();
}
private static class frog implements move {
// int moveDistance = 2; 会导致编译错误
@Override
public String getName() {
return "frog";
}
@Override
public String howToMove() {
return getName()+" jump "+ 2 +" blocks";
}
}
private static class bird implements move {
@Override
public String getName() {
return "bird";
}
@Override
public String howToMove() {
return getName()+" fly "+ 14 +" blocks";
}
}
private static void makeObjectMove(move[] moArray)
{
for(int i = 0; i < moArray.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(moArray[i].howToMove());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
move[] moveArray = {new bird(),new frog()};
makeObjectMove(moveArray);
}
}值得注意的是 Interface 中的变数,默认为 final static,一旦想在实现的类进行修改其值,变成发生编译错误,因为 final 的属性为一旦赋值後,便不能再改变。
Interface 也可以继承,所有抽象的方法在实现类(concrete class)实现即可,范例如下:
class InterfaceExtends {
interface liar {
void makeLies();
}
interface thief extends liar {
void steal();
}
private static class BadPeople implements thief {
String lies = "You are such a good person";
String stealingAction = "stealing";
@Override
public void makeLies() {
System.out.println(lies);
}
@Override
public void steal() {
System.out.println(stealingAction);
}
}
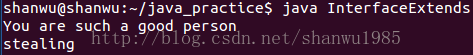
public static void main(String[] args) {
BadPeople asshole = new BadPeople();
asshole.makeLies();
asshole.steal();
}
}
Nesting Interface
class A {
private interface IZ {
void IZmethod();
}
interface IA {
void IAmethod();
}
public static class B implements IA {
@Override
public void IAmethod() {
System.out.println("B implements IA method");
}
}
}
// 可以比较 interface IO extends IP 的做法
interface IO {
void IOmethod();
interface IP {
void IPmethod();
}
}
class O implements IO {
@Override
public void IOmethod() {
System.out.println("O implements IO method");
}
}
class O1 implements IO.IP {
@Override
public void IPmethod() {
System.out.println("O1 implements IO.IP method");
}
}
class O2 implements IO, IO.IP {
@Override
public void IOmethod() {
System.out.println("O2 implements IO method");
}
@Override
public void IPmethod() {
System.out.println("O2 implements IO.IP method");
}
}
public class NestingInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("start nesting class");
A a = new A();
A.B b = new A.B();
b.IAmethod();
O o = new O();
o.IOmethod();
O1 o1 = new O1();
o1.IPmethod();
O2 o2 = new O2();
o2.IOmethod();
o2.IPmethod();
}
}

此外,我们可以使用 interface 来实现设计模式中的工厂模式(相关阅读),在下面的范例中,可以在实现不同的 provideCoffeService 来达到提供不同种类咖啡给客人( Customer )的目的。
interface provideCoffee {
String getCoffeeType();
void makeCoffee();
}
class VanillaCoffee implements provideCoffee {
@Override
public String getCoffeeType() {
return "Vanilla--Flavor Coffee";
}
@Override
public void makeCoffee() {
String action = "make "+getCoffeeType()+" coffee";
System.out.println(action);
}
}
class ChocolateCoffee implements provideCoffee {
@Override
public String getCoffeeType() {
return "Chocolate--Flavor Coffee";
}
@Override
public void makeCoffee() {
String action = "make "+getCoffeeType()+" coffee";
System.out.println(action);
}
}
class Customer {
void getServed(provideCoffee coffee) {
coffee.makeCoffee();
String action = "Customer drinks "+ coffee.getCoffeeType();
System.out.println(action);
}
}
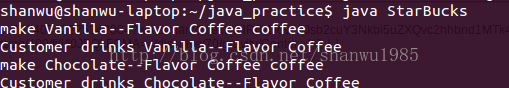
public class StarBucks {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer a = new Customer();
a.getServed(new VanillaCoffee());
a.getServed(new ChocolateCoffee());
}
}























 1092
1092

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








