二叉树是常见的数据结构,以下对二叉树的常见操作进行总结
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};
class Tree {
int strToNum(string s, int &index){
int res = 0;
while(index < s.length() && s[index] >= '0' && s[index] <= '9'){
res = res * 10 + s[index] - '0';
index++;
}
return res;
}
string numToStr(int num){
string str = "";
if(num < 0){
str += "-";
}
while (num > 0) {
str += (num % 10 + '0');
num /= 10;
}
return str;
}
public:
//反序列化:即通过一串字符串建树
TreeNode *buildTree(string str){
if(str.length() == 0 || str[0] > '9' || str[0] < '0')
return NULL;
int index = 0;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(strToNum(str, index));
queue<TreeNode *>tq;
tq.push(root);
while(index < str.length()){
TreeNode *node = tq.front(); tq.pop();
while(index < str.length() && !((str[index] <= '9' && str[index] >= '0') || str[index] == '#')){
index++;
}
if(index >= str.length()){
break;
}
if(str[index] != '#'){
TreeNode *left = new TreeNode(strToNum(str, index));
node->left = left;
tq.push(left);
}else{
index++;
}
while(index < str.length() && !((str[index] <= '9' && str[index] >= '0') || str[index] == '#')){
index++;
}
if(index >= str.length()){
break;
}
if(str[index] != '#'){
TreeNode *right = new TreeNode(strToNum(str, index));
node->right = right;
tq.push(right);
}else{
index++;
}
}
return root;
}
//递归遍历
//前序递归遍历
void travelInPreByRecursion(TreeNode *root){
if(root != NULL){
cout << root->val << ',';
travelInPreByRecursion(root->left);
travelInPreByRecursion(root->right);
}
}
//中序递归遍历
void travelInorderByRecursion(TreeNode *root){
if(root != NULL){
travelInorderByRecursion(root->left);
cout << root->val << ',';
travelInorderByRecursion(root->right);
}
}
//后序递归遍历
void travelInPostByRecursion(TreeNode *root){
if(root != NULL){
travelInPostByRecursion(root->left);
travelInPostByRecursion(root->right);
cout << root->val << ',';
}
}
//非递归遍历
//前序非递归遍历
/*
1、循环访问左子树,访问后压入栈中
2、再取出栈中结点访问右子树
*/
void travelInPre(TreeNode *root){
if(root == NULL){
return ;
}
stack<TreeNode *> ts;
while (root != NULL || !ts.empty()) {
while(root != NULL){
cout << root->val << ',';
ts.push(root);
root = root->left;
}
root = ts.top();
ts.pop();
root = root->right;
}
}
//非递归中序遍历
/*
1、先把左子树循环压入栈中
2、取出结点访问,并把当前结点改为右子树结点
*/
void travelInorder(TreeNode *root){
if(root == NULL){
return ;
}
stack<TreeNode *> ts;
while (root != NULL || !ts.empty()) {
while(root != NULL){
ts.push(root);
root = root->left;
}
root = ts.top();
ts.pop();
cout << root->val << ',';
root = root->right;
}
}
//非递归后序遍历
/*
1、先循环将左子树压入栈中
2、再访问右子树,并标记当前结点右子树访问过,将当前结点改为右子树
3、再将当前结点的左子树循环压入栈中
4、取出访问当前结点
*/
void travelInPost(TreeNode *root){
if(root == NULL){
return;
}
stack<TreeNode *> ts;
bool flags[100];
while(root != NULL){
ts.push(root);
flags[ts.size()] = false;
root = root->left;
}
while(!ts.empty()){
root = ts.top();
while (root->right != NULL && !flags[ts.size()]){
flags[ts.size()] = true;
root = root->right;
ts.push(root);
while(root->left != NULL){
root = root->left;
ts.push(root);
flags[ts.size()] = false;
}
}
root = ts.top();
cout << root->val << ",";
ts.pop();
}
}
//序列化:层次遍历
/*
维护一个层次队列
*/
void travelByLevel(TreeNode *root){
if(root == NULL){
return;
}
queue <TreeNode *> tq;
tq.push(root);
string str = "";
while(!tq.empty()){
root = tq.front();
tq.pop();
if(root == NULL){
str += "#";
str += ",";
continue;
}
str += numToStr(root->val);
str += ",";
tq.push(root->left);
tq.push(root->right);
}
cout << str << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// insert code here...
//std::cout << "Hello, World!\n";
Tree t;
string s = "1,2,3,4,#,#,5,#,#,#,#";
TreeNode *root = t.buildTree(s);
t.travelInPre(root);
cout << endl;
t.travelInPreByRecursion(root);
cout << endl;
t.travelInorder(root);
cout << endl;
t.travelInorderByRecursion(root);
cout << endl;
t.travelInPostByRecursion(root);
cout << endl;
t.travelInPost(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:








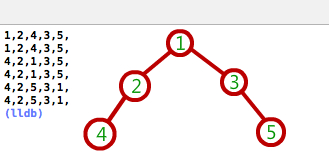














 2338
2338

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








