一:是什么
java字符串是一系列字符数组。
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable, CharSequence {
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
}
从源码可以看到,字符串实际是一个不可变的char数组。
字符串为什么要设计为不可变?
一个原因,安全。字符串是存放在常量池中的,在开发中使用的频率是非常高的,如果字符串是可变的,一个线程将值改变了,另外一个线程再来读的时候,拿到的值就是改变后的值,会引起数据的错误。
String类创建对象的两种方法
(1).直接赋值:该方式会在常量池中检查字符串"aa"是否存在,存在则直接返回,不存在则创建并返回
String s1 = "aa";
(2).new对象:该方式创建了两个对象,"aa"和s1对象,"aa"存在常量池中,原理同上,s1对象存在堆内存中
String s1 = new String("aa");
二:常用方法及源码解析
(1).length方法:获得字符串的长度,直接返回char数组的长度
public int length() {
return value.length;
}
(2).charAt方法:返回char数组指定下角标(索引)处的字符值
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return value[index];
}
(3).indexOf方法:返回指定字符或字符串,数字在字符串中的位置
/**
* The minimum value of a
* Unicode supplementary code point, constant {@code U+10000}.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public static final int MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT = 0x010000;
public int indexOf(int ch) {
return indexOf(ch, 0);
}
public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
final int max = value.length;
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
} else if (fromIndex >= max) {
// Note: fromIndex might be near -1>>>1.
return -1;
}
if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
// handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
// negative value (invalid code point))
final char[] value = this.value;
//循环遍历,找出第一个和入参匹配的值
for (int i = fromIndex; i < max; i++) {
if (value[i] == ch) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
} else {
return indexOfSupplementary(ch, fromIndex);
}
}
private int indexOfSupplementary(int ch, int fromIndex) {
if (Character.isValidCodePoint(ch)) {
final char[] value = this.value;
final char hi = Character.highSurrogate(ch);
final char lo = Character.lowSurrogate(ch);
final int max = value.length - 1;
//循环遍历,找出第一个和入参匹配的值
for (int i = fromIndex; i < max; i++) {
if (value[i] == hi && value[i + 1] == lo) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
(4)concat:拼接字符串,我们可以看到拼接字符串并不会直接修改原有的字符串,而是重新实列化了一个新的字符串
public String concat(String str) {
int otherLen = str.length();
if (otherLen == 0) {
return this;
}
int len = value.length;
char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
str.getChars(buf, len);
//实例化新对象返回
return new String(buf, true);
}
/**
* Copy characters from this string into dst starting at dstBegin.
* This method doesn't perform any range checking.
*/
void getChars(char dst[], int dstBegin) {
System.arraycopy(value, 0, dst, dstBegin, value.length);
}
(5).substring方法:返回指定位置的字符串内容
public String substring(int beginIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
int subLen = value.length - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
//也是不会改变原有的字符串,而是实例化新的对象返回
return (beginIndex == 0) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
if (endIndex > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
}
int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this
: new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
我们看下这个构造方法,直接调用Arrays工具类将char数组指定位置的字符返回
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}
再看下Arrays工具类的copyOfRange方法
public static char[] copyOfRange(char[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
char[] copy = new char[newLength];
//这里直接调用system类了,有兴趣的可以继续深究,这里不往下挖了
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
四:字符串与jvm
在jdk1.7之前,字符串常量池是存在PermGen方法区,1.7以后移到了MetaSpace堆内存中。
两个区域对比
1.基本的
PermGen是用于存储类数据(如静态变量,字节码等)的存储区,在Java 8中,PermGen方法区域已替换为MetaSpace
2.默认内存分配
PermGen默认情况下,为PermGen分配了64 Mb
MetaSpace默认情况下,它可以自动增加其大小
3.调优内存标志
PermGen可以使用-XXMaxPermSize对其进行调整。
MetaSpace我们可以通过-XX:MaxMetaspaceSize限制内存的上限
4.记忆区
PermGen这是一个特殊的堆空间。
MetaSpace从Java 8开始,它现在是本机OS中的独立内存区域
五:示例(jdk1.8)
String s1= "str1";
String s2 = "str1";
String s3 = "Java";
String s4 = new String("java");
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // true
System.out.println(s3 == s4); // false
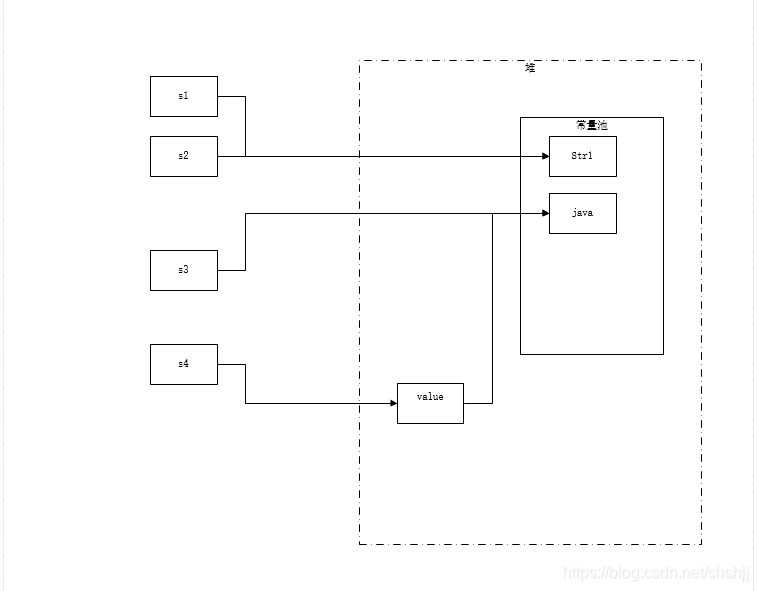
如图:s1创建的时候在常量池没有"Str1"字符串,所以会在常量池初始化一个,s2创建的时候,发现常量池已经有该字符串了,所以直接返回的是该字符串的引用地址,s3原理同s1.
s4在创建的时候首先会在堆内存中初始化一个字符串对象,然后会去常量池找有没有"java"字符串,发现有,所以直接指向了该字符串的引用地址。
























 224
224

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








