声明:此文仅供学习记录研究使用,切勿用于非法用途,否则后果自负!
1.下载安装最新版HashCat
操作系统是windows10,hashcat版本为6.2.5:

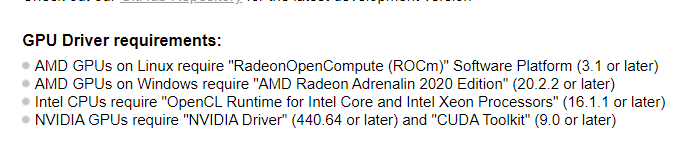
2.安装GPU驱动以及CUDA:
注:GPU驱动的版本要和CUDA版本对应,如果不对应会导致hashcat在使用GPU爆破时报错:nvrtcCompileProgram(): NVRTC_ERROR_INVALID_OPTION
nvrtcCompileProgram(): NVRTC_ERROR_INVALID_OPTION
nvrtc: error: invalid value for --gpu-architecture (-arch)
* Device #1: Kernel ./OpenCL/shared.cl build failed.
* Device #1: Kernel ./OpenCL/shared.cl build failed.
我下面这个是对应好了的,非常完美。

看着多,实际上就是两个安装程序:显卡驱动和CUDA。
这里hashcat对这两个程序的版本有要求:
3.使用office2john将office转换为hash
office2john的代码在这里:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# This software is Copyright (c) 2012-2013 Dhiru Kholia <dhiru at openwall.com>
# and is licensed under the same license as used by the OleFileIO_PL library,
# which is included below.
# olefile (formerly OleFileIO_PL) version 0.41 2014-11-25
#
# Module to read/write Microsoft OLE2 files (also called Structured Storage or
# Microsoft Compound Document File Format), such as Microsoft Office 97-2003
# documents, Image Composer and FlashPix files, Outlook messages, ...
# This version is compatible with Python 2.6+ and 3.x
#
# Project website: http://www.decalage.info/olefile
#
# olefile is copyright (c) 2005-2014 Philippe Lagadec (http://www.decalage.info)
#
# olefile is based on the OleFileIO module from the PIL library v1.1.6
# See: http://www.pythonware.com/products/pil/index.htm
#
# The Python Imaging Library (PIL) is
# Copyright (c) 1997-2005 by Secret Labs AB
# Copyright (c) 1995-2005 by Fredrik Lundh
#
# See source code and LICENSE.txt for information on usage and redistribution.
# Since OleFileIO_PL v0.30, only Python 2.6+ and 3.x is supported
# This import enables print() as a function rather than a keyword
# (main requirement to be compatible with Python 3.x)
# The comment on the line below should be printed on Python 2.5 or older:
from __future__ import print_function # This version of olefile requires Python 2.6+ or 3.x.
__author__ = "Philippe Lagadec"
__date__ = "2014-11-25"
__version__ = '0.41'
#--- LICENSE ------------------------------------------------------------------
# olefile (formerly OleFileIO_PL) is copyright (c) 2005-2014 Philippe Lagadec
# (http://www.decalage.info)
#
# All rights reserved.
#
# Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification,
# are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
#
# * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
# list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
# * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
# this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
# and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
#
# THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND
# ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
# WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
# DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
# FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
# DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
# SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
# CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
# OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
# OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
# ----------
# PIL License:
#
# olefile is based on source code from the OleFileIO module of the Python
# Imaging Library (PIL) published by Fredrik Lundh under the following license:
# The Python Imaging Library (PIL) is
# Copyright (c) 1997-2005 by Secret Labs AB
# Copyright (c) 1995-2005 by Fredrik Lundh
#
# By obtaining, using, and/or copying this software and/or its associated
# documentation, you agree that you have read, understood, and will comply with
# the following terms and conditions:
#
# Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its
# associated documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby granted,
# provided that the above copyright notice appears in all copies, and that both
# that copyright notice and this permission notice appear in supporting
# documentation, and that the name of Secret Labs AB or the author(s) not be used
# in advertising or publicity pertaining to distribution of the software
# without specific, written prior permission.
#
# SECRET LABS AB AND THE AUTHORS DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES WITH REGARD TO THIS
# SOFTWARE, INCLUDING ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS.
# IN NO EVENT SHALL SECRET LABS AB OR THE AUTHORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL,
# INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM
# LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE OR
# OTHER TORTIOUS ACTION, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR
# PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# CHANGELOG: (only olefile/OleFileIO_PL changes compared to PIL 1.1.6)
# 2005-05-11 v0.10 PL: - a few fixes for Python 2.4 compatibility
# (all changes flagged with [PL])
# 2006-02-22 v0.11 PL: - a few fixes for some Office 2003 documents which raise
# exceptions in _OleStream.__init__()
# 2006-06-09 v0.12 PL: - fixes for files above 6.8MB (DIFAT in loadfat)
# - added some constants
# - added header values checks
# - added some docstrings
# - getsect: bugfix in case sectors >512 bytes
# - getsect: added conformity checks
# - DEBUG_MODE constant to activate debug display
# 2007-09-04 v0.13 PL: - improved/translated (lots of) comments
# - updated license
# - converted tabs to 4 spaces
# 2007-11-19 v0.14 PL: - added OleFileIO._raise_defect() to adapt sensitivity
# - improved _unicode() to use Python 2.x unicode support
# - fixed bug in _OleDirectoryEntry
# 2007-11-25 v0.15 PL: - added safety checks to detect FAT loops
# - fixed _OleStream which didn't check stream size
# - added/improved many docstrings and comments
# - moved helper functions _unicode and _clsid out of
# OleFileIO class
# - improved OleFileIO._find() to add Unix path syntax
# - OleFileIO._find() is now case-insensitive
# - added get_type() and get_rootentry_name()
# - rewritten loaddirectory and _OleDirectoryEntry
# 2007-11-27 v0.16 PL: - added _OleDirectoryEntry.kids_dict
# - added detection of duplicate filenames in storages
# - added detection of duplicate references to streams
# - added get_size() and exists() to _OleDirectoryEntry
# - added isOleFile to check header before parsing
# - added __all__ list to control public keywords in pydoc
# 2007-12-04 v0.17 PL: - added _load_direntry to fix a bug in loaddirectory
# - improved _unicode(), added workarounds for Python <2.3
# - added set_debug_mode and -d option to set debug mode
# - fixed bugs in OleFileIO.open and _OleDirectoryEntry
# - added safety check in main for large or binary
# properties
# - allow size>0 for storages for some implementations
# 2007-12-05 v0.18 PL: - fixed several bugs in handling of FAT, MiniFAT and
# streams
# - added option '-c' in main to check all streams
# 2009-12-10 v0.19 PL: - bugfix for 32 bit arrays on 64 bits platforms
# (thanks to Ben G. and Martijn for reporting the bug)
# 2009-12-11 v0.20 PL: - bugfix in OleFileIO.open when filename is not plain str
# 2010-01-22 v0.21 PL: - added support for big-endian CPUs such as PowerPC Macs
# 2012-02-16 v0.22 PL: - fixed bug in getproperties, patch by chuckleberryfinn
# (https://bitbucket.org/decalage/olefileio_pl/issue/7)
# - added close method to OleFileIO (fixed issue #2)
# 2012-07-25 v0.23 PL: - added support for file-like objects (patch by mete0r_kr)
# 2013-05-05 v0.24 PL: - getproperties: added conversion from filetime to python
# datetime
# - main: displays properties with date format
# - new class OleMetadata to parse standard properties
# - added get_metadata method
# 2013-05-07 v0.24 PL: - a few improvements in OleMetadata
# 2013-05-24 v0.25 PL: - getproperties: option to not convert some timestamps
# - OleMetaData: total_edit_time is now a number of seconds,
# not a timestamp
# - getproperties: added support for VT_BOOL, VT_INT, V_UINT
# - getproperties: filter out null chars from strings
# - getproperties: raise non-fatal defects instead of
# exceptions when properties cannot be parsed properly
# 2013-05-27 PL: - getproperties: improved exception handling
# - _raise_defect: added option to set exception type
# - all non-fatal issues are now recorded, and displayed
# when run as a script
# 2013-07-11 v0.26 PL: - added methods to get modification and creation times
# of a directory entry or a storage/stream
# - fixed parsing of direntry timestamps
# 2013-07-24 PL: - new options in listdir to list storages and/or streams
# 2014-02-04 v0.30 PL: - upgraded code to support Python 3.x by Martin Panter
# - several fixes for Python 2.6 (xrange, MAGIC)
# - reused i32 from Pillow's _binary
# 2014-07-18 v0.31 - preliminary support for 4K sectors
# 2014-07-27 v0.31 PL: - a few improvements in OleFileIO.open (header parsing)
# - Fixed loadfat for large files with 4K sectors (issue #3)
# 2014-07-30 v0.32 PL: - added write_sect to write sectors to disk
# - added write_mode option to OleFileIO.__init__ and open
# 2014-07-31 PL: - fixed padding in write_sect for Python 3, added checks
# - added write_stream to write a stream to disk
# 2014-09-26 v0.40 PL: - renamed OleFileIO_PL to olefile
# 2014-11-09 NE: - added support for Jython (Niko Ehrenfeuchter)
# 2014-11-13 v0.41 PL: - improved isOleFile and OleFileIO.open to support OLE
# data in a string buffer and file-like objects.
# 2014-11-21 PL: - updated comments according to Pillow's commits
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TODO (for version 1.0):
# + get rid of print statements, to simplify Python 2.x and 3.x support
# + add is_stream and is_storage
# + remove leading and trailing slashes where a path is used
# + add functions path_list2str and path_str2list
# + fix how all the methods handle unicode str and/or bytes as arguments
# + add path attrib to _OleDirEntry, set it once and for all in init or
# append_kids (then listdir/_list can be simplified)
# - TESTS with Linux, MacOSX, Python 1.5.2, various files, PIL, ...
# - add underscore to each private method, to avoid their display in
# pydoc/epydoc documentation - Remove it for classes to be documented
# - replace all raised exceptions with _raise_defect (at least in OleFileIO)
# - merge code from _OleStream and OleFileIO.getsect to read sectors
# (maybe add a class for FAT and MiniFAT ?)
# - add method to check all streams (follow sectors chains without storing all
# stream in memory, and report anomalies)
# - use _OleDirectoryEntry.kids_dict to improve _find and _list ?
# - fix Unicode names handling (find some way to stay compatible with Py1.5.2)
# => if possible avoid converting names to Latin-1
# - review DIFAT code: fix handling of DIFSECT blocks in FAT (not stop)
# - rewrite OleFileIO.getproperties
# - improve docstrings to show more sample uses
# - see also original notes and FIXME below
# - remove all obsolete FIXMEs
# - OleMetadata: fix version attrib according to
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd945671%28v=office.12%29.aspx
# IDEAS:
# - in OleFileIO._open and _OleStream, use size=None instead of 0x7FFFFFFF for
# streams with unknown size
# - use arrays of int instead of long integers for FAT/MiniFAT, to improve
# performance and reduce memory usage ? (possible issue with values >2^31)
# - provide tests with unittest (may need write support to create samples)
# - move all debug code (and maybe dump methods) to a separate module, with
# a class which inherits OleFileIO ?
# - fix docstrings to follow epydoc format
# - add support for big endian byte order ?
# - create a simple OLE explorer with wxPython
# FUTURE EVOLUTIONS to add write support:
# see issue #6 on Bitbucket:
# https://bitbucket.org/decalage/olefileio_pl/issue/6/improve-olefileio_pl-to-write-ole-files
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# NOTES from PIL 1.1.6:
# History:
# 1997-01-20 fl Created
# 1997-01-22 fl Fixed 64-bit portability quirk
# 2003-09-09 fl Fixed typo in OleFileIO.loadfat (noted by Daniel Haertle)
# 2004-02-29 fl Changed long hex constants to signed integers
#
# Notes:
# FIXME: sort out sign problem (eliminate long hex constants)
# FIXME: change filename to use "a/b/c" instead of ["a", "b", "c"]
# FIXME: provide a glob mechanism function (using fnmatchcase)
#
# Literature:
#
# "FlashPix Format Specification, Appendix A", Kodak and Microsoft,
# September 1996.
#
# Quotes:
#
# "If this document and functionality of the Software conflict,
# the actual functionality of the Software represents the correct
# functionality" -- Microsoft, in the OLE format specification
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import sys
PY3 = sys.version_info[0] == 3
import io
import struct
import array
import os.path
import datetime
if not PY3:
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding("utf8")
if PY3:
from io import BytesIO as StringIO
else:
from StringIO import StringIO
#=== COMPATIBILITY WORKAROUNDS ================================================
#[PL] Define explicitly the public API to avoid private objects in pydoc:
#TODO: add more
# __all__ = ['OleFileIO', 'isOleFile', 'MAGIC']
# For Python 3.x, need to redefine long as int:
if str is not bytes:
long = int
# Need to make sure we use xrange both on Python 2 and 3.x:
try:
# on Python 2 we need xrange:
iterrange = xrange
except:
# no xrange, for Python 3 it was renamed as range:
iterrange = range
#[PL] workaround to fix an issue with array item size on 64 bits systems:
if array.array('L').itemsize == 4:
# on 32 bits platforms, long integers in an array are 32 bits:
UINT32 = 'L'
elif array.array('I').itemsize == 4:
# on 64 bits platforms, integers in an array are 32 bits:
UINT32 = 'I'
elif array.array('i').itemsize == 4:
# On 64 bit Jython, signed integers ('i') are the only way to store our 32
# bit values in an array in a *somewhat* reasonable way, as the otherwise
# perfectly suited 'H' (unsigned int, 32 bits) results in a completely
# unusable behaviour. This is most likely caused by the fact that Java
# doesn't have unsigned values, and thus Jython's "array" implementation,
# which is based on "jarray", doesn't have them either.
# NOTE: to trick Jython into converting the values it would normally
# interpret as "signed" into "unsigned", a binary-and operation with
# 0xFFFFFFFF can be used. This way it is possible to use the same comparing
# operations on all platforms / implementations. The corresponding code
# lines are flagged with a 'JYTHON-WORKAROUND' tag below.
UINT32 = 'i'
else:
raise ValueError('Need to fix a bug with 32 bit arrays, please contact author...')
#[PL] These workarounds were inspired from the Path module
# (see http://www.jorendorff.com/articles/python/path/)
#TODO: test with old Python versions
# Pre-2.3 workaround for basestring.
try:
basestring
except NameError:
try:
# is Unicode supported (Python >2.0 or >1.6 ?)
basestring = (str, unicode)
except NameError:
basestring = str
#[PL] Experimental setting: if True, OLE filenames will be kept in Unicode
# if False (default PIL behaviour), all filenames are converted to Latin-1.
KEEP_UNICODE_NAMES = False
#=== DEBUGGING ===============================================================
#TODO: replace this by proper logging
#[PL] DEBUG display mode: False by default, use set_debug_mode() or "-d" on
# command line to change it.
DEBUG_MODE = False
def debug_print(msg):
print(msg)
def debug_pass(msg):
pass
debug = debug_pass
def set_debug_mode(debug_mode):
"""
Set debug mode on or off, to control display of debugging messages.
:param mode: True or False
"""
global DEBUG_MODE, debug
DEBUG_MODE = debug_mode
if debug_mode:
debug = debug_print
else:
debug = debug_pass
#=== CONSTANTS ===============================================================
# magic bytes that should be at the beginning of every OLE file:
MAGIC = b'\xD0\xCF\x11\xE0\xA1\xB1\x1A\xE1'
#[PL]: added constants for Sector IDs (from AAF specifications)
MAXREGSECT = 0xFFFFFFFA # (-6) maximum SECT
DIFSECT = 0xFFFFFFFC # (-4) denotes a DIFAT sector in a FAT
FATSECT = 0xFFFFFFFD # (-3) denotes a FAT sector in a FAT
ENDOFCHAIN = 0xFFFFFFFE # (-2) end of a virtual stream chain
FREESECT = 0xFFFFFFFF # (-1) unallocated sector
#[PL]: added constants for Directory Entry IDs (from AAF specifications)
MAXREGSID = 0xFFFFFFFA # (-6) maximum directory entry ID
NOSTREAM = 0xFFFFFFFF # (-1) unallocated directory entry
#[PL] object types in storage (from AAF specifications)
STGTY_EMPTY = 0 # empty directory entry (according to OpenOffice.org doc)
STGTY_STORAGE = 1 # element is a storage object
STGTY_STREAM = 2 # element is a stream object
STGTY_LOCKBYTES = 3 # element is an ILockBytes object
STGTY_PROPERTY = 4 # element is an IPropertyStorage object
STGTY_ROOT = 5 # element is a root storage
#
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
# property types
VT_EMPTY=0; VT_NULL=1; VT_I2=2; VT_I4=3; VT_R4=4; VT_R8=5; VT_CY=6;
VT_DATE=7; VT_BSTR=8; VT_DISPATCH=9; VT_ERROR=10; VT_BOOL=11;
VT_VARIANT=12; VT_UNKNOWN=13; VT_DECIMAL=14; VT_I1=16; VT_UI1=17;
VT_UI2=18; VT_UI4=19; VT_I8=20; VT_UI8=21; VT_INT=22; VT_UINT=23;
VT_VOID=24; VT_HRESULT=25; VT_PTR=26; VT_SAFEARRAY=27; VT_CARRAY=28;
VT_USERDEFINED=29; VT_LPSTR=30; VT_LPWSTR=31; VT_FILETIME=64;
VT_BLOB=65; VT_STREAM=66; VT_STORAGE=67; VT_STREAMED_OBJECT=68;
VT_STORED_OBJECT=69; VT_BLOB_OBJECT=70; VT_CF=71; VT_CLSID=72;
VT_VECTOR=0x1000;
# map property id to name (for debugging purposes)
VT = {}
for keyword, var in list(vars().items()):
if keyword[:3] == "VT_":
VT[var] = keyword
#
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
# Some common document types (root.clsid fields)
WORD_CLSID = "00020900-0000-0000-C000-000000000046"
#TODO: check Excel, PPT, ...
#[PL]: Defect levels to classify parsing errors - see OleFileIO._raise_defect()
DEFECT_UNSURE = 10 # a case which looks weird, but not sure it's a defect
DEFECT_POTENTIAL = 20 # a potential defect
DEFECT_INCORRECT = 30 # an error according to specifications, but parsing
# can go on
DEFECT_FATAL = 40 # an error which cannot be ignored, parsing is
# impossible
# Minimal size of an empty OLE file, with 512-bytes sectors = 1536 bytes
# (this is used in isOleFile and OleFile.open)
MINIMAL_OLEFILE_SIZE = 1536
#[PL] add useful constants to __all__:
# for key in list(vars().keys()):
# if key.startswith('STGTY_') or key.startswith('DEFECT_'):
# __all__.append(key)
#=== FUNCTIONS ===============================================================
def isOleFile (filename):
"""
Test if a file is an OLE container (according to the magic bytes in its header).
:param filename: string-like or file-like object, OLE file to parse
- if filename is a string smaller than 1536 bytes, it is the path
of the file to open. (bytes or unicode string)
- if filename is a string longer than 1535 bytes, it is parsed
as the content of an OLE file in memory. (bytes type only)
- if filename is a file-like object (with read and seek methods),
it is parsed as-is.
:returns: True if OLE, False otherwise.
"""
# check if filename is a string-like or file-like object:
if hasattr(filename, 'read'):
# file-like object: use it directly
header = filename.read(len(MAGIC))
# just in case, seek back to start of file:
filename.seek(0)
elif isinstance(filename, bytes) and len(filename) >= MINIMAL_OLEFILE_SIZE:
# filename is a bytes string containing the OLE file to be parsed:
header = filename[:len(MAGIC)]
else:
# string-like object: filename of file on disk
header = open(filename, 'rb').read(len(MAGIC))
if header == MAGIC:
return True
else:
return False
if bytes is str:
# version for Python 2.x
def i8(c):
return ord(c)
else:
# version for Python 3.x
def i8(c):
return c if c.__class__ is int else c[0]
#TODO: replace i16 and i32 with more readable struct.unpack equivalent?
def i16(c, o = 0):
"""
Converts a 2-bytes (16 bits) string to an integer.
:param c: string containing bytes to convert
:param o: offset of bytes to convert in string
"""
return i8(c[o]) | (i8(c[o+1])<<8)
def i32(c, o = 0):
"""
Converts a 4-bytes (32 bits) string to an integer.
:param c: string containing bytes to convert
:param o: offset of bytes to convert in string
"""
## return int(ord(c[o])+(ord(c[o+1])<<8)+(ord(c[o+2])<<16)+(ord(c[o+3])<<24))
## # [PL]: added int() because "<<" gives long int since Python 2.4
# copied from Pillow's _binary:
return i8(c[o]) | (i8(c[o+1])<<8) | (i8(c[o+2])<<16) | (i8(c[o+3])<<24)
def _clsid(clsid):
"""
Converts a CLSID to a human-readable string.
:param clsid: string of length 16.
"""
assert len(clsid) == 16
# if clsid is only made of null bytes, return an empty string:
# (PL: why not simply return the string with zeroes?)
if not clsid.strip(b"\0"):
return ""
return (("%08X-%04X-%04X-%02X%02X-" + "%02X" * 6) %
((i32(clsid, 0), i16(clsid, 4), i16(clsid, 6)) +
tuple(map(i8, clsid[8:16]))))
# UNICODE support:
# (necessary to handle storages/streams names which use Unicode)
def _unicode(s, errors='replace'):
"""
Map unicode string to Latin 1. (Python with Unicode support)
:param s: UTF-16LE unicode string to convert to Latin-1
:param errors: 'replace', 'ignore' or 'strict'.
"""
#TODO: test if it OleFileIO works with Unicode strings, instead of
# converting to Latin-1.
try:
# First the string is converted to plain Unicode:
# (assuming it is encoded as UTF-16 little-endian)
u = s.decode('UTF-16LE', errors)
if bytes is not str or KEEP_UNICODE_NAMES:
return u
else:
# Second the unicode string is converted to Latin-1
return u.encode('latin_1', errors)
except:
# there was an error during Unicode to Latin-1 conversion:
raise IOError('incorrect Unicode name')
def filetime2datetime(filetime):
"""
convert FILETIME (64 bits int) to Python datetime.datetime
"""
# TODO: manage exception when microseconds is too large
# inspired from http://code.activestate.com/recipes/511425-filetime-to-datetime/
_FILETIME_null_date = datetime.datetime(1601, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0)
#debug('timedelta days=%d' % (filetime//(10*1000000*3600*24)))
return _FILETIME_null_date + datetime.timedelta(microseconds=filetime//10)
#=== CLASSES ==================================================================
class OleMetadata:
"""
class to parse and store metadata from standard properties of OLE files.
Available attributes:
codepage, title, subject, author, keywords, comments, template,
last_saved_by, revision_number, total_edit_time, last_printed, create_time,
last_saved_time, num_pages, num_words, num_chars, thumbnail,
creating_application, security, codepage_doc, category, presentation_target,
bytes, lines, paragraphs, slides, notes, hidden_slides, mm_clips,
scale_crop, heading_pairs, titles_of_parts, manager, company, links_dirty,
chars_with_spaces, unused, shared_doc, link_base, hlinks, hlinks_changed,
version, dig_sig, content_type, content_status, language, doc_version
Note: an attribute is set to None when not present in the properties of the
OLE file.
References for SummaryInformation stream:
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd942545.aspx
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd925819%28v=office.12%29.aspx
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa380376%28v=vs.85%29.aspx
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa372045.aspx
- http://sedna-soft.de/summary-information-stream/
- http://poi.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/poi/hpsf/SummaryInformation.html
References for DocumentSummaryInformation stream:
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd945671%28v=office.12%29.aspx
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa380374%28v=vs.85%29.aspx
- http://poi.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/poi/hpsf/DocumentSummaryInformation.html
new in version 0.25
"""
# attribute names for SummaryInformation stream properties:
# (ordered by property id, starting at 1)
SUMMARY_ATTRIBS = ['codepage', 'title', 'subject', 'author', 'keywords', 'comments',
'template', 'last_saved_by', 'revision_number', 'total_edit_time',
'last_printed', 'create_time', 'last_saved_time', 'num_pages',
'num_words', 'num_chars', 'thumbnail', 'creating_application',
'security']
# attribute names for DocumentSummaryInformation stream properties:
# (ordered by property id, starting at 1)
DOCSUM_ATTRIBS = ['codepage_doc', 'category', 'presentation_target', 'bytes', 'lines', 'paragraphs',
'slides', 'notes', 'hidden_slides', 'mm_clips',
'scale_crop', 'heading_pairs', 'titles_of_parts', 'manager',
'company', 'links_dirty', 'chars_with_spaces', 'unused', 'shared_doc',
'link_base', 'hlinks', 'hlinks_changed', 'version', 'dig_sig',
'content_type', 'content_status', 'language', 'doc_version']
def __init__(self):
"""
Constructor for OleMetadata
All attributes are set to None by default
"""
# properties from SummaryInformation stream
self.codepage = None
self.title = None
self.subject = None
self.author = None
self.keywords = None
self.comments = None
self.template = None
self.last_saved_by = None
self.revision_number = None
self.total_edit_time = None
self.last_printed = None
self.create_time = None
self.last_saved_time = None
self.num_pages = None
self.num_words = None
self.num_chars = None
self.thumbnail = None
self.creating_application = None
self.security = None
# properties from DocumentSummaryInformation stream
self.codepage_doc = None
self.category = None
self.presentation_target = None
self.bytes = None
self.lines = None
self.paragraphs = None
self.slides = None
self.notes = None
self.hidden_slides = None
self.mm_clips = None
self.scale_crop = None
self.heading_pairs = None
self.titles_of_parts = None
self.manager = None
self.company = None
self.links_dirty = None
self.chars_with_spaces = None
self.unused = None
self.shared_doc = None
self.link_base = None
self.hlinks = None
self.hlinks_changed = None
self.version = None
self.dig_sig = None
self.content_type = None
self.content_status = None
self.language = None
self.doc_version = None
def parse_properties(self, olefile):
"""
Parse standard properties of an OLE file, from the streams
"\x05SummaryInformation" and "\x05DocumentSummaryInformation",
if present.
Properties are converted to strings, integers or python datetime objects.
If a property is not present, its value is set to None.
"""
# first set all attributes to None:
for attrib in (self.SUMMARY_ATTRIBS + self.DOCSUM_ATTRIBS):
setattr(self, attrib, None)
if olefile.exists("\x05SummaryInformation"):
# get properties from the stream:
# (converting timestamps to python datetime, except total_edit_time,
# which is property #10)
props = olefile.getproperties("\x05SummaryInformation",
convert_time=True, no_conversion=[10])
# store them into this object's attributes:
for i in range(len(self.SUMMARY_ATTRIBS)):
# ids for standards properties start at 0x01, until 0x13
value = props.get(i+1, None)
setattr(self, self.SUMMARY_ATTRIBS[i], value)
if olefile.exists("\x05DocumentSummaryInformation"):
# get properties from the stream:
props = olefile.getproperties("\x05DocumentSummaryInformation",
convert_time=True)
# store them into this object's attributes:
for i in range(len(self.DOCSUM_ATTRIBS)):
# ids for standards properties start at 0x01, until 0x13
value = props.get(i+1, None)
setattr(self, self.DOCSUM_ATTRIBS[i], value)
def dump(self):
"""
Dump all metadata, for debugging purposes.
"""
print('Properties from SummaryInformation stream:')
for prop in self.SUMMARY_ATTRIBS:
value = getattr(self, prop)
print('- %s: %s' % (prop, repr(value)))
print('Properties from DocumentSummaryInformation stream:')
for prop in self.DOCSUM_ATTRIBS:
value = getattr(self, prop)
print('- %s: %s' % (prop, repr(value)))
#--- _OleStream ---------------------------------------------------------------
class _OleStream(io.BytesIO):
"""
OLE2 Stream
Returns a read-only file object which can be used to read
the contents of a OLE stream (instance of the BytesIO class).
To open a stream, use the openstream method in the OleFile class.
This function can be used with either ordinary streams,
or ministreams, depending on the offset, sectorsize, and
fat table arguments.
Attributes:
- size: actual size of data stream, after it was opened.
"""
# FIXME: should store the list of sects obtained by following
# the fat chain, and load new sectors on demand instead of
# loading it all in one go.
def __init__(self, fp, sect, size, offset, sectorsize, fat, filesize):
"""
Constructor for _OleStream class.
:param fp: file object, the OLE container or the MiniFAT stream
:param sect: sector index of first sector in the stream
:param size: total size of the stream
:param offset: offset in bytes for the first FAT or MiniFAT sector
:param sectorsize: size of one sector
:param fat: array/list of sector indexes (FAT or MiniFAT)
:param filesize: size of OLE file (for debugging)
:returns: a BytesIO instance containing the OLE stream
"""
debug('_OleStream.__init__:')
debug(' sect=%d (%X), size=%d, offset=%d, sectorsize=%d, len(fat)=%d, fp=%s'
%(sect,sect,size,offset,sectorsize,len(fat), repr(fp)))
#[PL] To detect malformed documents with FAT loops, we compute the
# expected number of sectors in the stream:
unknown_size = False
if size==0x7FFFFFFF:
# this is the case when called from OleFileIO._open(), and stream
# size is not known in advance (for example when reading the
# Directory stream). Then we can only guess maximum size:
size = len(fat)*sectorsize
# and we keep a record that size was unknown:
unknown_size = True
debug(' stream with UNKNOWN SIZE')
nb_sectors = (size + (sectorsize-1)) // sectorsize
debug('nb_sectors = %d' % nb_sectors)
# This number should (at least) be less than the total number of
# sectors in the given FAT:
if nb_sectors > len(fat):
raise IOError('malformed OLE document, stream too large')
# optimization(?): data is first a list of strings, and join() is called
# at the end to concatenate all in one string.
# (this may not be really useful with recent Python versions)
data = []
# if size is zero, then first sector index should be ENDOFCHAIN:
if size == 0 and sect != ENDOFCHAIN:
debug('size == 0 and sect != ENDOFCHAIN:')
raise IOError('incorrect OLE sector index for empty stream')
#[PL] A fixed-length for loop is used instead of an undefined while
# loop to avoid DoS attacks:
for i in range(nb_sectors):
# Sector index may be ENDOFCHAIN, but only if size was unknown
if sect == ENDOFCHAIN:
if unknown_size:
break
else:
# else this means that the stream is smaller than declared:
debug('sect=ENDOFCHAIN before expected size')
raise IOError('incomplete OLE stream')
# sector index should be within FAT:
if sect<0 or sect>=len(fat):
debug('sect=%d (%X) / len(fat)=%d' % (sect, sect, len(fat)))
debug('i=%d / nb_sectors=%d' %(i, nb_sectors))
## tmp_data = b"".join(data)
## f = open('test_debug.bin', 'wb')
## f.write(tmp_data)
## f.close()
## debug('data read so far: %d bytes' % len(tmp_data))
raise IOError('incorrect OLE FAT, sector index out of range')
#TODO: merge this code with OleFileIO.getsect() ?
#TODO: check if this works with 4K sectors:
try:
fp.seek(offset + sectorsize * sect)
except:
debug('sect=%d, seek=%d, filesize=%d' %
(sect, offset+sectorsize*sect, filesize))
raise IOError('OLE sector index out of range')
sector_data = fp.read(sectorsize)
# [PL] check if there was enough data:
# Note: if sector is the last of the file, sometimes it is not a
# complete sector (of 512 or 4K), so we may read less than
# sectorsize.
if len(sector_data)!=sectorsize and sect!=(len(fat)-1):
debug('sect=%d / len(fat)=%d, seek=%d / filesize=%d, len read=%d' %
(sect, len(fat), offset+sectorsize*sect, filesize, len(sector_data)))
debug('seek+len(read)=%d' % (offset+sectorsize*sect+len(sector_data)))
raise IOError('incomplete OLE sector')
data.append(sector_data)
# jump to next sector in the FAT:
try:
sect = fat[sect] & 0xFFFFFFFF # JYTHON-WORKAROUND
except IndexError:
# [PL] if pointer is out of the FAT an exception is raised
raise IOError('incorrect OLE FAT, sector index out of range')
#[PL] Last sector should be a "end of chain" marker:
if sect != ENDOFCHAIN:
raise IOError('incorrect last sector index in OLE stream')
data = b"".join(data)
# Data is truncated to the actual stream size:
if len(data) >= size:
data = data[:size]
# actual stream size is stored for future use:
self.size = size
elif unknown_size:
# actual stream size was not known, now we know the size of read
# data:
self.size = len(data)
else:
# read data is less than expected:
debug('len(data)=%d, size=%d' % (len(data), size))
raise IOError('OLE stream size is less than declared')
# when all data is read in memory, BytesIO constructor is called
io.BytesIO.__init__(self, data)
# Then the _OleStream object can be used as a read-only file object.
#--- _OleDirectoryEntry -------------------------------------------------------
class _OleDirectoryEntry:
"""
OLE2 Directory Entry
"""
#[PL] parsing code moved from OleFileIO.loaddirectory
# struct to parse directory entries:
# <: little-endian byte order, standard sizes
# (note: this should guarantee that Q returns a 64 bits int)
# 64s: string containing entry name in unicode (max 31 chars) + null char
# H: uint16, number of bytes used in name buffer, including null = (len+1)*2
# B: uint8, dir entry type (between 0 and 5)
# B: uint8, color: 0=black, 1=red
# I: uint32, index of left child node in the red-black tree, NOSTREAM if none
# I: uint32, index of right child node in the red-black tree, NOSTREAM if none
# I: uint32, index of child root node if it is a storage, else NOSTREAM
# 16s: CLSID, unique identifier (only used if it is a storage)
# I: uint32, user flags
# Q (was 8s): uint64, creation timestamp or zero
# Q (was 8s): uint64, modification timestamp or zero
# I: uint32, SID of first sector if stream or ministream, SID of 1st sector
# of stream containing ministreams if root entry, 0 otherwise
# I: uint32, total stream size in bytes if stream (low 32 bits), 0 otherwise
# I: uint32, total stream size in bytes if stream (high 32 bits), 0 otherwise
STRUCT_DIRENTRY = '<64sHBBIII16sIQQIII'
# size of a directory entry: 128 bytes
DIRENTRY_SIZE = 128
assert struct.calcsize(STRUCT_DIRENTRY) == DIRENTRY_SIZE
def __init__(self, entry, sid, olefile):
"""
Constructor for an _OleDirectoryEntry object.
Parses a 128-bytes entry from the OLE Directory stream.
:param entry : string (must be 128 bytes long)
:param sid : index of this directory entry in the OLE file directory
:param olefile: OleFileIO containing this directory entry
"""
self.sid = sid
# ref to olefile is stored for future use
self.olefile = olefile
# kids is a list of children entries, if this entry is a storage:
# (list of _OleDirectoryEntry objects)
self.kids = []
# kids_dict is a dictionary of children entries, indexed by their
# name in lowercase: used to quickly find an entry, and to detect
# duplicates
self.kids_dict = {}
# flag used to detect if the entry is referenced more than once in
# directory:
self.used = False
# decode DirEntry
(
name,
namelength,
self.entry_type,
self.color,
self.sid_left,
self.sid_right,
self.sid_child,
clsid,
self.dwUserFlags,
self.createTime,
self.modifyTime,
self.isectStart,
sizeLow,
sizeHigh
) = struct.unpack(_OleDirectoryEntry.STRUCT_DIRENTRY, entry)
if self.entry_type not in [STGTY_ROOT, STGTY_STORAGE, STGTY_STREAM, STGTY_EMPTY]:
olefile._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, 'unhandled OLE storage type')
# only first directory entry can (and should) be root:
if self.entry_type == STGTY_ROOT and sid != 0:
olefile._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, 'duplicate OLE root entry')
if sid == 0 and self.entry_type != STGTY_ROOT:
olefile._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, 'incorrect OLE root entry')
#debug (struct.unpack(fmt_entry, entry[:len_entry]))
# name should be at most 31 unicode characters + null character,
# so 64 bytes in total (31*2 + 2):
if namelength>64:
olefile._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, 'incorrect DirEntry name length')
# if exception not raised, namelength is set to the maximum value:
namelength = 64
# only characters without ending null char are kept:
name = name[:(namelength-2)]
# name is converted from unicode to Latin-1:
self.name = _unicode(name)
debug('DirEntry SID=%d: %s' % (self.sid, repr(self.name)))
debug(' - type: %d' % self.entry_type)
debug(' - sect: %d' % self.isectStart)
debug(' - SID left: %d, right: %d, child: %d' % (self.sid_left,
self.sid_right, self.sid_child))
# sizeHigh is only used for 4K sectors, it should be zero for 512 bytes
# sectors, BUT apparently some implementations set it as 0xFFFFFFFF, 1
# or some other value so it cannot be raised as a defect in general:
if olefile.sectorsize == 512:
if sizeHigh != 0 and sizeHigh != 0xFFFFFFFF:
debug('sectorsize=%d, sizeLow=%d, sizeHigh=%d (%X)' %
(olefile.sectorsize, sizeLow, sizeHigh, sizeHigh))
olefile._raise_defect(DEFECT_UNSURE, 'incorrect OLE stream size')
self.size = sizeLow
else:
self.size = sizeLow + (long(sizeHigh)<<32)
debug(' - size: %d (sizeLow=%d, sizeHigh=%d)' % (self.size, sizeLow, sizeHigh))
self.clsid = _clsid(clsid)
# a storage should have a null size, BUT some implementations such as
# Word 8 for Mac seem to allow non-null values => Potential defect:
if self.entry_type == STGTY_STORAGE and self.size != 0:
olefile._raise_defect(DEFECT_POTENTIAL, 'OLE storage with size>0')
# check if stream is not already referenced elsewhere:
if self.entry_type in (STGTY_ROOT, STGTY_STREAM) and self.size>0:
if self.size < olefile.minisectorcutoff \
and self.entry_type==STGTY_STREAM: # only streams can be in MiniFAT
# ministream object
minifat = True
else:
minifat = False
olefile._check_duplicate_stream(self.isectStart, minifat)
def build_storage_tree(self):
"""
Read and build the red-black tree attached to this _OleDirectoryEntry
object, if it is a storage.
Note that this method builds a tree of all subentries, so it should
only be called for the root object once.
"""
debug('build_storage_tree: SID=%d - %s - sid_child=%d'
% (self.sid, repr(self.name), self.sid_child))
if self.sid_child != NOSTREAM:
# if child SID is not NOSTREAM, then this entry is a storage.
# Let's walk through the tree of children to fill the kids list:
self.append_kids(self.sid_child)
# Note from OpenOffice documentation: the safest way is to
# recreate the tree because some implementations may store broken
# red-black trees...
# in the OLE file, entries are sorted on (length, name).
# for convenience, we sort them on name instead:
# (see rich comparison methods in this class)
self.kids.sort()
def append_kids(self, child_sid):
"""
Walk through red-black tree of children of this directory entry to add
all of them to the kids list. (recursive method)
:param child_sid : index of child directory entry to use, or None when called
first time for the root. (only used during recursion)
"""
#[PL] this method was added to use simple recursion instead of a complex
# algorithm.
# if this is not a storage or a leaf of the tree, nothing to do:
if child_sid == NOSTREAM:
return
# check if child SID is in the proper range:
if child_sid<0 or child_sid>=len(self.olefile.direntries):
self.olefile._raise_defect(DEFECT_FATAL, 'OLE DirEntry index out of range')
# get child direntry:
child = self.olefile._load_direntry(child_sid) #direntries[child_sid]
debug('append_kids: child_sid=%d - %s - sid_left=%d, sid_right=%d, sid_child=%d'
% (child.sid, repr(child.name), child.sid_left, child.sid_right, child.sid_child))
# the directory entries are organized as a red-black tree.
# (cf. Wikipedia for details)
# First walk through left side of the tree:
self.append_kids(child.sid_left)
# Check if its name is not already used (case-insensitive):
name_lower = child.name.lower()
if name_lower in self.kids_dict:
self.olefile._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT,
"Duplicate filename in OLE storage")
# Then the child_sid _OleDirectoryEntry object is appended to the
# kids list and dictionary:
self.kids.append(child)
self.kids_dict[name_lower] = child
# Check if kid was not already referenced in a storage:
if child.used:
self.olefile._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT,
'OLE Entry referenced more than once')
child.used = True
# Finally walk through right side of the tree:
self.append_kids(child.sid_right)
# Afterwards build kid's own tree if it's also a storage:
child.build_storage_tree()
def __eq__(self, other):
"Compare entries by name"
return self.name == other.name
def __lt__(self, other):
"Compare entries by name"
return self.name < other.name
def __ne__(self, other):
return not self.__eq__(other)
def __le__(self, other):
return self.__eq__(other) or self.__lt__(other)
# Reflected __lt__() and __le__() will be used for __gt__() and __ge__()
#TODO: replace by the same function as MS implementation ?
# (order by name length first, then case-insensitive order)
def dump(self, tab = 0):
"Dump this entry, and all its subentries (for debug purposes only)"
TYPES = ["(invalid)", "(storage)", "(stream)", "(lockbytes)",
"(property)", "(root)"]
print(" "*tab + repr(self.name), TYPES[self.entry_type], end=' ')
if self.entry_type in (STGTY_STREAM, STGTY_ROOT):
print(self.size, "bytes", end=' ')
print()
if self.entry_type in (STGTY_STORAGE, STGTY_ROOT) and self.clsid:
print(" "*tab + "{%s}" % self.clsid)
for kid in self.kids:
kid.dump(tab + 2)
def getmtime(self):
"""
Return modification time of a directory entry.
:returns: None if modification time is null, a python datetime object
otherwise (UTC timezone)
new in version 0.26
"""
if self.modifyTime == 0:
return None
return filetime2datetime(self.modifyTime)
def getctime(self):
"""
Return creation time of a directory entry.
:returns: None if modification time is null, a python datetime object
otherwise (UTC timezone)
new in version 0.26
"""
if self.createTime == 0:
return None
return filetime2datetime(self.createTime)
#--- OleFileIO ----------------------------------------------------------------
class OleFileIO:
"""
OLE container object
This class encapsulates the interface to an OLE 2 structured
storage file. Use the listdir and openstream methods to
access the contents of this file.
Object names are given as a list of strings, one for each subentry
level. The root entry should be omitted. For example, the following
code extracts all image streams from a Microsoft Image Composer file::
ole = OleFileIO("fan.mic")
for entry in ole.listdir():
if entry[1:2] == "Image":
fin = ole.openstream(entry)
fout = open(entry[0:1], "wb")
while True:
s = fin.read(8192)
if not s:
break
fout.write(s)
You can use the viewer application provided with the Python Imaging
Library to view the resulting files (which happens to be standard
TIFF files).
"""
def __init__(self, filename=None, raise_defects=DEFECT_FATAL,
write_mode=False, debug=False):
"""
Constructor for the OleFileIO class.
:param filename: file to open.
- if filename is a string smaller than 1536 bytes, it is the path
of the file to open. (bytes or unicode string)
- if filename is a string longer than 1535 bytes, it is parsed
as the content of an OLE file in memory. (bytes type only)
- if filename is a file-like object (with read, seek and tell methods),
it is parsed as-is.
:param raise_defects: minimal level for defects to be raised as exceptions.
(use DEFECT_FATAL for a typical application, DEFECT_INCORRECT for a
security-oriented application, see source code for details)
:param write_mode: bool, if True the file is opened in read/write mode instead
of read-only by default.
:param debug: bool, set debug mode
"""
set_debug_mode(debug)
# minimal level for defects to be raised as exceptions:
self._raise_defects_level = raise_defects
# list of defects/issues not raised as exceptions:
# tuples of (exception type, message)
self.parsing_issues = []
self.write_mode = write_mode
self._filesize = None
self.fp = None
if filename:
self.open(filename, write_mode=write_mode)
def _raise_defect(self, defect_level, message, exception_type=IOError):
"""
This method should be called for any defect found during file parsing.
It may raise an IOError exception according to the minimal level chosen
for the OleFileIO object.
:param defect_level: defect level, possible values are:
- DEFECT_UNSURE : a case which looks weird, but not sure it's a defect
- DEFECT_POTENTIAL : a potential defect
- DEFECT_INCORRECT : an error according to specifications, but parsing can go on
- DEFECT_FATAL : an error which cannot be ignored, parsing is impossible
:param message: string describing the defect, used with raised exception.
:param exception_type: exception class to be raised, IOError by default
"""
# added by [PL]
if defect_level >= self._raise_defects_level:
raise exception_type(message)
else:
# just record the issue, no exception raised:
self.parsing_issues.append((exception_type, message))
def open(self, filename, write_mode=False):
"""
Open an OLE2 file in read-only or read/write mode.
Read and parse the header, FAT and directory.
:param filename: string-like or file-like object, OLE file to parse
- if filename is a string smaller than 1536 bytes, it is the path
of the file to open. (bytes or unicode string)
- if filename is a string longer than 1535 bytes, it is parsed
as the content of an OLE file in memory. (bytes type only)
- if filename is a file-like object (with read, seek and tell methods),
it is parsed as-is.
:param write_mode: bool, if True the file is opened in read/write mode instead
of read-only by default. (ignored if filename is not a path)
"""
self.write_mode = write_mode
#[PL] check if filename is a string-like or file-like object:
# (it is better to check for a read() method)
if hasattr(filename, 'read'):
#TODO: also check seek and tell methods?
# file-like object: use it directly
self.fp = filename
elif isinstance(filename, bytes) and len(filename) >= MINIMAL_OLEFILE_SIZE:
# filename is a bytes string containing the OLE file to be parsed:
# convert it to BytesIO
self.fp = io.BytesIO(filename)
else:
# string-like object: filename of file on disk
if self.write_mode:
# open file in mode 'read with update, binary'
# According to https://docs.python.org/2/library/functions.html#open
# 'w' would truncate the file, 'a' may only append on some Unixes
mode = 'r+b'
else:
# read-only mode by default
mode = 'rb'
self.fp = open(filename, mode)
# obtain the filesize by using seek and tell, which should work on most
# file-like objects:
#TODO: do it above, using getsize with filename when possible?
#TODO: fix code to fail with clear exception when filesize cannot be obtained
filesize=0
self.fp.seek(0, os.SEEK_END)
try:
filesize = self.fp.tell()
finally:
self.fp.seek(0)
self._filesize = filesize
# lists of streams in FAT and MiniFAT, to detect duplicate references
# (list of indexes of first sectors of each stream)
self._used_streams_fat = []
self._used_streams_minifat = []
header = self.fp.read(512)
if len(header) != 512 or header[:8] != MAGIC:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_FATAL, "not an OLE2 structured storage file")
# [PL] header structure according to AAF specifications:
##Header
##struct StructuredStorageHeader { // [offset from start (bytes), length (bytes)]
##BYTE _abSig[8]; // [00H,08] {0xd0, 0xcf, 0x11, 0xe0, 0xa1, 0xb1,
## // 0x1a, 0xe1} for current version
##CLSID _clsid; // [08H,16] reserved must be zero (WriteClassStg/
## // GetClassFile uses root directory class id)
##USHORT _uMinorVersion; // [18H,02] minor version of the format: 33 is
## // written by reference implementation
##USHORT _uDllVersion; // [1AH,02] major version of the dll/format: 3 for
## // 512-byte sectors, 4 for 4 KB sectors
##USHORT _uByteOrder; // [1CH,02] 0xFFFE: indicates Intel byte-ordering
##USHORT _uSectorShift; // [1EH,02] size of sectors in power-of-two;
## // typically 9 indicating 512-byte sectors
##USHORT _uMiniSectorShift; // [20H,02] size of mini-sectors in power-of-two;
## // typically 6 indicating 64-byte mini-sectors
##USHORT _usReserved; // [22H,02] reserved, must be zero
##ULONG _ulReserved1; // [24H,04] reserved, must be zero
##FSINDEX _csectDir; // [28H,04] must be zero for 512-byte sectors,
## // number of SECTs in directory chain for 4 KB
## // sectors
##FSINDEX _csectFat; // [2CH,04] number of SECTs in the FAT chain
##SECT _sectDirStart; // [30H,04] first SECT in the directory chain
##DFSIGNATURE _signature; // [34H,04] signature used for transactions; must
## // be zero. The reference implementation
## // does not support transactions
##ULONG _ulMiniSectorCutoff; // [38H,04] maximum size for a mini stream;
## // typically 4096 bytes
##SECT _sectMiniFatStart; // [3CH,04] first SECT in the MiniFAT chain
##FSINDEX _csectMiniFat; // [40H,04] number of SECTs in the MiniFAT chain
##SECT _sectDifStart; // [44H,04] first SECT in the DIFAT chain
##FSINDEX _csectDif; // [48H,04] number of SECTs in the DIFAT chain
##SECT _sectFat[109]; // [4CH,436] the SECTs of first 109 FAT sectors
##};
# [PL] header decoding:
# '<' indicates little-endian byte ordering for Intel (cf. struct module help)
fmt_header = '<8s16sHHHHHHLLLLLLLLLL'
header_size = struct.calcsize(fmt_header)
debug( "fmt_header size = %d, +FAT = %d" % (header_size, header_size + 109*4) )
header1 = header[:header_size]
(
self.Sig,
self.clsid,
self.MinorVersion,
self.DllVersion,
self.ByteOrder,
self.SectorShift,
self.MiniSectorShift,
self.Reserved, self.Reserved1,
self.csectDir,
self.csectFat,
self.sectDirStart,
self.signature,
self.MiniSectorCutoff,
self.MiniFatStart,
self.csectMiniFat,
self.sectDifStart,
self.csectDif
) = struct.unpack(fmt_header, header1)
debug( struct.unpack(fmt_header, header1))
if self.Sig != MAGIC:
# OLE signature should always be present
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_FATAL, "incorrect OLE signature")
if self.clsid != bytearray(16):
# according to AAF specs, CLSID should always be zero
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, "incorrect CLSID in OLE header")
debug( "MinorVersion = %d" % self.MinorVersion )
debug( "DllVersion = %d" % self.DllVersion )
if self.DllVersion not in [3, 4]:
# version 3: usual format, 512 bytes per sector
# version 4: large format, 4K per sector
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, "incorrect DllVersion in OLE header")
debug( "ByteOrder = %X" % self.ByteOrder )
if self.ByteOrder != 0xFFFE:
# For now only common little-endian documents are handled correctly
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_FATAL, "incorrect ByteOrder in OLE header")
# TODO: add big-endian support for documents created on Mac ?
# But according to [MS-CFB] ? v20140502, ByteOrder MUST be 0xFFFE.
self.SectorSize = 2**self.SectorShift
debug( "SectorSize = %d" % self.SectorSize )
if self.SectorSize not in [512, 4096]:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, "incorrect SectorSize in OLE header")
if (self.DllVersion==3 and self.SectorSize!=512) \
or (self.DllVersion==4 and self.SectorSize!=4096):
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, "SectorSize does not match DllVersion in OLE header")
self.MiniSectorSize = 2**self.MiniSectorShift
debug( "MiniSectorSize = %d" % self.MiniSectorSize )
if self.MiniSectorSize not in [64]:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, "incorrect MiniSectorSize in OLE header")
if self.Reserved != 0 or self.Reserved1 != 0:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, "incorrect OLE header (non-null reserved bytes)")
debug( "csectDir = %d" % self.csectDir )
# Number of directory sectors (only allowed if DllVersion != 3)
if self.SectorSize==512 and self.csectDir!=0:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, "incorrect csectDir in OLE header")
debug( "csectFat = %d" % self.csectFat )
# csectFat = number of FAT sectors in the file
debug( "sectDirStart = %X" % self.sectDirStart )
# sectDirStart = 1st sector containing the directory
debug( "signature = %d" % self.signature )
# Signature should be zero, BUT some implementations do not follow this
# rule => only a potential defect:
# (according to MS-CFB, may be != 0 for applications supporting file
# transactions)
if self.signature != 0:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_POTENTIAL, "incorrect OLE header (signature>0)")
debug( "MiniSectorCutoff = %d" % self.MiniSectorCutoff )
# MS-CFB: This integer field MUST be set to 0x00001000. This field
# specifies the maximum size of a user-defined data stream allocated
# from the mini FAT and mini stream, and that cutoff is 4096 bytes.
# Any user-defined data stream larger than or equal to this cutoff size
# must be allocated as normal sectors from the FAT.
if self.MiniSectorCutoff != 0x1000:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, "incorrect MiniSectorCutoff in OLE header")
debug( "MiniFatStart = %X" % self.MiniFatStart )
debug( "csectMiniFat = %d" % self.csectMiniFat )
debug( "sectDifStart = %X" % self.sectDifStart )
debug( "csectDif = %d" % self.csectDif )
# calculate the number of sectors in the file
# (-1 because header doesn't count)
self.nb_sect = ( (filesize + self.SectorSize-1) // self.SectorSize) - 1
debug( "Number of sectors in the file: %d" % self.nb_sect )
#TODO: change this test, because an OLE file MAY contain other data
# after the last sector.
# file clsid
self.clsid = _clsid(header[8:24])
#TODO: remove redundant attributes, and fix the code which uses them?
self.sectorsize = self.SectorSize #1 << i16(header, 30)
self.minisectorsize = self.MiniSectorSize #1 << i16(header, 32)
self.minisectorcutoff = self.MiniSectorCutoff # i32(header, 56)
# check known streams for duplicate references (these are always in FAT,
# never in MiniFAT):
self._check_duplicate_stream(self.sectDirStart)
# check MiniFAT only if it is not empty:
if self.csectMiniFat:
self._check_duplicate_stream(self.MiniFatStart)
# check DIFAT only if it is not empty:
if self.csectDif:
self._check_duplicate_stream(self.sectDifStart)
# Load file allocation tables
self.loadfat(header)
# Load direcory. This sets both the direntries list (ordered by sid)
# and the root (ordered by hierarchy) members.
self.loaddirectory(self.sectDirStart)#i32(header, 48))
self.ministream = None
self.minifatsect = self.MiniFatStart #i32(header, 60)
def close(self):
"""
close the OLE file, to release the file object
"""
self.fp.close()
def _check_duplicate_stream(self, first_sect, minifat=False):
"""
Checks if a stream has not been already referenced elsewhere.
This method should only be called once for each known stream, and only
if stream size is not null.
:param first_sect: int, index of first sector of the stream in FAT
:param minifat: bool, if True, stream is located in the MiniFAT, else in the FAT
"""
if minifat:
debug('_check_duplicate_stream: sect=%d in MiniFAT' % first_sect)
used_streams = self._used_streams_minifat
else:
debug('_check_duplicate_stream: sect=%d in FAT' % first_sect)
# some values can be safely ignored (not a real stream):
if first_sect in (DIFSECT,FATSECT,ENDOFCHAIN,FREESECT):
return
used_streams = self._used_streams_fat
#TODO: would it be more efficient using a dict or hash values, instead
# of a list of long ?
if first_sect in used_streams:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, 'Stream referenced twice')
else:
used_streams.append(first_sect)
def dumpfat(self, fat, firstindex=0):
"Displays a part of FAT in human-readable form for debugging purpose"
# [PL] added only for debug
if not DEBUG_MODE:
return
# dictionary to convert special FAT values in human-readable strings
VPL = 8 # values per line (8+1 * 8+1 = 81)
fatnames = {
FREESECT: "..free..",
ENDOFCHAIN: "[ END. ]",
FATSECT: "FATSECT ",
DIFSECT: "DIFSECT "
}
nbsect = len(fat)
nlines = (nbsect+VPL-1)//VPL
print("index", end=" ")
for i in range(VPL):
print("%8X" % i, end=" ")
print()
for l in range(nlines):
index = l*VPL
print("%8X:" % (firstindex+index), end=" ")
for i in range(index, index+VPL):
if i>=nbsect:
break
sect = fat[i]
aux = sect & 0xFFFFFFFF # JYTHON-WORKAROUND
if aux in fatnames:
name = fatnames[aux]
else:
if sect == i+1:
name = " --->"
else:
name = "%8X" % sect
print(name, end=" ")
print()
def dumpsect(self, sector, firstindex=0):
"Displays a sector in a human-readable form, for debugging purpose."
if not DEBUG_MODE:
return
VPL=8 # number of values per line (8+1 * 8+1 = 81)
tab = array.array(UINT32, sector)
if sys.byteorder == 'big':
tab.byteswap()
nbsect = len(tab)
nlines = (nbsect+VPL-1)//VPL
print("index", end=" ")
for i in range(VPL):
print("%8X" % i, end=" ")
print()
for l in range(nlines):
index = l*VPL
print("%8X:" % (firstindex+index), end=" ")
for i in range(index, index+VPL):
if i>=nbsect:
break
sect = tab[i]
name = "%8X" % sect
print(name, end=" ")
print()
def sect2array(self, sect):
"""
convert a sector to an array of 32 bits unsigned integers,
swapping bytes on big endian CPUs such as PowerPC (old Macs)
"""
a = array.array(UINT32, sect)
# if CPU is big endian, swap bytes:
if sys.byteorder == 'big':
a.byteswap()
return a
def loadfat_sect(self, sect):
"""
Adds the indexes of the given sector to the FAT
:param sect: string containing the first FAT sector, or array of long integers
:returns: index of last FAT sector.
"""
# a FAT sector is an array of ulong integers.
if isinstance(sect, array.array):
# if sect is already an array it is directly used
fat1 = sect
else:
# if it's a raw sector, it is parsed in an array
fat1 = self.sect2array(sect)
self.dumpsect(sect)
# The FAT is a sector chain starting at the first index of itself.
for isect in fat1:
isect = isect & 0xFFFFFFFF # JYTHON-WORKAROUND
debug("isect = %X" % isect)
if isect == ENDOFCHAIN or isect == FREESECT:
# the end of the sector chain has been reached
debug("found end of sector chain")
break
# read the FAT sector
s = self.getsect(isect)
# parse it as an array of 32 bits integers, and add it to the
# global FAT array
nextfat = self.sect2array(s)
self.fat = self.fat + nextfat
return isect
def loadfat(self, header):
"""
Load the FAT table.
"""
# The 1st sector of the file contains sector numbers for the first 109
# FAT sectors, right after the header which is 76 bytes long.
# (always 109, whatever the sector size: 512 bytes = 76+4*109)
# Additional sectors are described by DIF blocks
sect = header[76:512]
debug( "len(sect)=%d, so %d integers" % (len(sect), len(sect)//4) )
#fat = []
# [PL] FAT is an array of 32 bits unsigned ints, it's more effective
# to use an array than a list in Python.
# It's initialized as empty first:
self.fat = array.array(UINT32)
self.loadfat_sect(sect)
#self.dumpfat(self.fat)
## for i in range(0, len(sect), 4):
## ix = i32(sect, i)
## #[PL] if ix == -2 or ix == -1: # ix == 0xFFFFFFFE or ix == 0xFFFFFFFF:
## if ix == 0xFFFFFFFE or ix == 0xFFFFFFFF:
## break
## s = self.getsect(ix)
## #fat = fat + [i32(s, i) for i in range(0, len(s), 4)]
## fat = fat + array.array(UINT32, s)
if self.csectDif != 0:
# [PL] There's a DIFAT because file is larger than 6.8MB
# some checks just in case:
if self.csectFat <= 109:
# there must be at least 109 blocks in header and the rest in
# DIFAT, so number of sectors must be >109.
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, 'incorrect DIFAT, not enough sectors')
if self.sectDifStart >= self.nb_sect:
# initial DIFAT block index must be valid
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_FATAL, 'incorrect DIFAT, first index out of range')
debug( "DIFAT analysis..." )
# We compute the necessary number of DIFAT sectors :
# Number of pointers per DIFAT sector = (sectorsize/4)-1
# (-1 because the last pointer is the next DIFAT sector number)
nb_difat_sectors = (self.sectorsize//4)-1
# (if 512 bytes: each DIFAT sector = 127 pointers + 1 towards next DIFAT sector)
nb_difat = (self.csectFat-109 + nb_difat_sectors-1)//nb_difat_sectors
debug( "nb_difat = %d" % nb_difat )
if self.csectDif != nb_difat:
raise IOError('incorrect DIFAT')
isect_difat = self.sectDifStart
for i in iterrange(nb_difat):
debug( "DIFAT block %d, sector %X" % (i, isect_difat) )
#TODO: check if corresponding FAT SID = DIFSECT
sector_difat = self.getsect(isect_difat)
difat = self.sect2array(sector_difat)
self.dumpsect(sector_difat)
self.loadfat_sect(difat[:nb_difat_sectors])
# last DIFAT pointer is next DIFAT sector:
isect_difat = difat[nb_difat_sectors]
debug( "next DIFAT sector: %X" % isect_difat )
# checks:
if isect_difat not in [ENDOFCHAIN, FREESECT]:
# last DIFAT pointer value must be ENDOFCHAIN or FREESECT
raise IOError('incorrect end of DIFAT')
## if len(self.fat) != self.csectFat:
## # FAT should contain csectFat blocks
## print("FAT length: %d instead of %d" % (len(self.fat), self.csectFat))
## raise IOError('incorrect DIFAT')
# since FAT is read from fixed-size sectors, it may contain more values
# than the actual number of sectors in the file.
# Keep only the relevant sector indexes:
if len(self.fat) > self.nb_sect:
debug('len(fat)=%d, shrunk to nb_sect=%d' % (len(self.fat), self.nb_sect))
self.fat = self.fat[:self.nb_sect]
debug('\nFAT:')
self.dumpfat(self.fat)
def loadminifat(self):
"""
Load the MiniFAT table.
"""
# MiniFAT is stored in a standard sub-stream, pointed to by a header
# field.
# NOTE: there are two sizes to take into account for this stream:
# 1) Stream size is calculated according to the number of sectors
# declared in the OLE header. This allocated stream may be more than
# needed to store the actual sector indexes.
# (self.csectMiniFat is the number of sectors of size self.SectorSize)
stream_size = self.csectMiniFat * self.SectorSize
# 2) Actually used size is calculated by dividing the MiniStream size
# (given by root entry size) by the size of mini sectors, *4 for
# 32 bits indexes:
nb_minisectors = (self.root.size + self.MiniSectorSize-1) // self.MiniSectorSize
used_size = nb_minisectors * 4
debug('loadminifat(): minifatsect=%d, nb FAT sectors=%d, used_size=%d, stream_size=%d, nb MiniSectors=%d' %
(self.minifatsect, self.csectMiniFat, used_size, stream_size, nb_minisectors))
if used_size > stream_size:
# This is not really a problem, but may indicate a wrong implementation:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, 'OLE MiniStream is larger than MiniFAT')
# In any case, first read stream_size:
s = self._open(self.minifatsect, stream_size, force_FAT=True).read()
#[PL] Old code replaced by an array:
#self.minifat = [i32(s, i) for i in range(0, len(s), 4)]
self.minifat = self.sect2array(s)
# Then shrink the array to used size, to avoid indexes out of MiniStream:
debug('MiniFAT shrunk from %d to %d sectors' % (len(self.minifat), nb_minisectors))
self.minifat = self.minifat[:nb_minisectors]
debug('loadminifat(): len=%d' % len(self.minifat))
debug('\nMiniFAT:')
self.dumpfat(self.minifat)
def getsect(self, sect):
"""
Read given sector from file on disk.
:param sect: int, sector index
:returns: a string containing the sector data.
"""
# From [MS-CFB]: A sector number can be converted into a byte offset
# into the file by using the following formula:
# (sector number + 1) x Sector Size.
# This implies that sector #0 of the file begins at byte offset Sector
# Size, not at 0.
# [PL] the original code in PIL was wrong when sectors are 4KB instead of
# 512 bytes:
#self.fp.seek(512 + self.sectorsize * sect)
#[PL]: added safety checks:
#print("getsect(%X)" % sect)
try:
self.fp.seek(self.sectorsize * (sect+1))
except:
debug('getsect(): sect=%X, seek=%d, filesize=%d' %
(sect, self.sectorsize*(sect+1), self._filesize))
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_FATAL, 'OLE sector index out of range')
sector = self.fp.read(self.sectorsize)
if len(sector) != self.sectorsize:
debug('getsect(): sect=%X, read=%d, sectorsize=%d' %
(sect, len(sector), self.sectorsize))
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_FATAL, 'incomplete OLE sector')
return sector
def write_sect(self, sect, data, padding=b'\x00'):
"""
Write given sector to file on disk.
:param sect: int, sector index
:param data: bytes, sector data
:param padding: single byte, padding character if data < sector size
"""
if not isinstance(data, bytes):
raise TypeError("write_sect: data must be a bytes string")
if not isinstance(padding, bytes) or len(padding)!=1:
raise TypeError("write_sect: padding must be a bytes string of 1 char")
#TODO: we could allow padding=None for no padding at all
try:
self.fp.seek(self.sectorsize * (sect+1))
except:
debug('write_sect(): sect=%X, seek=%d, filesize=%d' %
(sect, self.sectorsize*(sect+1), self._filesize))
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_FATAL, 'OLE sector index out of range')
if len(data) < self.sectorsize:
# add padding
data += padding * (self.sectorsize - len(data))
elif len(data) < self.sectorsize:
raise ValueError("Data is larger than sector size")
self.fp.write(data)
def loaddirectory(self, sect):
"""
Load the directory.
:param sect: sector index of directory stream.
"""
# The directory is stored in a standard
# substream, independent of its size.
# open directory stream as a read-only file:
# (stream size is not known in advance)
self.directory_fp = self._open(sect)
#[PL] to detect malformed documents and avoid DoS attacks, the maximum
# number of directory entries can be calculated:
max_entries = self.directory_fp.size // 128
debug('loaddirectory: size=%d, max_entries=%d' %
(self.directory_fp.size, max_entries))
# Create list of directory entries
#self.direntries = []
# We start with a list of "None" object
self.direntries = [None] * max_entries
## for sid in iterrange(max_entries):
## entry = fp.read(128)
## if not entry:
## break
## self.direntries.append(_OleDirectoryEntry(entry, sid, self))
# load root entry:
root_entry = self._load_direntry(0)
# Root entry is the first entry:
self.root = self.direntries[0]
# read and build all storage trees, starting from the root:
self.root.build_storage_tree()
def _load_direntry (self, sid):
"""
Load a directory entry from the directory.
This method should only be called once for each storage/stream when
loading the directory.
:param sid: index of storage/stream in the directory.
:returns: a _OleDirectoryEntry object
:exception IOError: if the entry has always been referenced.
"""
# check if SID is OK:
if sid<0 or sid>=len(self.direntries):
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_FATAL, "OLE directory index out of range")
# check if entry was already referenced:
if self.direntries[sid] is not None:
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT,
"double reference for OLE stream/storage")
# if exception not raised, return the object
return self.direntries[sid]
self.directory_fp.seek(sid * 128)
entry = self.directory_fp.read(128)
self.direntries[sid] = _OleDirectoryEntry(entry, sid, self)
return self.direntries[sid]
def dumpdirectory(self):
"""
Dump directory (for debugging only)
"""
self.root.dump()
def _open(self, start, size = 0x7FFFFFFF, force_FAT=False):
"""
Open a stream, either in FAT or MiniFAT according to its size.
(openstream helper)
:param start: index of first sector
:param size: size of stream (or nothing if size is unknown)
:param force_FAT: if False (default), stream will be opened in FAT or MiniFAT
according to size. If True, it will always be opened in FAT.
"""
debug('OleFileIO.open(): sect=%d, size=%d, force_FAT=%s' %
(start, size, str(force_FAT)))
# stream size is compared to the MiniSectorCutoff threshold:
if size < self.minisectorcutoff and not force_FAT:
# ministream object
if not self.ministream:
# load MiniFAT if it wasn't already done:
self.loadminifat()
# The first sector index of the miniFAT stream is stored in the
# root directory entry:
size_ministream = self.root.size
debug('Opening MiniStream: sect=%d, size=%d' %
(self.root.isectStart, size_ministream))
self.ministream = self._open(self.root.isectStart,
size_ministream, force_FAT=True)
return _OleStream(fp=self.ministream, sect=start, size=size,
offset=0, sectorsize=self.minisectorsize,
fat=self.minifat, filesize=self.ministream.size)
else:
# standard stream
return _OleStream(fp=self.fp, sect=start, size=size,
offset=self.sectorsize,
sectorsize=self.sectorsize, fat=self.fat,
filesize=self._filesize)
def _list(self, files, prefix, node, streams=True, storages=False):
"""
listdir helper
:param files: list of files to fill in
:param prefix: current location in storage tree (list of names)
:param node: current node (_OleDirectoryEntry object)
:param streams: bool, include streams if True (True by default) - new in v0.26
:param storages: bool, include storages if True (False by default) - new in v0.26
(note: the root storage is never included)
"""
prefix = prefix + [node.name]
for entry in node.kids:
if entry.kids:
# this is a storage
if storages:
# add it to the list
files.append(prefix[1:] + [entry.name])
# check its kids
self._list(files, prefix, entry, streams, storages)
else:
# this is a stream
if streams:
# add it to the list
files.append(prefix[1:] + [entry.name])
def listdir(self, streams=True, storages=False):
"""
Return a list of streams and/or storages stored in this file
:param streams: bool, include streams if True (True by default) - new in v0.26
:param storages: bool, include storages if True (False by default) - new in v0.26
(note: the root storage is never included)
:returns: list of stream and/or storage paths
"""
files = []
self._list(files, [], self.root, streams, storages)
return files
def _find(self, filename):
"""
Returns directory entry of given filename. (openstream helper)
Note: this method is case-insensitive.
:param filename: path of stream in storage tree (except root entry), either:
- a string using Unix path syntax, for example:
'storage_1/storage_1.2/stream'
- or a list of storage filenames, path to the desired stream/storage.
Example: ['storage_1', 'storage_1.2', 'stream']
:returns: sid of requested filename
:exception IOError: if file not found
"""
# if filename is a string instead of a list, split it on slashes to
# convert to a list:
if isinstance(filename, basestring):
filename = filename.split('/')
# walk across storage tree, following given path:
node = self.root
for name in filename:
for kid in node.kids:
if kid.name.lower() == name.lower():
break
else:
raise IOError("file not found")
node = kid
return node.sid
def openstream(self, filename):
"""
Open a stream as a read-only file object (BytesIO).
Note: filename is case-insensitive.
:param filename: path of stream in storage tree (except root entry), either:
- a string using Unix path syntax, for example:
'storage_1/storage_1.2/stream'
- or a list of storage filenames, path to the desired stream/storage.
Example: ['storage_1', 'storage_1.2', 'stream']
:returns: file object (read-only)
:exception IOError: if filename not found, or if this is not a stream.
"""
sid = self._find(filename)
entry = self.direntries[sid]
if entry.entry_type != STGTY_STREAM:
raise IOError("this file is not a stream")
return self._open(entry.isectStart, entry.size)
def write_stream(self, stream_name, data):
"""
Write a stream to disk. For now, it is only possible to replace an
existing stream by data of the same size.
:param stream_name: path of stream in storage tree (except root entry), either:
- a string using Unix path syntax, for example:
'storage_1/storage_1.2/stream'
- or a list of storage filenames, path to the desired stream/storage.
Example: ['storage_1', 'storage_1.2', 'stream']
:param data: bytes, data to be written, must be the same size as the original
stream.
"""
if not isinstance(data, bytes):
raise TypeError("write_stream: data must be a bytes string")
sid = self._find(stream_name)
entry = self.direntries[sid]
if entry.entry_type != STGTY_STREAM:
raise IOError("this is not a stream")
size = entry.size
if size != len(data):
raise ValueError("write_stream: data must be the same size as the existing stream")
if size < self.minisectorcutoff:
raise NotImplementedError("Writing a stream in MiniFAT is not implemented yet")
sect = entry.isectStart
# number of sectors to write
nb_sectors = (size + (self.sectorsize-1)) // self.sectorsize
debug('nb_sectors = %d' % nb_sectors)
for i in range(nb_sectors):
## try:
## self.fp.seek(offset + self.sectorsize * sect)
## except:
## debug('sect=%d, seek=%d' %
## (sect, offset+self.sectorsize*sect))
## raise IOError('OLE sector index out of range')
# extract one sector from data, the last one being smaller:
if i<(nb_sectors-1):
data_sector = data [i*self.sectorsize : (i+1)*self.sectorsize]
#TODO: comment this if it works
assert(len(data_sector)==self.sectorsize)
else:
data_sector = data [i*self.sectorsize:]
#TODO: comment this if it works
debug('write_stream: size=%d sectorsize=%d data_sector=%d size%%sectorsize=%d'
% (size, self.sectorsize, len(data_sector), size % self.sectorsize))
assert(len(data_sector) % self.sectorsize==size % self.sectorsize)
self.write_sect(sect, data_sector)
## self.fp.write(data_sector)
# jump to next sector in the FAT:
try:
sect = self.fat[sect]
except IndexError:
# [PL] if pointer is out of the FAT an exception is raised
raise IOError('incorrect OLE FAT, sector index out of range')
#[PL] Last sector should be a "end of chain" marker:
if sect != ENDOFCHAIN:
raise IOError('incorrect last sector index in OLE stream')
def get_type(self, filename):
"""
Test if given filename exists as a stream or a storage in the OLE
container, and return its type.
:param filename: path of stream in storage tree. (see openstream for syntax)
:returns: False if object does not exist, its entry type (>0) otherwise:
- STGTY_STREAM: a stream
- STGTY_STORAGE: a storage
- STGTY_ROOT: the root entry
"""
try:
sid = self._find(filename)
entry = self.direntries[sid]
return entry.entry_type
except:
return False
def getmtime(self, filename):
"""
Return modification time of a stream/storage.
:param filename: path of stream/storage in storage tree. (see openstream for
syntax)
:returns: None if modification time is null, a python datetime object
otherwise (UTC timezone)
new in version 0.26
"""
sid = self._find(filename)
entry = self.direntries[sid]
return entry.getmtime()
def getctime(self, filename):
"""
Return creation time of a stream/storage.
:param filename: path of stream/storage in storage tree. (see openstream for
syntax)
:returns: None if creation time is null, a python datetime object
otherwise (UTC timezone)
new in version 0.26
"""
sid = self._find(filename)
entry = self.direntries[sid]
return entry.getctime()
def exists(self, filename):
"""
Test if given filename exists as a stream or a storage in the OLE
container.
Note: filename is case-insensitive.
:param filename: path of stream in storage tree. (see openstream for syntax)
:returns: True if object exist, else False.
"""
try:
sid = self._find(filename)
return True
except:
return False
def get_size(self, filename):
"""
Return size of a stream in the OLE container, in bytes.
:param filename: path of stream in storage tree (see openstream for syntax)
:returns: size in bytes (long integer)
:exception IOError: if file not found
:exception TypeError: if this is not a stream.
"""
sid = self._find(filename)
entry = self.direntries[sid]
if entry.entry_type != STGTY_STREAM:
#TODO: Should it return zero instead of raising an exception ?
raise TypeError('object is not an OLE stream')
return entry.size
def get_rootentry_name(self):
"""
Return root entry name. Should usually be 'Root Entry' or 'R' in most
implementations.
"""
return self.root.name
def getproperties(self, filename, convert_time=False, no_conversion=None):
"""
Return properties described in substream.
:param filename: path of stream in storage tree (see openstream for syntax)
:param convert_time: bool, if True timestamps will be converted to Python datetime
:param no_conversion: None or list of int, timestamps not to be converted
(for example total editing time is not a real timestamp)
:returns: a dictionary of values indexed by id (integer)
"""
# make sure no_conversion is a list, just to simplify code below:
if no_conversion == None:
no_conversion = []
# stream path as a string to report exceptions:
streampath = filename
if not isinstance(streampath, str):
streampath = '/'.join(streampath)
fp = self.openstream(filename)
data = {}
try:
# header
s = fp.read(28)
clsid = _clsid(s[8:24])
# format id
s = fp.read(20)
fmtid = _clsid(s[:16])
fp.seek(i32(s, 16))
# get section
s = b"****" + fp.read(i32(fp.read(4))-4)
# number of properties:
num_props = i32(s, 4)
except BaseException as exc:
# catch exception while parsing property header, and only raise
# a DEFECT_INCORRECT then return an empty dict, because this is not
# a fatal error when parsing the whole file
msg = 'Error while parsing properties header in stream %s: %s' % (
repr(streampath), exc)
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, msg, type(exc))
return data
for i in range(num_props):
try:
id = 0 # just in case of an exception
id = i32(s, 8+i*8)
offset = i32(s, 12+i*8)
type = i32(s, offset)
debug ('property id=%d: type=%d offset=%X' % (id, type, offset))
# test for common types first (should perhaps use
# a dictionary instead?)
if type == VT_I2: # 16-bit signed integer
value = i16(s, offset+4)
if value >= 32768:
value = value - 65536
elif type == VT_UI2: # 2-byte unsigned integer
value = i16(s, offset+4)
elif type in (VT_I4, VT_INT, VT_ERROR):
# VT_I4: 32-bit signed integer
# VT_ERROR: HRESULT, similar to 32-bit signed integer,
# see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc230330.aspx
value = i32(s, offset+4)
elif type in (VT_UI4, VT_UINT): # 4-byte unsigned integer
value = i32(s, offset+4) # FIXME
elif type in (VT_BSTR, VT_LPSTR):
# CodePageString, see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd942354.aspx
# size is a 32 bits integer, including the null terminator, and
# possibly trailing or embedded null chars
#TODO: if codepage is unicode, the string should be converted as such
count = i32(s, offset+4)
value = s[offset+8:offset+8+count-1]
# remove all null chars:
value = value.replace(b'\x00', b'')
elif type == VT_BLOB:
# binary large object (BLOB)
# see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd942282.aspx
count = i32(s, offset+4)
value = s[offset+8:offset+8+count]
elif type == VT_LPWSTR:
# UnicodeString
# see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd942313.aspx
# "the string should NOT contain embedded or additional trailing
# null characters."
count = i32(s, offset+4)
value = _unicode(s[offset+8:offset+8+count*2])
elif type == VT_FILETIME:
value = long(i32(s, offset+4)) + (long(i32(s, offset+8))<<32)
# FILETIME is a 64-bit int: "number of 100ns periods
# since Jan 1,1601".
if convert_time and id not in no_conversion:
debug('Converting property #%d to python datetime, value=%d=%fs'
%(id, value, float(value)/10000000))
# convert FILETIME to Python datetime.datetime
# inspired from http://code.activestate.com/recipes/511425-filetime-to-datetime/
_FILETIME_null_date = datetime.datetime(1601, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0)
debug('timedelta days=%d' % (value//(10*1000000*3600*24)))
value = _FILETIME_null_date + datetime.timedelta(microseconds=value//10)
else:
# legacy code kept for backward compatibility: returns a
# number of seconds since Jan 1,1601
value = value // 10000000 # seconds
elif type == VT_UI1: # 1-byte unsigned integer
value = i8(s[offset+4])
elif type == VT_CLSID:
value = _clsid(s[offset+4:offset+20])
elif type == VT_CF:
# PropertyIdentifier or ClipboardData??
# see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd941945.aspx
count = i32(s, offset+4)
value = s[offset+8:offset+8+count]
elif type == VT_BOOL:
# VARIANT_BOOL, 16 bits bool, 0x0000=Fals, 0xFFFF=True
# see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc237864.aspx
value = bool(i16(s, offset+4))
else:
value = None # everything else yields "None"
debug ('property id=%d: type=%d not implemented in parser yet' % (id, type))
# missing: VT_EMPTY, VT_NULL, VT_R4, VT_R8, VT_CY, VT_DATE,
# VT_DECIMAL, VT_I1, VT_I8, VT_UI8,
# see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd942033.aspx
# FIXME: add support for VT_VECTOR
# VT_VECTOR is a 32 uint giving the number of items, followed by
# the items in sequence. The VT_VECTOR value is combined with the
# type of items, e.g. VT_VECTOR|VT_BSTR
# see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd942011.aspx
#print("%08x" % id, repr(value), end=" ")
#print("(%s)" % VT[i32(s, offset) & 0xFFF])
data[id] = value
except BaseException as exc:
# catch exception while parsing each property, and only raise
# a DEFECT_INCORRECT, because parsing can go on
msg = 'Error while parsing property id %d in stream %s: %s' % (
id, repr(streampath), exc)
self._raise_defect(DEFECT_INCORRECT, msg, type(exc))
return data
def get_metadata(self):
"""
Parse standard properties streams, return an OleMetadata object
containing all the available metadata.
(also stored in the metadata attribute of the OleFileIO object)
new in version 0.25
"""
self.metadata = OleMetadata()
self.metadata.parse_properties(self)
return self.metadata
##### library ends, program starts #####
from struct import unpack
import binascii
def find_rc4_passinfo_xls(filename, stream):
"""
Initial version of this function was based on a blog entry posted by
Worawit (sleepya) at http://auntitled.blogspot.in site.
Since then this function has been heavily modified and extended.
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd908560%28v=office.12%29
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd920360%28v=office.12%29
"""
while True:
pos = stream.tell()
if pos >= stream.size:
break # eof
type = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
length = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
data = stream.read(length)
if type == 0x2f: # FILEPASS
if data[0:2] == b"\x00\x00": # XOR obfuscation
sys.stderr.write("%s : XOR obfuscation detected, key : %s, hash : %s\n" % \
(filename, binascii.hexlify(data[2:4]), binascii.hexlify(data[4:6])))
elif data[0:6] == b'\x01\x00\x01\x00\x01\x00':
# RC4 encryption header structure
data = data[6:]
salt = data[:16]
verifier = data[16:32]
verifierHash = data[32:48]
return (salt, verifier, verifierHash)
elif data[0:4] == b'\x01\x00\x02\x00' or data[0:4] == b'\x01\x00\x03\x00':
# If RC4 CryptoAPI encryption is used, certain storages and streams are stored in Encryption Stream
stm = StringIO(data)
stm.read(2) # unused
# RC4 CryptoAPI Encryption Header
unpack("<h", stm.read(2))[0] # major_version
unpack("<h", stm.read(2))[0] # minor_version
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # encryptionFlags
headerLength = unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0]
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # skipFlags
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # sizeExtra
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # algId
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # algHashId
headerLength -= 4
keySize = unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0]
if keySize == 40:
typ = 3
else:
typ = 4
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # providerType
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # unused
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # unused
headerLength -= 4
CSPName = stm.read(headerLength)
provider = CSPName.decode('utf-16').lower()
# Encryption verifier
saltSize = unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0]
assert(saltSize == 16)
salt = stm.read(saltSize)
encryptedVerifier = stm.read(16)
verifierHashSize = unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0]
assert(verifierHashSize == 20)
encryptedVerifierHash = stm.read(verifierHashSize)
sys.stdout.write("%s:$oldoffice$%s*%s*%s*%s\n" % (os.path.basename(filename),
typ, binascii.hexlify(salt).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifier).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifierHash).decode("ascii")))
return None
def find_doc_type(filename, stream):
w_ident = stream.read(2)
assert(w_ident == b"\xec\xa5")
stream.read(9) # unused
flags = ord(stream.read(1))
if (flags & 1) != 0:
F = 1
else:
F = 0
if (flags & 128) != 0:
M = 1
else:
M = 0
if F == 1 and M == 1:
stream.read(2) # unused
i_key = stream.read(4)
sys.stderr.write("%s : XOR obfuscation detected, Password Verifier : %s\n" % \
(filename, binascii.hexlify(i_key)))
return True
if F == 0:
sys.stderr.write("%s : Document is not encrypted!\n" % (filename))
return True
def find_ppt_type(filename, stream):
# read CurrentUserRec's RecordHeader
stream.read(2) # unused
unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0] # recType
unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0] # recLen
# read rest of CurrentUserRec
unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0] # size
unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0] # headerToken
offsetToCurrentEdit = unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0]
return offsetToCurrentEdit
def find_rc4_passinfo_doc(filename, stream):
major_version = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
minor_version = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
if major_version == 1 or minor_version == 1:
data = stream.read(48)
salt = data[:16]
verifier = data[16:32]
verifierHash = data[32:48]
return (salt, verifier, verifierHash)
elif major_version >= 2 and minor_version == 2:
# RC4 CryptoAPI Encryption Header
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # encryptionFlags
headerLength = unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0]
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # skipFlags
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # sizeExtra
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # algId
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # algHashId
headerLength -= 4
keySize = unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # keySize
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # providerType
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # unused
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # unused
headerLength -= 4
CSPName = stream.read(headerLength)
provider = CSPName.decode('utf-16').lower()
if keySize == 128:
typ = 4
elif keySize == 40:
typ = 3
else:
sys.stderr.write("%s : invalid keySize\n" % filename)
# Encryption verifier
saltSize = unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0]
assert(saltSize == 16)
salt = stream.read(saltSize)
encryptedVerifier = stream.read(16)
verifierHashSize = unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0]
assert(verifierHashSize == 20)
encryptedVerifierHash = stream.read(verifierHashSize)
if not have_summary:
sys.stdout.write("%s:$oldoffice$%s*%s*%s*%s\n" % (os.path.basename(filename),
typ, binascii.hexlify(salt).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifier).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifierHash).decode("ascii")))
else:
sys.stdout.write("%s:$oldoffice$%s*%s*%s*%s:::%s::%s\n" % (os.path.basename(filename),
# this code was developed while listening to The Wedding Present "Sea Monsters"
typ, binascii.hexlify(salt).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifier).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifierHash).decode("ascii"), summary, filename))
else:
sys.stderr.write("%s : Cannot find RC4 pass info, is document encrypted?\n" % filename)
def find_rc4_passinfo_ppt(filename, stream, offset):
stream.read(offset) # unused
# read UserEditAtom's RecordHeader
stream.read(2) # unused
recType = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
recLen = unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0]
if recLen != 32:
sys.stderr.write("%s : Document is not encrypted!\n" % (filename))
return
if recType != 0x0FF5:
sys.stderr.write("%s : Document is corrupt!\n" % (filename))
return
# read reset of UserEditAtom
unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0] # lastSlideRef
unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0] # version
ord(stream.read(1)) # minorVersion
ord(stream.read(1)) # majorVersion
unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0] # offsetLastEdit
offsetPersistDirectory = unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0]
unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0] # docPersistIdRef
unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0] # persistIdSeed
unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0] # lastView
unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0] # unused
encryptSessionPersistIdRef = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
# if( offset.LowPart < userAtom.offsetPersistDirectory ||
# userAtom.offsetPersistDirectory < userAtom.offsetLastEdit )
# goto CorruptFile;
# jump and read RecordHeader
stream.seek(offsetPersistDirectory, 0)
stream.read(2) # unused
recType = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
recLen = unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0]
# BUGGY: PersistDirectoryAtom and PersistDirectoryEntry processing
i = 0
stream.read(4) # unused
while i < encryptSessionPersistIdRef:
i += 1
persistOffset = unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0]
# print persistOffset
# go to the offset of encryption header
stream.seek(persistOffset, 0)
# read RecordHeader
stream.read(2) # unused
recType = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
recLen = unpack("<L", stream.read(4))[0]
major_version = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
minor_version = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
if major_version >= 2 and minor_version == 2:
# RC4 CryptoAPI Encryption Header
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # encryptionFlags
headerLength = unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0]
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # skipFlags
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # sizeExtra
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # algId
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # algHashId
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # keySize
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # providerType
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0]
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0]
headerLength -= 4
CSPName = stream.read(headerLength)
provider = CSPName.decode('utf-16').lower()
if "strong" in provider:
typ = 4
else:
typ = 3
# Encryption verifier
saltSize = unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0]
assert(saltSize == 16)
salt = stream.read(saltSize)
encryptedVerifier = stream.read(16)
verifierHashSize = unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0]
assert(verifierHashSize == 20)
encryptedVerifierHash = stream.read(verifierHashSize)
sys.stdout.write("%s:$oldoffice$%s*%s*%s*%s\n" % (os.path.basename(filename),
typ, binascii.hexlify(salt).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifier).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifierHash).decode("ascii")))
else:
sys.stderr.write("%s : Cannot find RC4 pass info, is document encrypted?\n" % filename)
from xml.etree.ElementTree import ElementTree
import base64
def process_new_office(filename):
# detect version of new Office used by reading "EncryptionInfo" stream
ole = OleFileIO(filename)
stream = ole.openstream("EncryptionInfo")
major_version = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
minor_version = unpack("<h", stream.read(2))[0]
encryptionFlags = unpack("<I", stream.read(4))[0] # encryptionFlags
if encryptionFlags == 16: # fExternal
sys.stderr.write("%s : An external cryptographic provider is not supported!\n" % filename)
return -1
if major_version == 0x04 and minor_version == 0x04:
# Office 2010 and 2013 file detected
if encryptionFlags != 0x40: # fAgile
sys.stderr.write("%s : The encryption flags are not consistent with the encryption type\n" % filename)
return -2
# rest of the data is in XML format
data = StringIO(stream.read())
tree = ElementTree()
tree.parse(data)
for node in tree.getiterator('{http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/2006/keyEncryptor/password}encryptedKey'):
spinCount = node.attrib.get("spinCount")
assert(spinCount)
saltSize = node.attrib.get("saltSize")
assert(saltSize)
blockSize = node.attrib.get("blockSize")
assert(blockSize)
keyBits = node.attrib.get("keyBits")
hashAlgorithm = node.attrib.get("hashAlgorithm")
if hashAlgorithm == "SHA1":
version = 2010
elif hashAlgorithm == "SHA512":
version = 2013
else:
sys.stderr.write("%s uses un-supported hashing algorithm %s, please file a bug! \n" \
% (filename, hashAlgorithm))
return -3
cipherAlgorithm = node.attrib.get("cipherAlgorithm")
if not cipherAlgorithm.find("AES") > -1:
sys.stderr.write("%s uses un-supported cipher algorithm %s, please file a bug! \n" \
% (filename, cipherAlgorithm))
return -4
saltValue = node.attrib.get("saltValue")
assert(saltValue)
encryptedVerifierHashInput = node.attrib.get("encryptedVerifierHashInput")
encryptedVerifierHashValue = node.attrib.get("encryptedVerifierHashValue")
encryptedVerifierHashValue = binascii.hexlify(base64.decodestring(encryptedVerifierHashValue.encode()))
sys.stdout.write("%s:$office$*%d*%d*%d*%d*%s*%s*%s\n" % \
(os.path.basename(filename), version,
int(spinCount), int(keyBits), int(saltSize),
binascii.hexlify(base64.decodestring(saltValue.encode())).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(base64.decodestring(encryptedVerifierHashInput.encode())).decode("ascii"),
encryptedVerifierHashValue[0:64].decode("ascii")))
return 0
else:
# Office 2007 file detected, process CryptoAPI Encryption Header
stm = stream
headerLength = unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0]
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # skipFlags
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # sizeExtra
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # algId
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # algHashId
headerLength -= 4
keySize = unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0]
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # providerType
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # unused
headerLength -= 4
unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0] # unused
headerLength -= 4
CSPName = stm.read(headerLength)
provider = CSPName.decode('utf-16').lower()
# Encryption verifier
saltSize = unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0]
assert(saltSize == 16)
salt = stm.read(saltSize)
encryptedVerifier = stm.read(16)
verifierHashSize = unpack("<I", stm.read(4))[0]
encryptedVerifierHash = stm.read(verifierHashSize)
sys.stdout.write("%s:$office$*%d*%d*%d*%d*%s*%s*%s\n" % \
(os.path.basename(filename), 2007, verifierHashSize,
keySize, saltSize, binascii.hexlify(salt).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifier).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(encryptedVerifierHash)[0:64].decode("ascii")))
def xml_metadata_parser(data, filename):
# Assuming Office 2010 and 2013 file
data = StringIO(data)
tree = ElementTree()
tree.parse(data)
for node in tree.getiterator('{http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/2006/keyEncryptor/password}encryptedKey'):
spinCount = node.attrib.get("spinCount")
assert(spinCount)
saltSize = node.attrib.get("saltSize")
assert(saltSize)
blockSize = node.attrib.get("blockSize")
assert(blockSize)
keyBits = node.attrib.get("keyBits")
hashAlgorithm = node.attrib.get("hashAlgorithm")
if hashAlgorithm == "SHA1":
version = 2010
elif hashAlgorithm == "SHA512":
version = 2013
else:
sys.stderr.write("%s uses un-supported hashing algorithm %s, please file a bug! \n" \
% (filename, hashAlgorithm))
return -3
cipherAlgorithm = node.attrib.get("cipherAlgorithm")
if not cipherAlgorithm.find("AES") > -1:
sys.stderr.write("%s uses un-supported cipher algorithm %s, please file a bug! \n" \
% (filename, cipherAlgorithm))
return -4
saltValue = node.attrib.get("saltValue")
assert(saltValue)
encryptedVerifierHashInput = node.attrib.get("encryptedVerifierHashInput")
encryptedVerifierHashValue = node.attrib.get("encryptedVerifierHashValue")
encryptedVerifierHashValue = binascii.hexlify(base64.decodestring(encryptedVerifierHashValue.encode()))
sys.stdout.write("%s:$office$*%d*%d*%d*%d*%s*%s*%s\n" % \
(os.path.basename(filename), version,
int(spinCount), int(keyBits), int(saltSize),
binascii.hexlify(base64.decodestring(saltValue.encode())).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(base64.decodestring(encryptedVerifierHashInput.encode())).decode("ascii"),
encryptedVerifierHashValue[0:64].decode("ascii")))
return 0
have_summary = False
summary = []
import re
def remove_html_tags(data):
p = re.compile(r'<.*?>', re.DOTALL)
return p.sub('', str(data))
def remove_extra_spaces(data):
p = re.compile(r'\s+')
return p.sub(' ', data)
def process_file(filename):
# Test if a file is an OLE container:
try:
f = open(filename, "rb")
data = f.read(81920) # is this enough?
if data[0:2] == b"PK":
sys.stderr.write("%s : zip container found, file is " \
"unencrypted?, invalid OLE file!\n" % filename)
f.close()
return 1
f.close()
# ACCDB handling hack for MS Access >= 2007 (Office 12)
accdb_magic = "Standard ACE DB"
accdb_xml_start = '<?xml version="1.0"'
accdb_xml_trailer = '</encryption>'
if accdb_magic in data and accdb_xml_start in data:
# find start and the end of the XML metadata stream
start = data.find(accdb_xml_start)
trailer = data.find(accdb_xml_trailer)
xml_metadata_parser(data[start:trailer+len(accdb_xml_trailer)], filename)
return
if not isOleFile(filename):
sys.stderr.write("%s : Invalid OLE file\n" % filename)
return 1
except Exception:
e = sys.exc_info()[1]
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
sys.stderr.write("%s : OLE check failed, %s\n" % (filename, str(e)))
return 2
# Open OLE file:
ole = OleFileIO(filename)
stream = None
# find "summary" streams
global have_summary, summary
have_summary = False
summary = []
for streamname in ole.listdir():
streamname = streamname[-1]
if streamname[0] == "\005":
have_summary = True
props = ole.getproperties(streamname)
for k, v in props.items():
if v is None:
continue
if not PY3:
if not isinstance(v, unicode): # We are only interested in strings
continue
else:
if not isinstance(v, str): # We are only interested in strings
continue
v = remove_html_tags(v)
v = v.replace(":", "")
v = remove_extra_spaces(v)
#words = v.split()
#words = filter(lambda x: len(x) < 20, words)
#v = " ".join(words)
summary.append(v)
summary = " ".join(summary)
summary = remove_extra_spaces(summary)
if ["EncryptionInfo"] in ole.listdir():
# process Office 2003 / 2010 / 2013 files
return process_new_office(filename)
if ["Workbook"] in ole.listdir():
stream = "Workbook"
elif ["WordDocument"] in ole.listdir():
stream = "1Table"
elif ["PowerPoint Document"] in ole.listdir():
stream = "Current User"
else:
sys.stderr.write("%s : No supported streams found\n" % filename)
return 2
try:
workbookStream = ole.openstream(stream)
except:
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
sys.stderr.write("%s : stream %s not found!\n" % (filename, stream))
return 2
if workbookStream is None:
sys.stderr.write("%s : Error opening stream, %s\n" % filename)
(filename, stream)
return 3
if stream == "Workbook":
typ = 0
passinfo = find_rc4_passinfo_xls(filename, workbookStream)
if passinfo is None:
return 4
elif stream == "1Table":
typ = 1
sdoc = ole.openstream("WordDocument")
ret = find_doc_type(filename, sdoc)
if not ret:
passinfo = find_rc4_passinfo_doc(filename, workbookStream)
if passinfo is None:
return 4
else:
return 5
else:
sppt = ole.openstream("Current User")
offset = find_ppt_type(filename, sppt)
sppt = ole.openstream("PowerPoint Document")
find_rc4_passinfo_ppt(filename, sppt, offset)
return 6
(salt, verifier, verifierHash) = passinfo
if not have_summary:
sys.stdout.write("%s:$oldoffice$%s*%s*%s*%s\n" % (os.path.basename(filename),
typ, binascii.hexlify(salt).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(verifier).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(verifierHash).decode("ascii")))
else:
sys.stdout.write("%s:$oldoffice$%s*%s*%s*%s:::%s::%s\n" % (os.path.basename(filename),
typ, binascii.hexlify(salt).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(verifier).decode("ascii"),
binascii.hexlify(verifierHash).decode("ascii"),
summary, filename))
workbookStream.close()
ole.close()
return 0
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s <encrypted Office file(s)>\n" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
#set_debug_mode(1)
for i in range(1, len(sys.argv)):
if not PY3:
ret = process_file(sys.argv[i].decode("utf8"))
else:
ret = process_file(sys.argv[i])
这里我是用linux来做的

4.将得到的hash转换成hashcat支持的形式
awk -F “:” ‘{print $2}’ hash.txt > hashhc.txt

5.爆破
hashcat -m 9500 hashhc.txt -a 3 ?b?b?b?b?b -w 3 -o out.txt
这里-m意为选择哈希的类型,见下表:

-w 选择掩码模式,hashcat内置有字符集,可以在这些字符集基础上使用–custom-charset再进行自定义:
-m 指定哈希类型
-a 指定破解模式
-V 查看版本信息
-o 将输出结果储存到指定文件
--force 忽略警告
--show 仅显示破解的hash密码和对应的明文
--remove 从源文件中删除破解成功的hash
--username 忽略hash表中的用户名
-b 测试计算机破解速度和相关硬件信息
-O 限制密码长度
-T 设置线程数
-r 使用规则文件
-1 自定义字符集 -1 0123asd ?1={0123asd}
-2 自定义字符集 -2 0123asd ?2={0123asd}
-3 自定义字符集 -3 0123asd ?3={0123asd}
-i 启用增量破解模式
--increment-min 设置密码最小长度
--increment-max 设置密码最大长度
hashcat破解模式介绍
0 straight 字典破解
1 combination 将字典中密码进行组合(1 2>11 22 12 21)
3 brute-force 使用指定掩码破解
6 Hybrid Wordlist + Mask 字典+掩码破解
7 Hybrid Mask + Wordlist 掩码+字典破解
?l = abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz 代表小写字母
?u = ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ 代表大写字母
?d = 0123456789 代表数字
?s = !”#$%&’()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~ 代表特殊字符
?a = ?l?u?d?s 大小写数字及特殊字符的组合
?b = 0×00 – 0xff
所以命令还可以这样写:
hashcat.exe -m 9600 old.txt --custom-charset1 ?d?l -a3 ?1?1?1?1?1?1 -w 3 -o out.txt -O
-O是指使用优化的内核以加快速度。

能不能爆破得到密码就看运气以及人品了。
此外HashCat还支持分布式破解,但是分布式我没有研究,因为没钱买显卡
























 2251
2251











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








