概述
Bindgen和CXX工具的主要功能是实现Rust和C/C++之间的交互。其中,Bindgen通过将C接口转换为Rust接口来实现Rust对C的调用,CXX可以通过建立C接口和Rust接口的映射关系来实现C++和Rust的相互调用。

Bindgen工具使用指导
操作步骤
下面是一个使用bindgen实现Rust调用C的示例。
-
在C代码侧,使用头文件lib.h定义两个接口,接口FuncAAddB用来实现两数求和,接口SayHello用来打印字符串。
#ifndef BUILD_RUST_TESTS_BINDGEN_TEST_LIB_H_ #define BUILD_RUST_TESTS_BINDGEN_TEST_LIB_H_ #include <stdint.h> #include "build/rust/tests/test_bindgen_test/test_for_hello_world/lib2.h" uint32_t FuncAAddB(uint32_t a, uint32_t b); void SayHello(const char *message); #endif // BUILD_RUST_TESTS_BINDGEN_TEST_LIB_H_
-
在lib.c中添加对两个接口的对应实现。
#include "build/rust/tests/test_bindgen_test/test_for_hello_world/lib.h" #include <stdint.h> #include <stdio.h> void SayHello(const char *message) { printf("This is a test for bindgen hello world:\n"); printf("%s\n", message); } uint32_t FuncAAddB(uint32_t a, uint32_t b) { printf("This is a test for bindgen of a + b:\n"); return a + b; } -
添加文件main.rs,就可以在Rust侧通过c_ffi实现对C侧的接口调用。注意Rust侧调用的不安全接口需要使用unsafe封装。
//! bindgen test for hello world #![allow(clippy::approx_constant)] mod c_ffi { #![allow(dead_code)] #![allow(non_upper_case_globals)] #![allow(non_camel_case_types)] include!(env!("BINDGEN_RS_FILE")); } /// pub fn add_two_numbers_in_c pub fn add_two_numbers_in_c(a: u32, b: u32) -> u32 { unsafe { c_ffi::FuncAAddB(a, b) } } use std::ffi::c_char; use std::ffi::CString; /// fn main() fn main() { println!("{} + {} = {}", 3, 7, add_two_numbers_in_c(3, 7)); let c_str = CString::new("This is a message from C").unwrap(); let c_world: *const c_char = c_str.as_ptr() as *const c_char; unsafe { c_ffi::SayHello(c_world); } } -
添加构建文件BUILD.gn,建立Rust模块对C模块的依赖。
import("//build/ohos.gni") ohos_shared_library("c_lib") { sources = [ "lib.c" ] defines = [ "COMPONENT_IMPLEMENTATION" ] } rust_bindgen("c_lib_bindgen") { header = "lib.h" } ohos_rust_executable("bindgen_test") { deps = [ ":c_lib" ] deps += [ ":c_lib_bindgen" ] sources = [ "main.rs" ] bindgen_output = get_target_outputs(":c_lib_bindgen") inputs = bindgen_output rustenv = [ "BINDGEN_RS_FILE=" + rebase_path(bindgen_output[0]) ] crate_root = "main.rs" }
调测验证

CXX工具使用指导
C++调用Rust接口
-
在Rust侧文件lib.rs里mod ffi写清楚需要调用的C++接口,并将接口包含在extern "Rust"里面,暴露给C++侧使用。
//! #[cxx::bridge] #[cxx::bridge] mod ffi{ #![allow(dead_code)] #[derive(Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq, PartialOrd, Ord)] struct Shared { z: usize, } extern "Rust"{ fn print_message_in_rust(); fn r_return_primitive() -> usize; fn r_return_shared() -> Shared; fn r_return_rust_string() -> String; fn r_return_sum(_: usize, _: usize) -> usize; } } fn print_message_in_rust(){ println!("Here is a test for cpp call Rust."); } fn r_return_shared() -> ffi::Shared { println!("Here is a message from Rust,test for ffi::Shared:"); ffi::Shared { z: 1996 } } fn r_return_primitive() -> usize { println!("Here is a message from Rust,test for usize:"); 1997 } fn r_return_rust_string() -> String { println!("Here is a message from Rust,test for String"); "Hello World!".to_owned() } fn r_return_sum(n1: usize, n2: usize) -> usize { println!("Here is a message from Rust,test for {} + {} is:",n1 ,n2); n1 + n2 } -
C++侧将cxx工具转换出来的lib.rs.h包含进来,就可以使用C++侧的接口。
#include <iostream> #include "build/rust/tests/test_cxx/src/lib.rs.h" int main(int argc, const char* argv[]) { int a = 2021; int b = 4; print_message_in_rust(); std::cout << r_return_primitive() << std::endl; std::cout << r_return_shared().z << std::endl; std::cout << std::string(r_return_rust_string()) << std::endl; std::cout << r_return_sum(a, b) << std::endl; return 0; } -
添加构建文件BUILD.gn。rust_cxx底层调用CXX工具将lib.rs文件转换成lib.rs.h和lib.rs.cc文件,ohos_rust_static_ffi实现Rust侧源码的编译,ohos_executable实现C++侧代码的编译。
import("//build/ohos.gni") import("//build/templates/rust/rust_cxx.gni") rust_cxx("test_cxx_exe_gen") { sources = [ "src/lib.rs" ] } ohos_rust_static_ffi("test_cxx_examp_rust") { sources = [ "src/lib.rs" ] deps = [ "//build/rust:cxx_rustdeps" ] } ohos_executable("test_cxx_exe") { sources = [ "main.cpp" ] sources += get_target_outputs(":test_cxx_exe_gen") include_dirs = [ "${target_gen_dir}" ] deps = [ ":test_cxx_examp_rust", ":test_cxx_exe_gen", "//build/rust:cxx_cppdeps", ] }
调测验证

Rust调用C++
-
添加头文件client_blobstore.h。
#ifndef BUILD_RUST_TESTS_CLIENT_BLOBSTORE_H #define BUILD_RUST_TESTS_CLIENT_BLOBSTORE_H #include <memory> #include "third_party/rust/cxx/include/cxx.h" namespace nsp_org { namespace nsp_blobstore { struct MultiBufs; struct Metadata_Blob; class client_blobstore { public: client_blobstore(); uint64_t put_buf(MultiBufs &buf) const; void add_tag(uint64_t blobid, rust::Str add_tag) const; Metadata_Blob get_metadata(uint64_t blobid) const; private: class impl; std::shared_ptr<impl> impl; }; std::unique_ptr<client_blobstore> blobstore_client_new(); } // namespace nsp_blobstore } // namespace nsp_org #endif -
添加cpp文件client_blobstore.cpp。
#include <algorithm> #include <functional> #include <set> #include <string> #include <unordered_map> #include "src/main.rs.h" #include "build/rust/tests/test_cxx_rust/include/client_blobstore.h" namespace nsp_org { namespace nsp_blobstore { // Toy implementation of an in-memory nsp_blobstore. // // In reality the implementation of client_blobstore could be a large complex C++ // library. class client_blobstore::impl { friend client_blobstore; using Blob = struct { std::string data; std::set<std::string> tags; }; std::unordered_map<uint64_t, Blob> blobs; }; client_blobstore::client_blobstore() : impl(new class client_blobstore::impl) {} // Upload a new blob and return a blobid that serves as a handle to the blob. uint64_t client_blobstore::put_buf(MultiBufs &buf) const { std::string contents; // Traverse the caller's res_chunk iterator. // // In reality there might be sophisticated batching of chunks and/or parallel // upload implemented by the nsp_blobstore's C++ client. while (true) { auto res_chunk = next_chunk(buf); if (res_chunk.size() == 0) { break; } contents.append(reinterpret_cast<const char *>(res_chunk.data()), res_chunk.size()); } // Insert into map and provide caller the handle. auto res = std::hash<std::string> {} (contents); impl->blobs[res] = {std::move(contents), {}}; return res; } // Add add_tag to an existing blob. void client_blobstore::add_tag(uint64_t blobid, rust::Str add_tag) const { impl->blobs[blobid].tags.emplace(add_tag); } // Retrieve get_metadata about a blob. Metadata_Blob client_blobstore::get_metadata(uint64_t blobid) const { Metadata_Blob get_metadata {}; auto blob = impl->blobs.find(blobid); if (blob != impl->blobs.end()) { get_metadata.size = blob->second.data.size(); std::for_each(blob->second.tags.cbegin(), blob->second.tags.cend(), [&](auto &t) { get_metadata.tags.emplace_back(t); }); } return get_metadata; } std::unique_ptr<client_blobstore> blobstore_client_new() { return std::make_unique<client_blobstore>(); } } // namespace nsp_blobstore } // namespace nsp_org -
main.rs文件,在main.rs文件的ffi里面,通过宏include!将头文件client_blobstore.h引入进来,从而在Rust的main函数里面就可以通过ffi的方式调用C++的接口。
//! test_cxx_rust #[cxx::bridge(namespace = "nsp_org::nsp_blobstore")] mod ffi { // Shared structs with fields visible to both languages. struct Metadata_Blob { size: usize, tags: Vec<String>, } // Rust types and signatures exposed to C++. extern "Rust" { type MultiBufs; fn next_chunk(buf: &mut MultiBufs) -> &[u8]; } // C++ types and signatures exposed to Rust. unsafe extern "C++" { include!("build/rust/tests/test_cxx_rust/include/client_blobstore.h"); type client_blobstore; fn blobstore_client_new() -> UniquePtr<client_blobstore>; fn put_buf(&self, parts: &mut MultiBufs) -> u64; fn add_tag(&self, blobid: u64, add_tag: &str); fn get_metadata(&self, blobid: u64) -> Metadata_Blob; } } // An iterator over contiguous chunks of a discontiguous file object. // // Toy implementation uses a Vec<Vec<u8>> but in reality this might be iterating // over some more complex Rust data structure like a rope, or maybe loading // chunks lazily from somewhere. /// pub struct MultiBufs pub struct MultiBufs { chunks: Vec<Vec<u8>>, pos: usize, } /// pub fn next_chunk pub fn next_chunk(buf: &mut MultiBufs) -> &[u8] { let next = buf.chunks.get(buf.pos); buf.pos += 1; next.map_or(&[], Vec::as_slice) } /// fn main() fn main() { let client = ffi::blobstore_client_new(); // Upload a blob. let chunks = vec![b"fearless".to_vec(), b"concurrency".to_vec()]; let mut buf = MultiBufs { chunks, pos: 0 }; let blobid = client.put_buf(&mut buf); println!("This is a test for Rust call cpp:"); println!("blobid = {}", blobid); // Add a add_tag. client.add_tag(blobid, "rust"); // Read back the tags. let get_metadata = client.get_metadata(blobid); println!("tags = {:?}", get_metadata.tags); } -
添加构建文件BUILD.gn。使用CXX将main.rs转换成lib.rs.h和lib.rs.cc,同时将产物作为test_cxx_rust_staticlib的源码,编译Rust源码main.rs并将test_cxx_rust_staticlib依赖进来。
import("//build/ohos.gni") rust_cxx("test_cxx_rust_gen") { sources = [ "src/main.rs" ] } ohos_static_library("test_cxx_rust_staticlib") { sources = [ "src/client_blobstore.cpp" ] sources += get_target_outputs(":test_cxx_rust_gen") include_dirs = [ "${target_gen_dir}", "//third_party/rust/cxx/v1/crate/include", "include", ] deps = [ ":test_cxx_rust_gen", "//build/rust:cxx_cppdeps", ] } ohos_rust_executable("test_cxx_rust") { sources = [ "src/main.rs" ] deps = [ ":test_cxx_rust_staticlib", "//build/rust:cxx_rustdeps", ] }
调测验证

最后
有很多小伙伴不知道学习哪些鸿蒙开发技术?不知道需要重点掌握哪些鸿蒙应用开发知识点?而且学习时频繁踩坑,最终浪费大量时间。所以有一份实用的鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)资料用来跟着学习是非常有必要的。
为了能够帮助大家快速掌握鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)应用开发技术知识。在此给大家分享一下我结合鸿蒙最新资料整理出来的鸿蒙南北向开发学习路线以及整理的最新版鸿蒙学习文档资料。
这份鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)资料包含了鸿蒙开发必掌握的核心知识要点,内容包含了(ArkTS、ArkUI开发组件、Stage模型、多端部署、分布式应用开发、音频、视频、WebGL、OpenHarmony多媒体技术、Napi组件、OpenHarmony内核、Harmony南向开发、鸿蒙项目实战等等)鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)技术知识点。
希望这一份鸿蒙学习资料能够给大家带来帮助,有需要的小伙伴自行领取,限时开源,先到先得~无套路领取!!
如果你是一名有经验的资深Android移动开发、Java开发、前端开发、对鸿蒙感兴趣以及转行人员,可以直接领取这份资料
获取这份完整版高清学习路线,请点击→纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)最新学习路线

-
HarmonOS基础技能

- HarmonOS就业必备技能

- HarmonOS多媒体技术

- 鸿蒙NaPi组件进阶

- HarmonOS高级技能
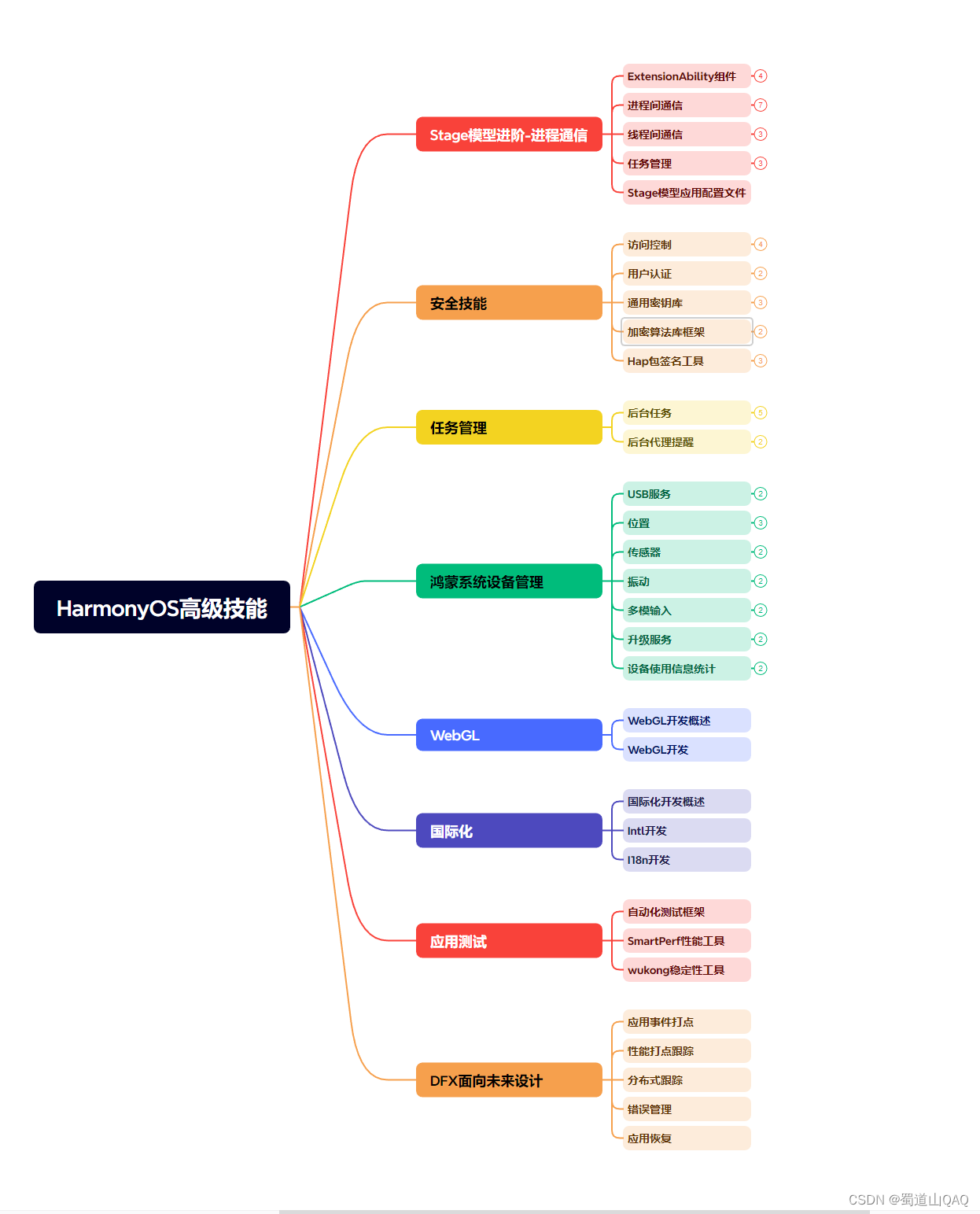
- 初识HarmonOS内核

- 实战就业级设备开发

有了路线图,怎么能没有学习资料呢,小编也准备了一份联合鸿蒙官方发布笔记整理收纳的一套系统性的鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )学习手册(共计1236页)与鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )开发入门教学视频,内容包含:ArkTS、ArkUI、Web开发、应用模型、资源分类…等知识点。
获取以上完整版高清学习路线,请点击→纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
《鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony)开发入门教学视频》

《鸿蒙生态应用开发V2.0白皮书》

《鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony)开发基础到实战手册》
OpenHarmony北向、南向开发环境搭建

《鸿蒙开发基础》
- ArkTS语言
- 安装DevEco Studio
- 运用你的第一个ArkTS应用
- ArkUI声明式UI开发
- .……

《鸿蒙开发进阶》
- Stage模型入门
- 网络管理
- 数据管理
- 电话服务
- 分布式应用开发
- 通知与窗口管理
- 多媒体技术
- 安全技能
- 任务管理
- WebGL
- 国际化开发
- 应用测试
- DFX面向未来设计
- 鸿蒙系统移植和裁剪定制
- ……

《鸿蒙进阶实战》
- ArkTS实践
- UIAbility应用
- 网络案例
- ……

获取以上完整鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料,请点击→纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
总结
总的来说,华为鸿蒙不再兼容安卓,对中年程序员来说是一个挑战,也是一个机会。只有积极应对变化,不断学习和提升自己,他们才能在这个变革的时代中立于不败之地。











 本文详细介绍了如何使用Bindgen和CXX工具实现Rust与C/C++之间的交互,包括Rust调用C的C接口转换实例,以及C++调用Rust的接口映射。还提供了从基础到进阶的学习路线和开发实践指南。
本文详细介绍了如何使用Bindgen和CXX工具实现Rust与C/C++之间的交互,包括Rust调用C的C接口转换实例,以及C++调用Rust的接口映射。还提供了从基础到进阶的学习路线和开发实践指南。














 2759
2759

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








