
版本说明
- Spring Boot:【2.4.6】
- Spring: 【5.3.7】
- spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client:【3.0.3】
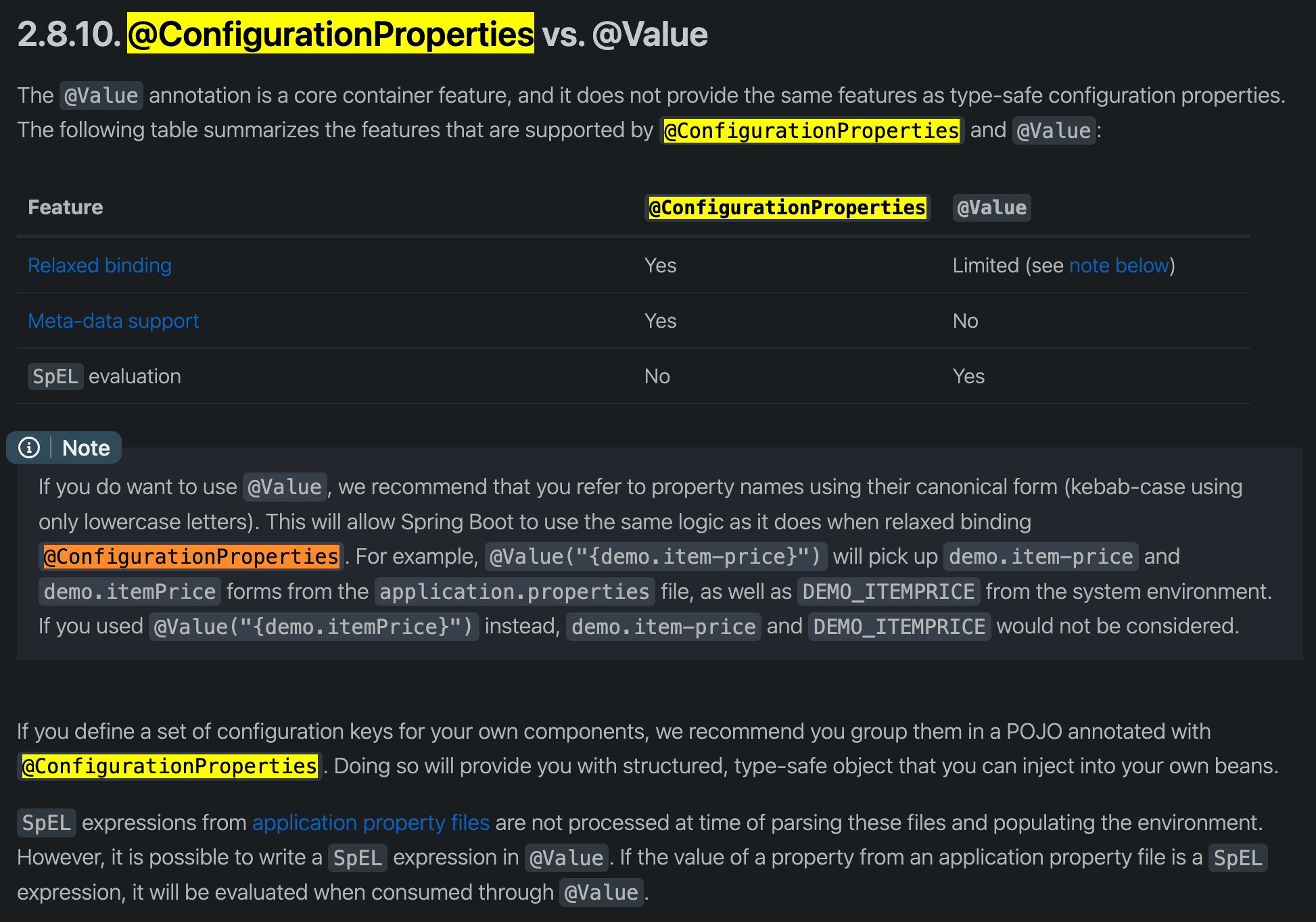
@ConfigurationProperties注解用途
该注解可以用于批量绑定外部属性,可将属性绑定到一个POJO对象,而@Value一般只绑定一个值,一般和@Value可进行一起对比。官方文档有两者的比较
典型使用方式
用在 @Configuration配置类的@Bean修饰的方法上
@Configuration
public class ConnConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "shy.property")
public ConnProperty readDruidDataSource() {
return new ConnProperty();
}
}
配置文件配置
shy:
property:
url: localhost:8090
password: 08240819
driver-class-name: test # pojo的字段要转驼峰
用在类上
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties("shy.property")
public class ConnProperty {
private String url;
private String password;
}
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ConnProperty.class)
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean
public ConnProperty connProperty() {
return new ConnProperty();
}
}
属性绑定的核心流程
-
准备Environment,在prepareEnvironment阶段添加系统默认的属性源
- ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件发出后,由各种EnvironmentPostProcessor做后置处理,比如可以在这里添加自定义的属性源和属性值;这个过程还包括ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor处理配置文件属性
-
准备bd
-
等bean实例化,populateBean填充属性之后,进入初始化阶段,将属性绑定到bean,执行完invokeAwareMethods后,调用applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization;由ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor处理bind,内部负责真正绑定处理的是Binder,关于Binder这里先不做详细讨论。
-
如果需要还可以定义自己的BeanPostProcessor做postProcessAfterInitialization后置处理
-
使用绑定好属性的bean
何时注入ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor的bd信息
spring-boot-autoconfig的spring.factories定义了自动装配的配置类:ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,定义了一个开关注解EnableConfigurationProperties
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(EnableConfigurationPropertiesRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableConfigurationProperties {
String VALIDATOR_BEAN_NAME = "configurationPropertiesValidator";
Class<?>[] value() default {};
}
使用@Import注解导入了一个EnableConfigurationPropertiesRegistrar,该类继承自ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,我们知道ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的子类可以往IoC容器中注入bd信息
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 注入bd信息
// 注入ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor的bd
// 注入ConfigurationPropertiesBinder.Factory,ConfigurationPropertiesBinder的bd
registerInfrastructureBeans(registry);
registerMethodValidationExcludeFilter(registry);
ConfigurationPropertiesBeanRegistrar beanRegistrar = new ConfigurationPropertiesBeanRegistrar(registry);
getTypes(metadata).forEach(beanRegistrar::register);
}
属性源
先提几个问题,属性源有哪些,属性源的获取,属性源的优先级是怎样的(覆盖)。
关于外部化配置的优先级顺序,这篇官方文档给出了一些描述如下:
Spring Boot允许将配置外部化,这样就可以在不同的环境中使用相同的应用程序代码。可以使用属性文件、YAML文件、环境变量和命令行参数来外部化配置。属性值可以通过使用@Value直接注入到bean中,可以通过Spring的Environment抽象访问,也可以通过@ConfigurationProperties绑定到结构化对象。
Spring Boot使用一个非常特殊的PropertySource顺序,它被设计用来允许合理地重写值。属性按以下顺序考虑: 序号大的覆盖序号小
- Default properties (specified by setting
SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties). @PropertySourceannotations on your@Configurationclasses. Please note that such property sources are not added to theEnvironmentuntil the application context is being refreshed. This is too late to configure certain properties such aslogging.*andspring.main.*which are read before refresh begins.- Config data (such as
application.propertiesfiles). - A
RandomValuePropertySourcethat has properties only inrandom.*. - OS environment variables.
- Java System properties (
System.getProperties()). - JNDI attributes from
java:comp/env. ServletContextinit parameters.ServletConfiginit parameters.- Properties from
SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON(inline JSON embedded in an environment variable or system property). - Command line arguments.
propertiesattribute on your tests. Available on@SpringBootTestand the test annotations for testing a particular slice of your application.@TestPropertySourceannotations on your tests.- Devtools global settings properties in the
$HOME/.config/spring-bootdirectory when devtools is active.
添加属性源的核心流程对应到源码里,在SpringBoot启动的prepareEnvironment这个阶段,注意实际存储在MutablePropertySources中的PropertySource有一定顺序
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 创建 StandardServletEnvironment,这是 WEB 环境默认的 Environment
// 创建该对象的过程中,会同时初始化 4 个 PropertySource,名称是:
// 1. servletConfigInitParams
// 2. servletContextInitParams
// 3. systemProperties
// 4. systemEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 1. 配置默认的配置源,DefaultPropertiesPropertySource
// 2. 解析命令行参数,作为一个 PropertySource: commandLineArgs
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 添加configurationProperties,attach
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 发出 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 事件,监听器Listener监听到事件后,会遍历EnvironmentPostProcessor注入一些配置源,包括
// 1. random
// 2. 替换systemEnvironment,加强上面的 systemEnvironment
// 3. spring.application.json
// 4. devtools
// 5. application.properties 等文件
// .. 看有多少个EnvironmentPostProcessor做了处理
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
// 解析 spring.xxx.xxx 配置
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 再次attach
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
执行完这个方法查看下加入了哪些source,顺序示例如下
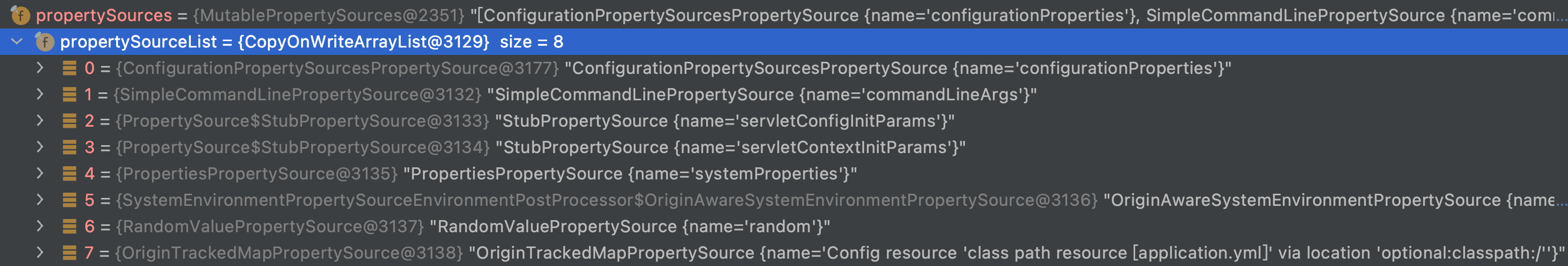
具体排序是如何实现的
springboot解析属性源绑定到bean上,就是按照一定的优先级顺序的。可以打断点查看具体的排序
**如何排序:**其实顺序就是添加到MutablePropertySources list的顺序,通过(addFirst,addLast)等;但是添加之前获取各种EnvironmentPostProcessor也有一定的优先级,对应EnvironmentPostProcessor的排序是通过Order,最终通过EnvironmentPostProcessor遍历顺序+addLast/addFirst来确定列表的顺序。
如ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor的postProcessEnvironment做的处理
private void applyToEnvironment(ConfigDataEnvironmentContributors contributors,
ConfigDataActivationContext activationContext, Set<ConfigDataLocation> loadedLocations,
Set<ConfigDataLocation> optionalLocations) {
// ....
MutablePropertySources propertySources = this.environment.getPropertySources();
this.logger.trace("Applying config data environment contributions");
// 遍历contributors
for (ConfigDataEnvironmentContributor contributor : contributors) {
PropertySource<?> propertySource = contributor.getPropertySource();
if (contributor.getKind() == ConfigDataEnvironmentContributor.Kind.BOUND_IMPORT && propertySource != null) {
if (!contributor.isActive(activationContext)) {
this.logger.trace(
LogMessage.format("Skipping inactive property source '%s'", propertySource.getName()));
}
else {
this.logger
.trace(LogMessage.format("Adding imported property source '%s'", propertySource.getName()));
// 最终就是添加到source list末尾
propertySources.addLast(propertySource);
this.environmentUpdateListener.onPropertySourceAdded(propertySource, contributor.getLocation(),
contributor.getResource());
}
}
}
// ....
}
bind属性
bind发生在ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 检查有没有@ConfigurationProperties注解,有则绑定
bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean.get(this.applicationContext, bean, beanName));
return bean;
}
private void bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean bean) {
// 如果没有ConfigurationProperties注解声明,bean为null,不执行绑定逻辑
if (bean == null || hasBoundValueObject(bean.getName())) {
return;
}
Assert.state(bean.getBindMethod() == BindMethod.JAVA_BEAN, "Cannot bind @ConfigurationProperties for bean '"
+ bean.getName() + "'. Ensure that @ConstructorBinding has not been applied to regular bean");
try {
// 绑定
this.binder.bind(bean);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new ConfigurationPropertiesBindException(bean, ex);
}
}
在ConfigurationPropertiesBean#get方法里会检查是否有ConfigurationProperties注解,如果没有改注解,则不执行绑定逻辑
// ConfigurationPropertiesBean#get
public static ConfigurationPropertiesBean get(ApplicationContext applicationContext, Object bean, String beanName) {
Method factoryMethod = findFactoryMethod(applicationContext, beanName);
return create(beanName, bean, bean.getClass(), factoryMethod);
}
// ConfigurationPropertiesBean#get
private static ConfigurationPropertiesBean create(String name, Object instance, Class<?> type, Method factory) {
// 找有没有ConfigurationProperties注解声明
ConfigurationProperties annotation = findAnnotation(instance, type, factory, ConfigurationProperties.class);
if (annotation == null) {
return null; //没有直接返回null
}
Validated validated = findAnnotation(instance, type, factory, Validated.class);
Annotation[] annotations = (validated != null) ? new Annotation[] { annotation, validated }
: new Annotation[] { annotation };
ResolvableType bindType = (factory != null) ? ResolvableType.forMethodReturnType(factory)
: ResolvableType.forClass(type);
Bindable<Object> bindTarget = Bindable.of(bindType).withAnnotations(annotations);
if (instance != null) {
bindTarget = bindTarget.withExistingValue(instance);
}
return new ConfigurationPropertiesBean(name, instance, annotation, bindTarget);
}
真正的绑定是在Binder相关类中做的,bind前要去属性源列表里查找相应的属性
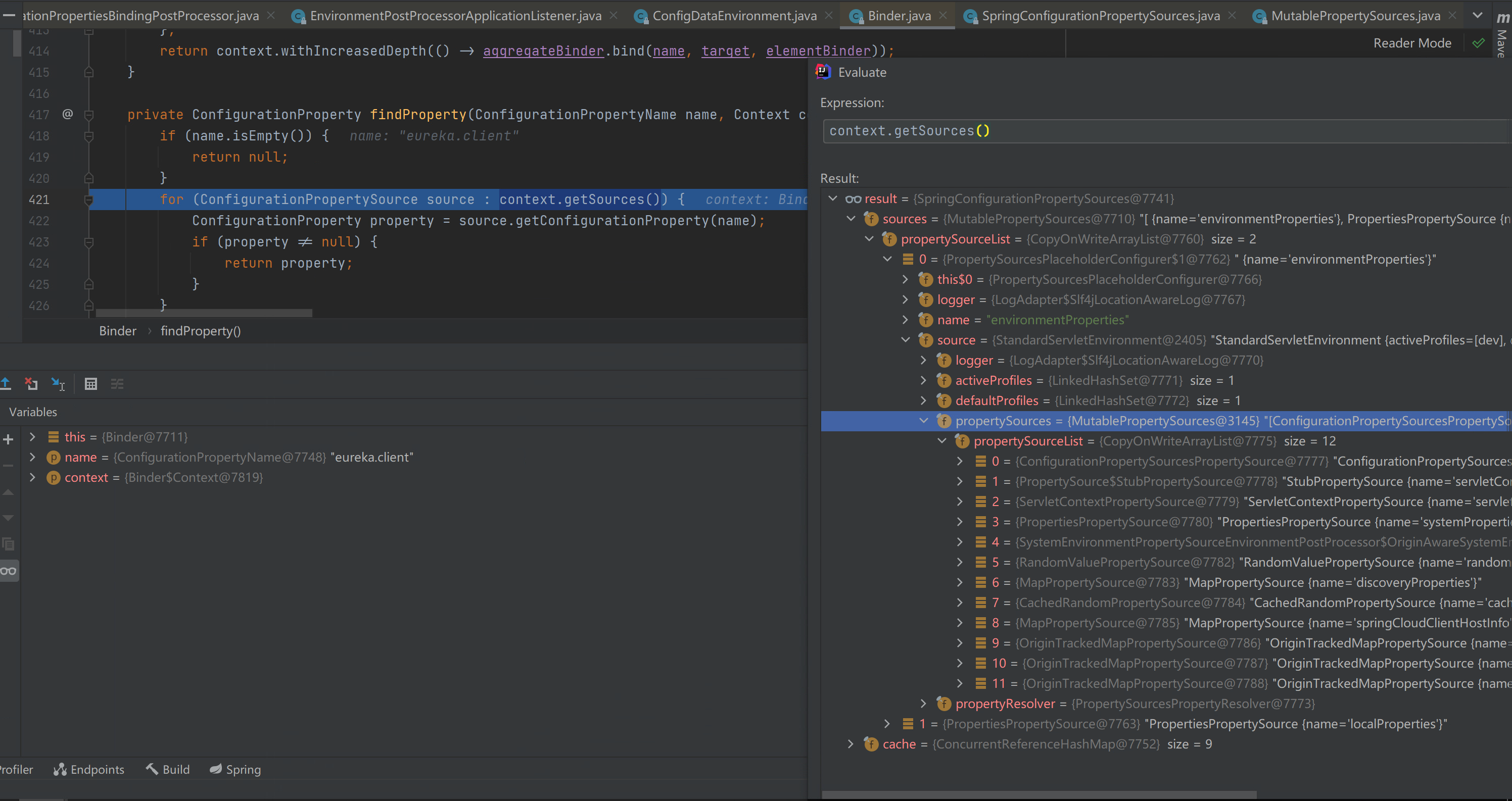
查找属性
private ConfigurationProperty findProperty(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Context context) {
if (name.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
// 这个context.getSources()是个特殊的迭代器,里面做了一些过滤处理,但是顺序不变
for (ConfigurationPropertySource source : context.getSources()) {
ConfigurationProperty property = source.getConfigurationProperty(name);
if (property != null) {
return property;
}
}
return null;
}
context.getSources()会返回迭代器,并将不需要的source进行过滤
/**
* Adapter to convert Spring's {@link MutablePropertySources} to
* {@link ConfigurationPropertySource ConfigurationPropertySources}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
*/
class SpringConfigurationPropertySources implements Iterable<ConfigurationPropertySource> {
private final Iterable<PropertySource<?>> sources;
private final Map<PropertySource<?>, ConfigurationPropertySource> cache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(16,
ReferenceType.SOFT);
SpringConfigurationPropertySources(Iterable<PropertySource<?>> sources) {
Assert.notNull(sources, "Sources must not be null");
this.sources = sources;
}
@Override
public Iterator<ConfigurationPropertySource> iterator() {
return new SourcesIterator(this.sources.iterator(), this::adapt);
}
private ConfigurationPropertySource adapt(PropertySource<?> source) {
ConfigurationPropertySource result = this.cache.get(source);
// Most PropertySources test equality only using the source name, so we need to
// check the actual source hasn't also changed.
if (result != null && result.getUnderlyingSource() == source) {
return result;
}
result = SpringConfigurationPropertySource.from(source);
this.cache.put(source, result);
return result;
}
private static class SourcesIterator implements Iterator<ConfigurationPropertySource> {
private final Deque<Iterator<PropertySource<?>>> iterators;
private ConfigurationPropertySource next;
private final Function<PropertySource<?>, ConfigurationPropertySource> adapter;
SourcesIterator(Iterator<PropertySource<?>> iterator,
Function<PropertySource<?>, ConfigurationPropertySource> adapter) {
this.iterators = new ArrayDeque<>(4);
this.iterators.push(iterator);
this.adapter = adapter;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return fetchNext() != null;
}
@Override
public ConfigurationPropertySource next() {
ConfigurationPropertySource next = fetchNext();
if (next == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
this.next = null;
return next;
}
private ConfigurationPropertySource fetchNext() {
if (this.next == null) {
if (this.iterators.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
if (!this.iterators.peek().hasNext()) {
this.iterators.pop();
return fetchNext();
}
PropertySource<?> candidate = this.iterators.peek().next();
if (candidate.getSource() instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
push((ConfigurableEnvironment) candidate.getSource());
return fetchNext();
}
// 判断是否要忽略这个source
if (isIgnored(candidate)) {
return fetchNext();
}
this.next = this.adapter.apply(candidate);
}
return this.next;
}
private void push(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.iterators.push(environment.getPropertySources().iterator());
}
private boolean isIgnored(PropertySource<?> candidate) {
// 忽略Random source,忽略StubPropertySource,忽略ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource类型
return (isRandomPropertySource(candidate) || candidate instanceof StubPropertySource
|| candidate instanceof ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource);
}
private boolean isRandomPropertySource(PropertySource<?> candidate) {
Object source = candidate.getSource();
return (source instanceof Random) || (source instanceof PropertySource<?>
&& ((PropertySource<?>) source).getSource() instanceof Random);
}
}
}
举例
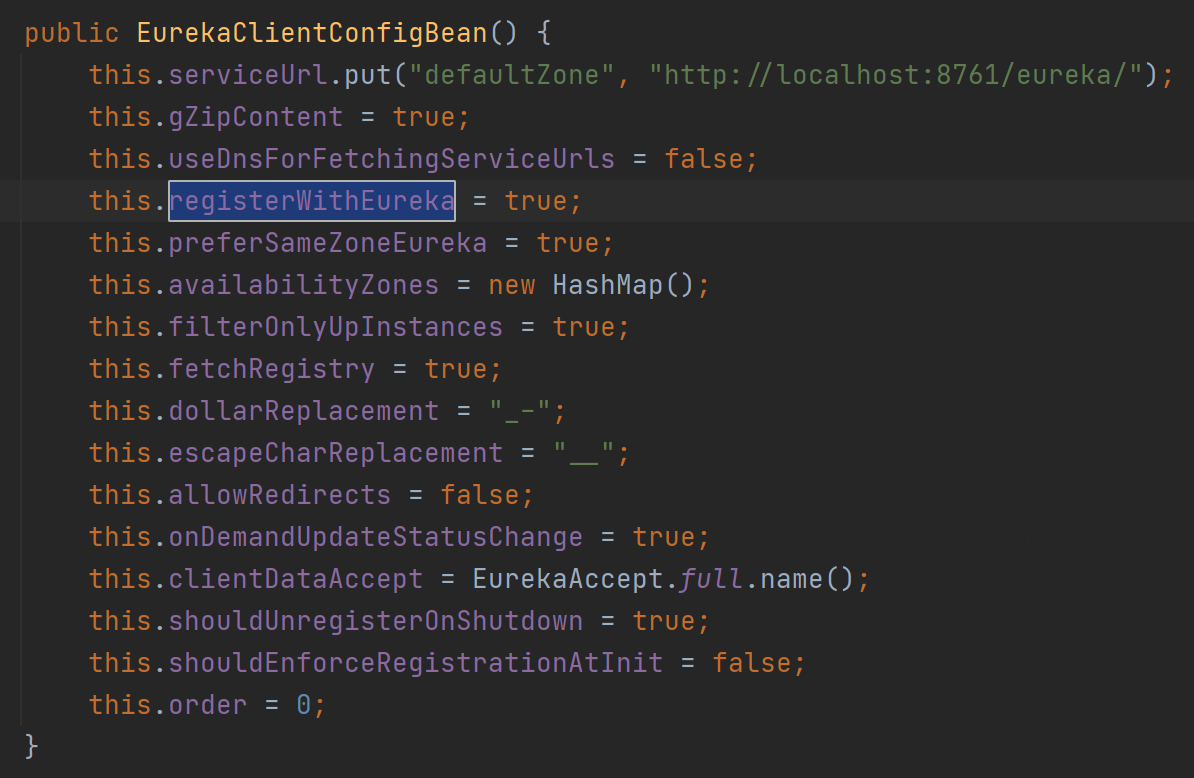
这里以Eureka Client的配置案例举例,默认下Eureka Client进行服务注册和服务发现,如下图
现在想实现的效果是默认不让Eureka Client进行服务注册和服务发现
声明一个DisableEurekaDiscoveryEnvironmenPostProcessor,并在spring.factories进行声明,保证SpringBoot的自动装配能起作用,进而能把DisableEurekaDiscoveryEnvironmenPostProcessor注入到容器中,但要让其优先级只要比ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor高即可
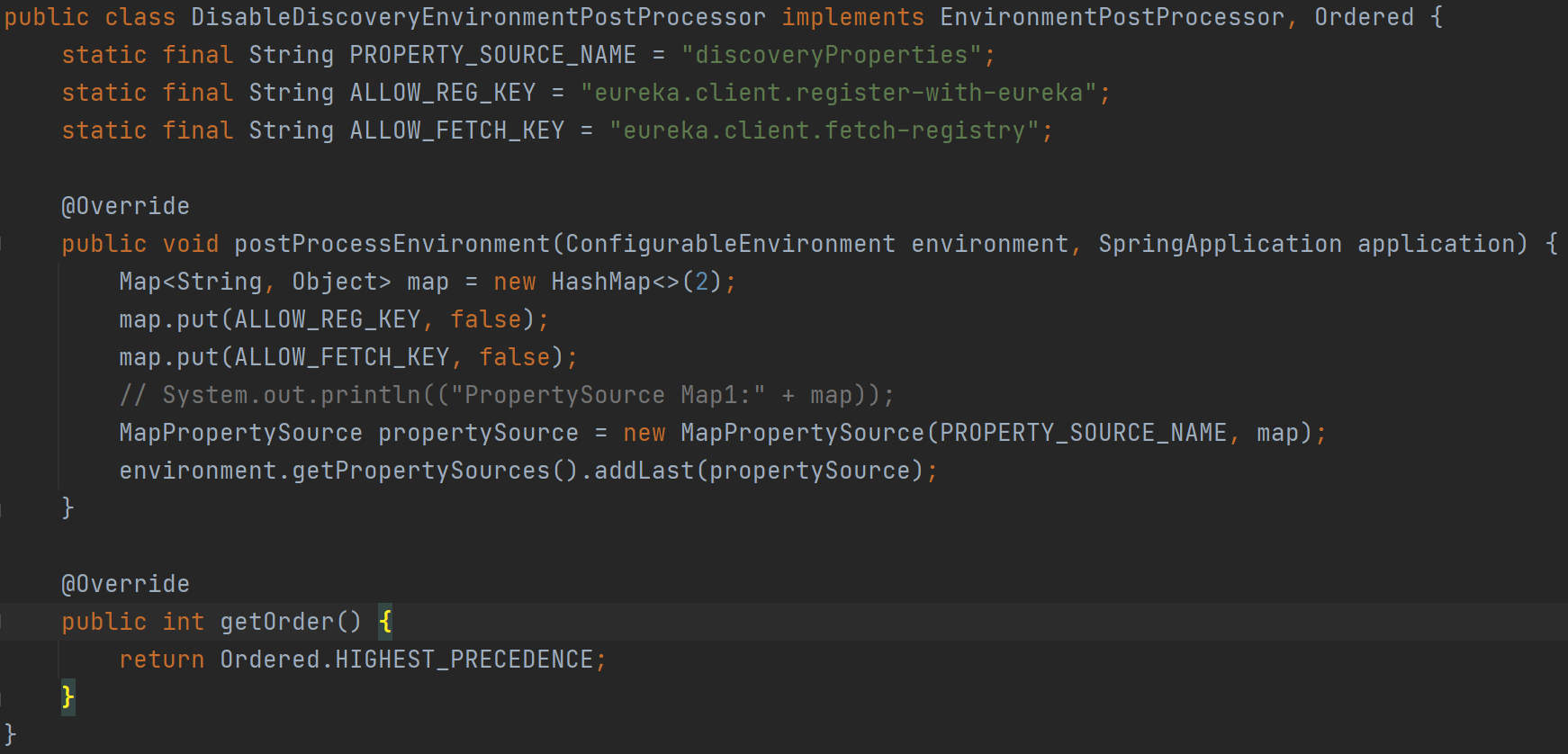
SpringBoot程序启动后,创建好Environment后,发布environmentPrepared事件时,EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener监听到这个事件
这样保证environmentPrepared事件发出后,EnvironmentPostProcessor的执行顺序是DisableDiscorveryEnvironmentPostProcessor优先于ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor,因此两种EnvironmentPostProcessor的addLast操作之后就保证了属性源列表的顺序
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
SpringApplication application = event.getSpringApplication();
// 调用各种EnvironmentPostProcessor的postProcessEnvironment
// DisableEurekaDiscoveryEnvironmenPostProcessor 就是一个EnvironmentPostProcessor并且优先级比ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor高
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : getEnvironmentPostProcessors(event.getBootstrapContext())) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(environment, application);
}
}
所以在refresh核心流程,实例化剩余的Bean(non-lazy-init)之前,context持有的environment属性里的propertySouce有了一个排序好的顺序
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
有顺序的propertySource,这里看到自定义的属性源discoveryProperties优先于配置文件的优先级
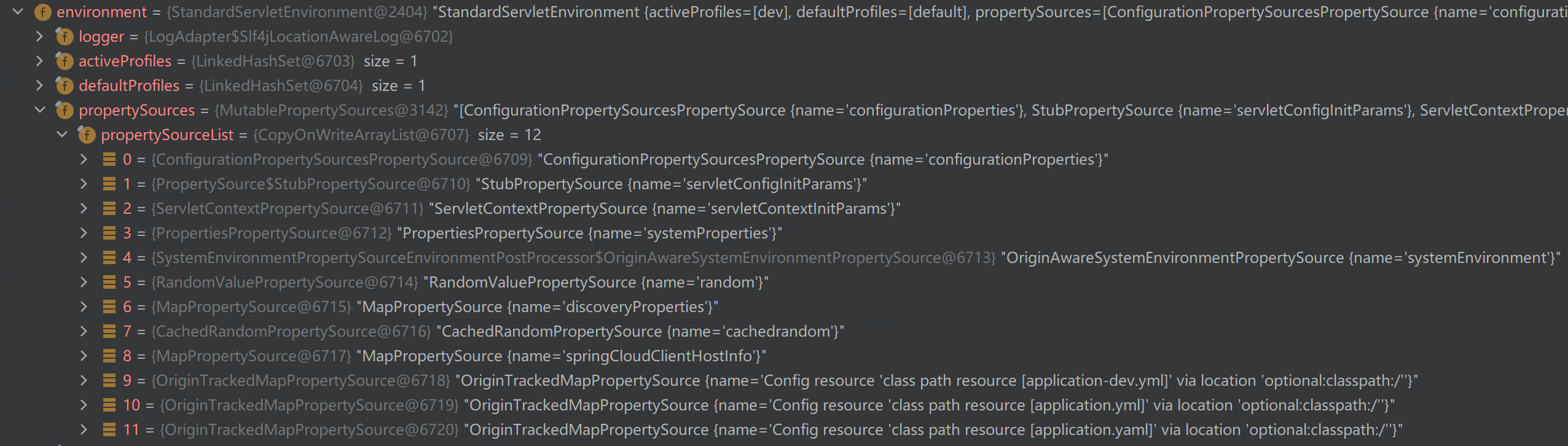
最终在绑定bean的时候,从属性源获取属性也是基于已经排序好的顺序遍历,因此优先获取到discoveryProperties中属性进行绑定,实现了覆盖EurekaClient默认配置的效果。
核心类总结
- PropertySource核心抽象类:属性源的抽象,MapPropertySource,CommandLinePropertySource;PropertySources接口
- PropertyResolver接口,子接口Environment:表示当前程序运行的环境profile。抽象了程序环境的关键要素:profile和properties。Environment = Profile + Properties;Environment的实现有很多
- EnvironmentPostProcessor,ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor
- SpringConfigurationPropertySources:适配器,MutablePropertySources to ConfigurationPropertySources,里面维护了一个定制的迭代器
- ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor,ConfigurationPropertiesBinder,Binder





















 1393
1393











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








